Section | 1.3 Direction-Finding Algorithms
5
vector is represented (up to a common factor) by the array manifold a(θ).
Combining the signals “in phase” is accomplished by the complex conjugate
of the array manifold. Thus, we compute |a(θ)
H
a(θ
0
)|. If the assumed direction
θ equals the true emitter direction, we get the largest value of the combined
signals |a(θ
0
)
H
a(θ
0
)|=M.Ifθ =θ
0
, the signals are not added in phase and the
result of the sum is smaller. This type of processing is called frequency domain
beamforming or just beamforming.
In its most general form, a beamformer uses a weight vector W(θ) to lin-
early combine the array outputs. In most applications we are interested in the
magnitude or the power of the combiner output. In the latter case the output is
given by
p(θ) =|W(θ)
H
y|
2
(1.9)
where y is the received signal. In the absence of noise and assuming a unit power
signal, the beamformer output is
p(θ) =SNR|W(θ)
H
a(θ
0
)|
2
(1.10)
When the beamformer is used for direction finding, its output p(θ) is computed
over a range of directions θ. The direction where p(θ) reaches its largest value
is the estimated emitter direction.
In this discussion we assume that W(θ) =a(θ). In practice, this weight vector
will be modified by a window chosen to suppress the sidelobe level of the beam
pattern to a desired level. We use a normalized but nonwindowed weight vector
W(θ) =a(θ)/|a(θ)|, which makes the noise power at the beamformer output the
same as at the antenna elements.
It should be noted that the beamformer with this choice of weight vector is
in fact the generalized maximum likelihood estimator of the direction θ, for the
signal model
y =α
0
a(θ
0
) +v (1.11)
where y is the vector of the signals at the array output, α
0
is a complex scale
factor assumed to be unknown (α
0
=
√
SNR s in the previous notation), a(θ) is
the array manifold, θ
0
is the unknown emitter direction, and v is a noise vector
composed of independent zero-mean unit-variance Gaussian random variables.
The generalized maximum likelihood estimate is given by joint minimization
of the error |y−α
0
a(θ
0
)|
2
over the unknowns θ
0
and α
0
. Minimizing first over
α
0
we have α
0
=a
H
(θ
0
)y/a
H
(θ
0
)a(θ
0
). Inserting this into the error function we
have |y −a(θ
0
)a
H
(θ
0
)/|a(θ
0
)|
2
y|
2
. Minimizing this cost function with respect to
θ
0
is equivalent to maximizing y
H
a(θ
0
)a
H
(θ
0
)y/|a(θ
0
)|
2
, which can be written
as |W
H
(θ
0
)y|
2
, the output of the beamformer presented earlier. Thus, the estimate
ˆ
θ
0
obtained by maximizing the output power of the beamformer is the generalized
likelihood direction estimate.
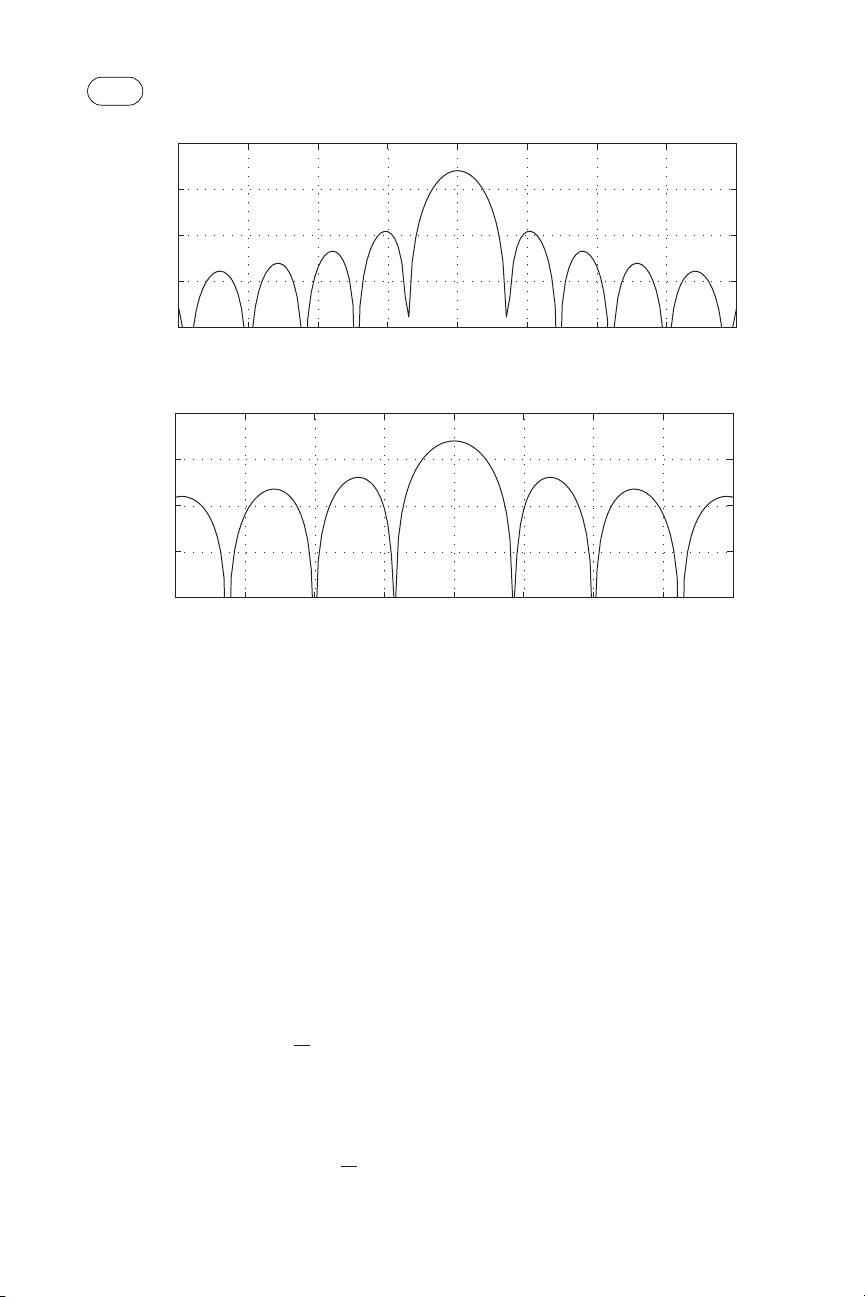
Figure 1.2 depicts the beam pattern p(θ) for 16-element circular and linear
arrays in the case where θ
0
=0. As can be seen, p(θ) is maximized at the source