Introduction to the AMBA Buses
ARM IHI 0011A
© Copyright ARM Limited 1999. All rights reserved.
1-7
1.5 Introducing the AMBA AHB
AHB is a new generation of AMBA bus which is intended to address the requirements
of high-performance synthesizable designs. It is a high-performance system bus that
supports multiple bus masters and provides high-bandwidth operation.
AMBA AHB implements the features required for high-performance, high clock
frequency systems including:
• burst transfers
• split transactions
• single-cycle bus master handover
• single-clock edge operation
• non-tristate implementation
• wider data bus configurations (64/128 bits).
Bridging between this higher level of bus and the current ASB/APB can be done
efficiently to ensure that any existing designs can be easily integrated.
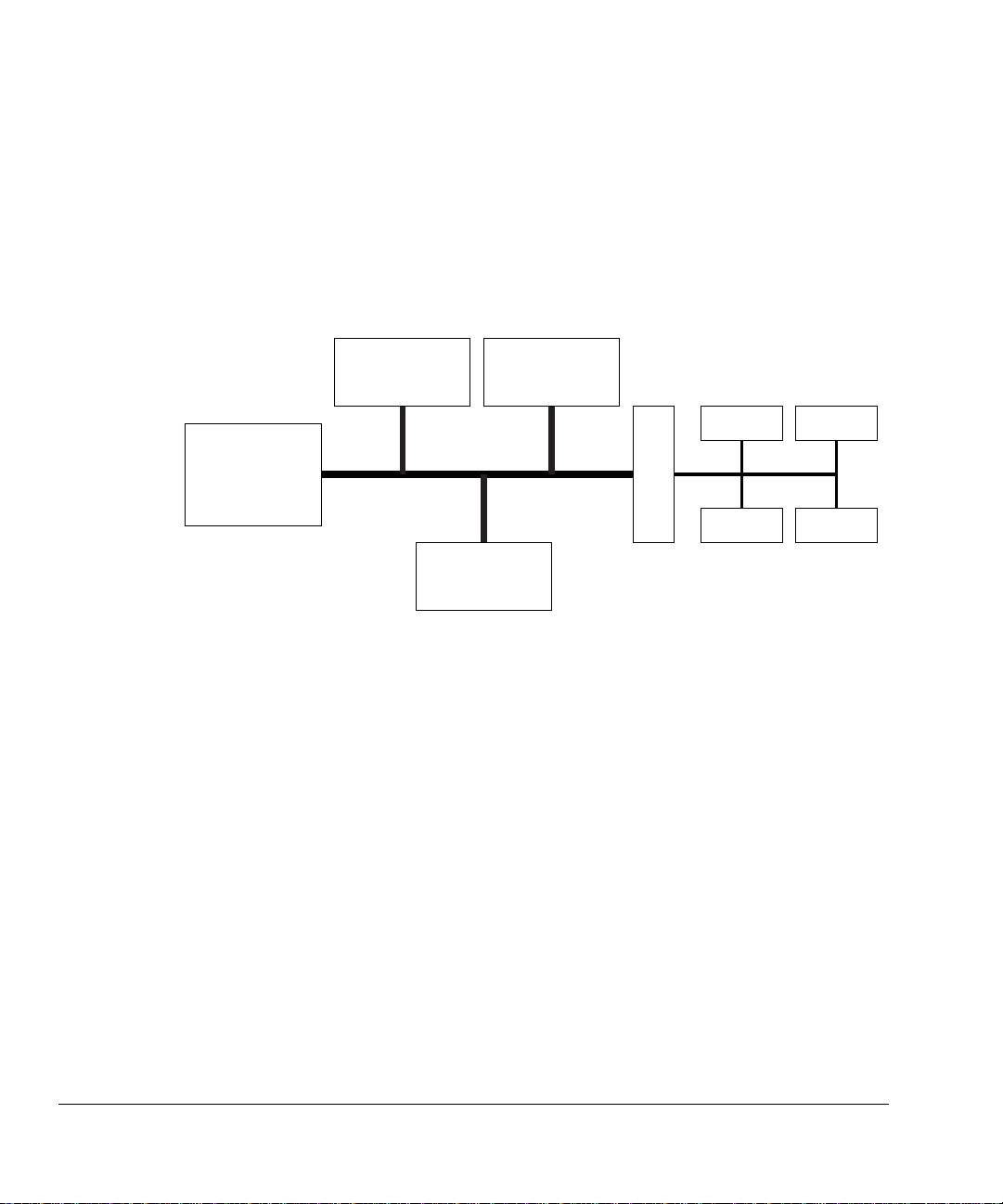
An AMBA AHB design may contain one or more bus masters, typically a system would
contain at least the processor and test interface. However, it would also be common for
a Direct Memory Access (DMA) or Digital Signal Processor (DSP) to be included as
bus masters.
The external memory interface, APB bridge and any internal memory are the most
common AHB slaves. Any other peripheral in the system could also be included as an
AHB slave. However, low-bandwidth peripherals typically reside on the APB.
A typical AMBA AHB system design contains the following components:
AHB master A bus master is able to initiate read and write operations by
providing an address and control information. Only one bus
master is allowed to actively use the bus at any one time.
AHB slave A bus slave responds to a read or write operation within a given
address-space range. The bus slave signals back to the active
master the success, failure or waiting of the data transfer.
AHB arbiter The bus arbiter ensures that only one bus master at a time is
allowed to initiate data transfers. Even though the arbitration
protocol is fixed, any arbitration algorithm, such as highest
priority or fair access can be implemented depending on the
application requirements.
An AHB would include only one arbiter, although this would be
trivial in single bus master systems.