Silicon Image Confidential for
BEIJING SHINYVIEW TECH CO., LTD.
Internal Use Only
SiI9136-3 HDMI Deep Color Transmitter
Data Sheet
Silicon Image, Inc.
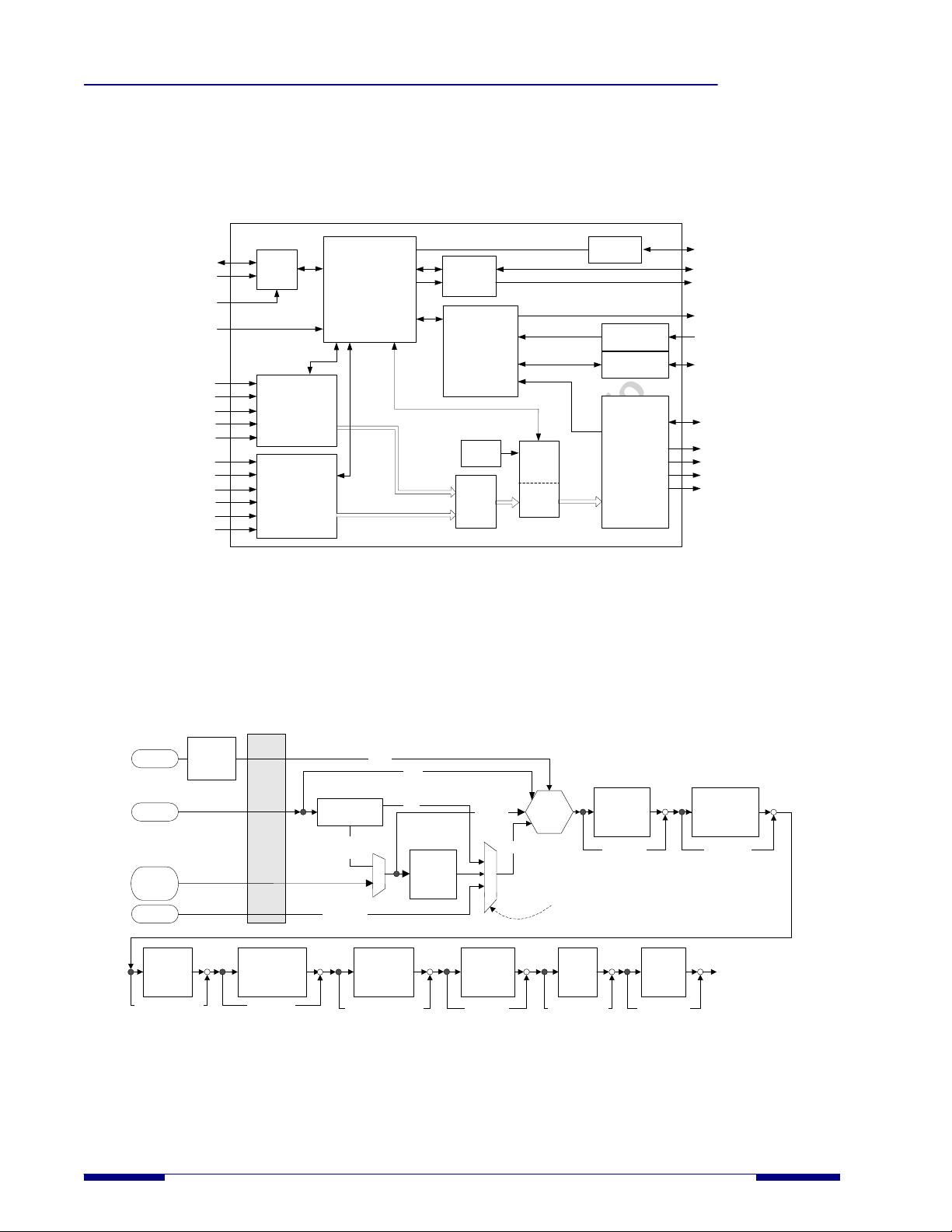
Video Data Capture
The bus configurations support most standardized video input formats as well as other widely used non-standard formats.
Each configuration has four key attributes: data width, input mode, clock mode, and synchronization.
The video input port is a 36-bit wide bus that can be configured to any of the following data widths:
• 8-, 10-, or 12-bit input in double speed clock mode
• 12-, 15-, 18-, or 24-bit input in dual edge clock mode
• 16-, 20-, 24-, 30-, or 36-input in single speed clock mode
The input mode includes color format such as RGB, YCbCr, or xvYCC, and color sampling such as 4:4:4 or 4:2:2.
Clock mode refers to the input clock rate relative to the pixel clock rate. The SiI9136-3 device supports 1x mode and
2x mode, or dual edge mode. 1x mode and 2x mode means that the input clock operates at one or two times the pixel
clock rate. Dual edge mode means that the input clock rate equals the pixel clock rate, but a sample is captured on both
the rising edge and the falling edge of the input clock. Thus, with the Video Input configured for 24 bits with a dual edge
clock, 48 bits of video data are received per clock cycle. The 24 MSBs of the video data are latched on the first clock
edge, and the 24 LSBs are latched on the next clock edge. The first clock edge is programmable and can be either the
rising or falling edge.
Synchronization attributes refer to how the horizontal and vertical sync signals are configured. Separate synchronization
involves placing the horizontal sync, vertical sync, and data enable signals on separate input pins. Embedded
synchronization combines these signals with one or more of the data inputs.
Embedded Sync Decoder
The transmitter can create DE, HSYNC, and VSYNC signals using the Start of Active Video (SAV) and End of Active
Video (EAV) codes within the ITU-R BT.656-format video stream.
Data Enable Generator
The transmitter includes logic to construct a Data Enable (DE) signal from the incoming HSYNC, VSYNC, and IDCK.
This signal is used to correct timing from sync extraction to conform to CEA-861D timing specifications. By
programming registers, the DE signal can define the size of the active display region. This feature is particularly useful
when the transmitter connects to MPEG decoders that do not provide a specific DE output signal.
Combiner
The clock, data, and sync information is combined into a complete set of signals required for TMDS encoding. From
here, the signals are manipulated by the register-selected video processing blocks.
4:2:2 to 4:4:4 Upsampler
Chrominance upsampling doubles the number of chrominance samples per line, converting 4:2:2 sampled video to 4:4:4.
RGB Range Expansion
The SiI9136-3 transmitter can scale the input color range from limited-range into full-range using the range expansion
block. When enabled by itself, the range expansion block expands 16–235 (64–943 to 256–3775, 4096-60415 for
30/36/48-bit color depth) limited-range data into 0–255 (0–1023, 0–4095 to 0-65535 for 30/36/48-bit color depth) full-
range data for each video channel. When range expansion and the YCbCr to RGB color space converter are both
enabled, the input conversion range for the Cb and Cr channels is 16–240 (64–963, 256–3855 to 4096-61695 for
30/36/48-bit color depth).
Color Space Converter
Two color space converters (CSCs) (YCbCr to RGB and RGB to YCbCr) are available to interface to the many video
formats supplied by A/V processors and to provide full DVI backward compatibility. The CSC can be adjusted to
perform standard-definition conversions (ITU.601) or high-definition conversions (ITU.709) by setting the appropriate
registers.
SiI-DS-1084-B © 2010-2013 Silicon Image, Inc. All rights reserved. 5
CONFIDENTIAL