Research for Pedestrian Navigation Positioning Method Based on MEMS
Sensors
XIONG Yunqiang
1
, ZHANG Yanshun
1
, WANG Zhan Qing
2
, LI Ming
1
1. College of Instrument Science and Opto-electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
E-mail:yunqiangxiong@buaa.edu.cn, zhangyanshun@buaa.edu.cn, liliyalm@buaa.edu.cn
2. School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
E-mail: bitwangzhanqing@163.com
Abstract: With the development of MEMS sensors, pedestrian navigation has been a popular research. The paper realizes step
detection and estimation for step length by only vertical accelerometer. It determines initial heading using accelerometers and
magnetometers and calculates latter heading using gyroscopes by strap-down inertial navigation algorithm. Afterwards, it
achieves the positioning goal for pedestrian using dead reckoning method. Definitively, the effectiveness of this approach is
demonstrated through two different field trials and the results indicate that the positioning method for pedestrian proposed is
efficient and has a small positioning error.
Key Words: MEMS, Pedestrian Navigation, Dead Reckoning
1 Introduction
Research for pedestrian navigation based on MEMS
sensors has been the popular study because MEMS inertial
sensors possess advantages of small volume and low cost and
weight.
[1-3]
Pedestrian navigation system is very helpful to
monitor location of firemen and the aged, offer navigation
service for blind persons and everyman. So a mass of
different researches have been carried on according to the
human body different parts mounted MEMS sensors.
[4-6]
Among them, kun-chan Lan
[7]
models step length using leg
length, height and proposes a waist-mounted pedestrian dead
reckoning. Pragun Goya
[8]
mounts MEMS sensors on the
body waist and calculates heading combining gyroscopes
with magnetometers to achieve the positioning goal for
pedestrian in a longer time. A.R.Jim´enez
[9]
and Seong Yun
Cho
[10]
proposes a foot-mounted pedestrian navigation
positioning method and adopts zero velocity update (ZUPT)
method to calibrate the sensors drift errors from the
accelerometers and gyroscopes.
It’s convenient to wear and possesses better reliability
when MEMS sensors are mounted on human body waist. For
the pedestrian navigation based on waist mounted MEMS
sensors, this paper studies the methods for step detection,
step length estimation only through a vertical accelerometer
and heading algorithm and carries out some researches of
pedestrian positioning method based on dead reckoning.
2 Pedestrian Navigation Positioning Principle
2.1 Dead Reckoning
Dead Reckoning (DR) is a navigation method that reckons
next location by current location and velocity, direction and
time of motion. The method has advantages of full autonomy,
flexible and undisturbed and it is able to offer
two-dimensional position anytime and anywhere. The basic
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation (NNSF)
of China under Grant (61473019, 11202010 , 61273033).
principle of pedestrian dead reckoning positioning
[11]
is
shown in Fig. 1.
(
N
1
.
(
N
1
.
(
1
6/N
6/N
R
k)
˄
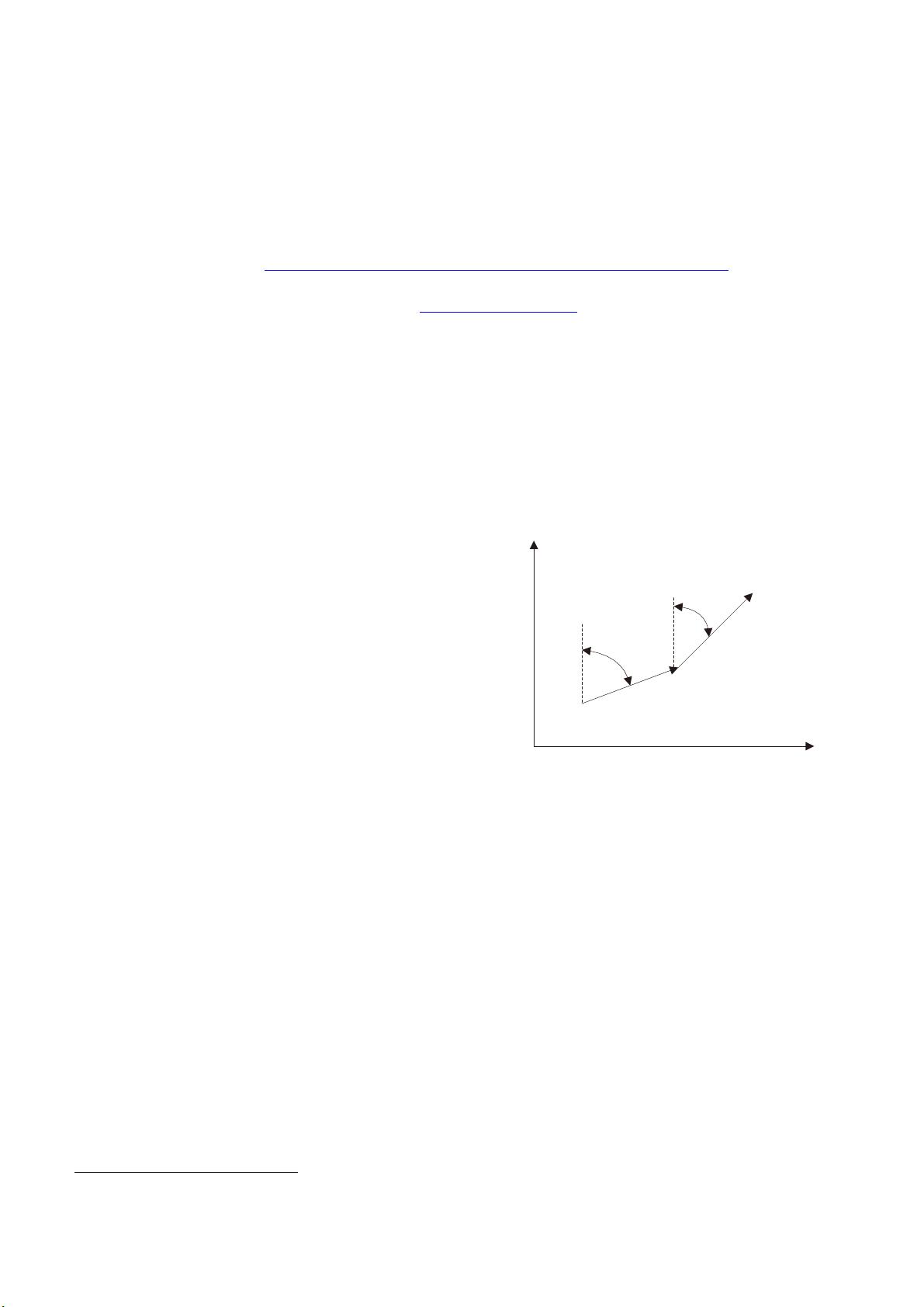
Fig. 1: The principle of dead reckoning
Pedestrian locates
11
(, )
kk
EN
and heading is
(1)k
when time is
1
t
k
.The next step length is
(1)SL k
. It can
reckon the position of next moment
t
k
on the basis of the
equation (1). It can calculate the position of moment
t
k
using the initial position
00
(, )EN
, step length
(1)SL k
and
pedestrian’s heading according to equation (2).
1
1
SL( 1)*sin( ( 1))
SL( 1)*cos( ( 1))
°
®
°
¯
kk
kk
EE k k
NN k k
\
\
(1)
0
1
0
1
(-1 *sin( ( 1))
(-1 *cos( ( 1))
°
°
®
°
°
¯
¦
¦
k
k
i
k
k
i
EE SLi i
NN SLi i
\
\
˅
˅
(2)
Through the principle of dead reckoning, it can realize
self-localization for pedestrian under the condition of the
initial position information.
Proceedings of the 34th Chinese Control Conference
Jul
28-30, 2015, Han
zhou, China
5315


















