Sensors 2016, 16, 520 3 of 15
Sensors 2016, 16, x 3 of 14
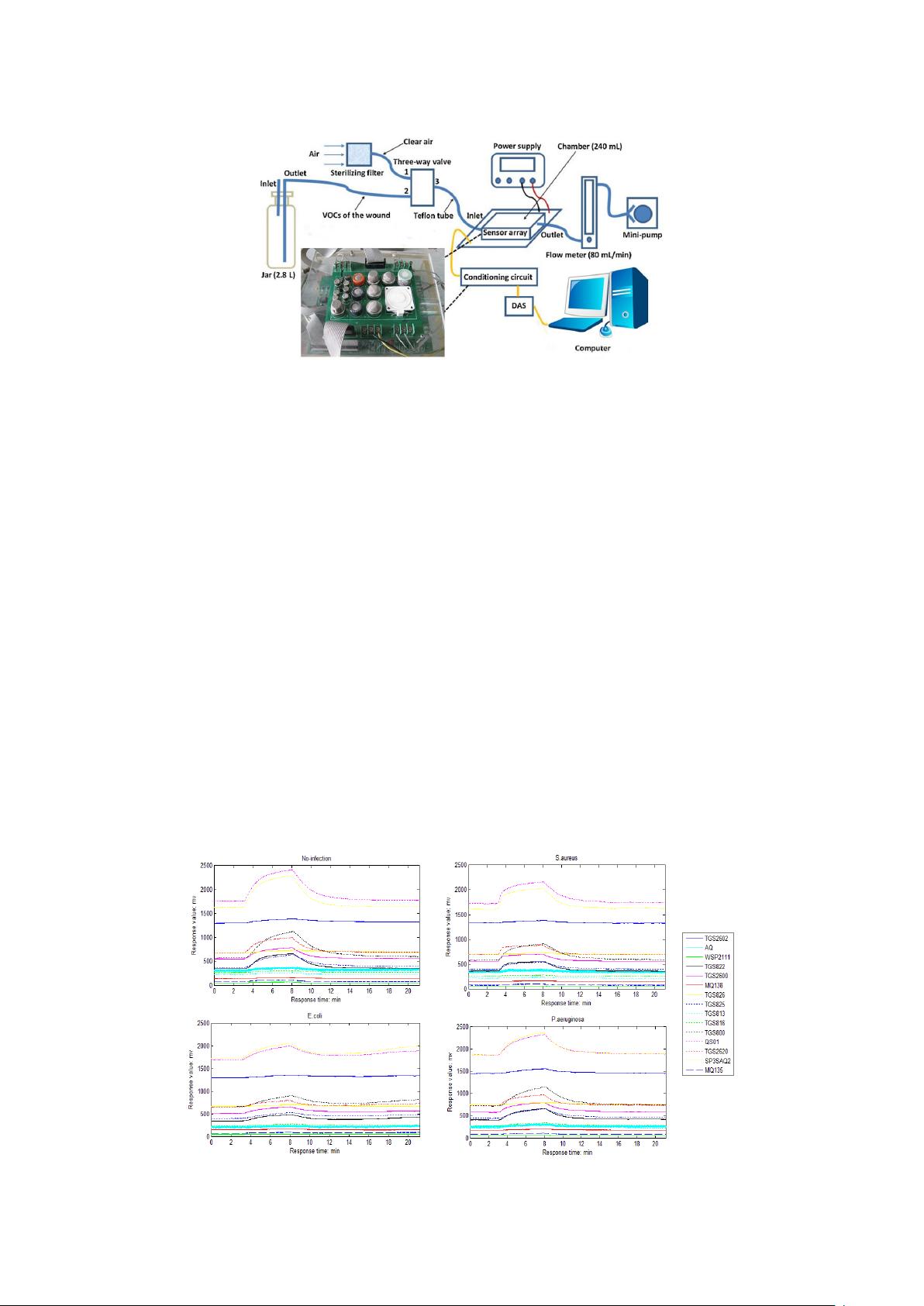
switch between VOCs and clean air. The experimental setup has also been mentioned in [33]. The
experimental procedure in this paper can be summarized as follows.
Each mouse was put in a big glass bottle with a rubber stopper. Two holes were made in the
rubber stopper with two thin glass tubes inserted. One longer glass tube was used as an exit pipe
and hung above the wound as close as possible while the shorter one was used as an intake-tube,
inserted into the glass a little and was close to the bottleneck. The gases which contained the VOCs
of the wound on the mouse outflowed along the longer glass tube and flowed into the sensor
chamber. The air flowed into the glass along the shorter glass tube. Each test process comprises
three stages: the baseline stage, the response stage and the recovery stage. In the baseline stage, the
three-way valve switched on Port 1 and the clean air purified by the filter flowed through the
sensor chamber for 3 min. In the response stage, the three-way valve switched on Port 2 and the
gases containing the VOCs of the wound flowed through the sensor chamber for 5 min. In the
recovery stage, the three-way valve switched on Port 1 again and the clean air flowed through the
sensor chamber for 15 min. During the three stages of one test, the DAS always sampled the data
and stored them in the computer. After one test and before the next one, for eliminating the
influence of the residual odors, the sensor chamber was purged by the clean air for 5 min and in the
purging process the DAS did not sample the data.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental system.
Figure 2. E-nose response to four wounds.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental system.
Each mouse was put in a big glass bottle with a rubber stopper. Two holes were made in the
rubber stopper with two thin glass tubes inserted. One longer glass tube was used as an exit pipe
and hung above the wound as close as possible while the shorter one was used as an intake-tube,
inserted into the glass a little and was close to the bottleneck. The gases which contained the VOCs of
the wound on the mouse outflowed along the longer glass tube and flowed into the sensor chamber.
The air flowed into the glass along the shorter glass tube. Each test process comprises three stages:
the baseline stage, the response stage and the recovery stage. In the baseline stage, the three-way valve
switched on Port 1 and the clean air purified by the filter flowed through the sensor chamber for 3 min.
In the response stage, the three-way valve switched on Port 2 and the gases containing the VOCs of
the wound flowed through the sensor chamber for 5 min. In the recovery stage, the three-way valve
switched on Port 1 again and the clean air flowed through the sensor chamber for 15 min. During the
three stages of one test, the DAS always sampled the data and stored them in the computer. After one
test and before the next one, for eliminating the influence of the residual odors, the sensor chamber
was purged by the clean air for 5 min and in the purging process the DAS did not sample the data.
Four groups of mice were tested in the research, including one control group and three groups
infected by Staphylococcu aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. Twenty tests
for each groups of mice in the same conditions were made, and finally 80 samples for all four groups of
mice were collected from the above procedures. Figure 2 illustrates the sensor responses process when
they are exposed to four different target wounds, where X-axis is the response time of the sensors and
Y-axis is the output voltage of the sensors.
Sensors 2016, 16, x 3 of 14
switch between VOCs and clean air. The experimental setup has also been mentioned in [33]. The
experimental procedure in this paper can be summarized as follows.
Each mouse was put in a big glass bottle with a rubber stopper. Two holes were made in the
rubber stopper with two thin glass tubes inserted. One longer glass tube was used as an exit pipe
and hung above the wound as close as possible while the shorter one was used as an intake-tube,
inserted into the glass a little and was close to the bottleneck. The gases which contained the VOCs
of the wound on the mouse outflowed along the longer glass tube and flowed into the sensor
chamber. The air flowed into the glass along the shorter glass tube. Each test process comprises
three stages: the baseline stage, the response stage and the recovery stage. In the baseline stage, the
three-way valve switched on Port 1 and the clean air purified by the filter flowed through the
sensor chamber for 3 min. In the response stage, the three-way valve switched on Port 2 and the
gases containing the VOCs of the wound flowed through the sensor chamber for 5 min. In the
recovery stage, the three-way valve switched on Port 1 again and the clean air flowed through the
sensor chamber for 15 min. During the three stages of one test, the DAS always sampled the data
and stored them in the computer. After one test and before the next one, for eliminating the
influence of the residual odors, the sensor chamber was purged by the clean air for 5 min and in the
purging process the DAS did not sample the data.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental system.
Figure 2. E-nose response to four wounds.
Figure 2. E-nose response to four wounds.









