332 CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS / Vol. 4, No. 6 / June 10, 2006
Passively Q-switched Nd
3+
:YAG laser with corner cube
Weiqing Gao (
ppp
)
1
, Gongmin Yao (
õõõ
¬¬¬
)
1
, Lixin Xu (
NNN
ááá
###
)
1
,
Yong Cheng (
§§§
℄℄℄
)
2
, Hai Ming (
²²²
°°°
)
1
, and Jianping Xie (
ïïï
²²²
)
1
1
Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026
2
Optics Teaching and Research Room of Ordnance Noncommissioned Of f icer School, Wuhan 430064
Received January 9, 2006
A passively Q-switched Nd
3+
:YAG laser with corner cube is theoretically and experimentally studied. We
analyze the polarization variation in cavity and simulate the peak power, pulse energy and pulse width
changed with the rotation angle of corner cube numerically. An experiment is made to verify the theoretical
results. With rotating the angle of corner cube about the axis the variation range of peak power is 1.77 MW
(from 10.36 to 8.59 MW), and that of pulse energy is 14.9 mJ (from 159.5 to 174.4 mJ), the fluctuation
of pulse width is 2.95 ns. The experimental results agree with the theoretical analysis to the extent of
variation rules. The most dynamic to static energy ratio of 62.5% is achieved.
OCIS codes: 140.3540, 140.3580, 260.5430.
Because of low saturation intensity, high damaged
threshold, and excellent optical, chemical, and thermal
characteristics
[1]
, Cr
4+
:YAG can be used as passive Q -
switch in Nd
3+
:YAG laser
[2−6]
. Corner cube is insensitive
to vibration, impact, and great variety of temperature,
and can be used in adjust-free lasers
[7,8]
. The combina-
tion of Cr
4+
:YAG with corner cube will obtain adjust-free
Q-switched laser. Chun
[9]
and Singh
[10]
made use of the
crossed Porro prism to realize electro-optical Q-switched
laser. But this kind of resonant cavity is adjust-free only
in one dimension. Chen used corner cube as the resonant
cavity of passively Q-switched laser, and got the pulse
energy of 8.8 mJ and the peak power of 400 kW
[11]
. Shi-
mony et al. also realized passively Q-switched laser with
corner cube
[12]
. But none of them thought of the polar-
ization properties of corner cube, and the effects of the
polarization on the peak power, pulse energy, and pulse
width. We describe the polarization variation with the
rotation of corner cube about the axis in cavity
[13,14]
, and
simulate the peak power, pulse energy, and pulse width
changed with the rotation angle of corner cube numeri-
cally. An experiment is executed to verify the theoretical
results.
The polarization state of incident light will be changed
from linear polarization to elliptical polarization because
of the polarization properties of corner cube. When the
incident light comes to the bottom of corner cube ver-
tically, Liu et al. deduced the Jones matrix by vector
optics as
[15]
J
123
= R(−120
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
)
J
231
= R(120
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(180
◦
)
J
312
= R(0
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
)
J
321
= R(−60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(−120
◦
)
J
132
= R(180
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(120
◦
)
J
213
= R(60
◦
) · T · R(−60
◦
) · T · R(60
◦
) · T · R(0
◦
), (1)
where subscripts 123—213 are in correspondence with six
reflecting orders of incident light on three flanks of corner
cube. R(ε) =
cos ε sin ε
− sin ε cos ε
describes the coordinate
variation when light is reflected from one flank to an-
other. T =
r
p
0
0 r
s
is the variation of amplitude and
polarization between incident light and reflected light, r
p
and r
s
can be got from Fresnel formula.
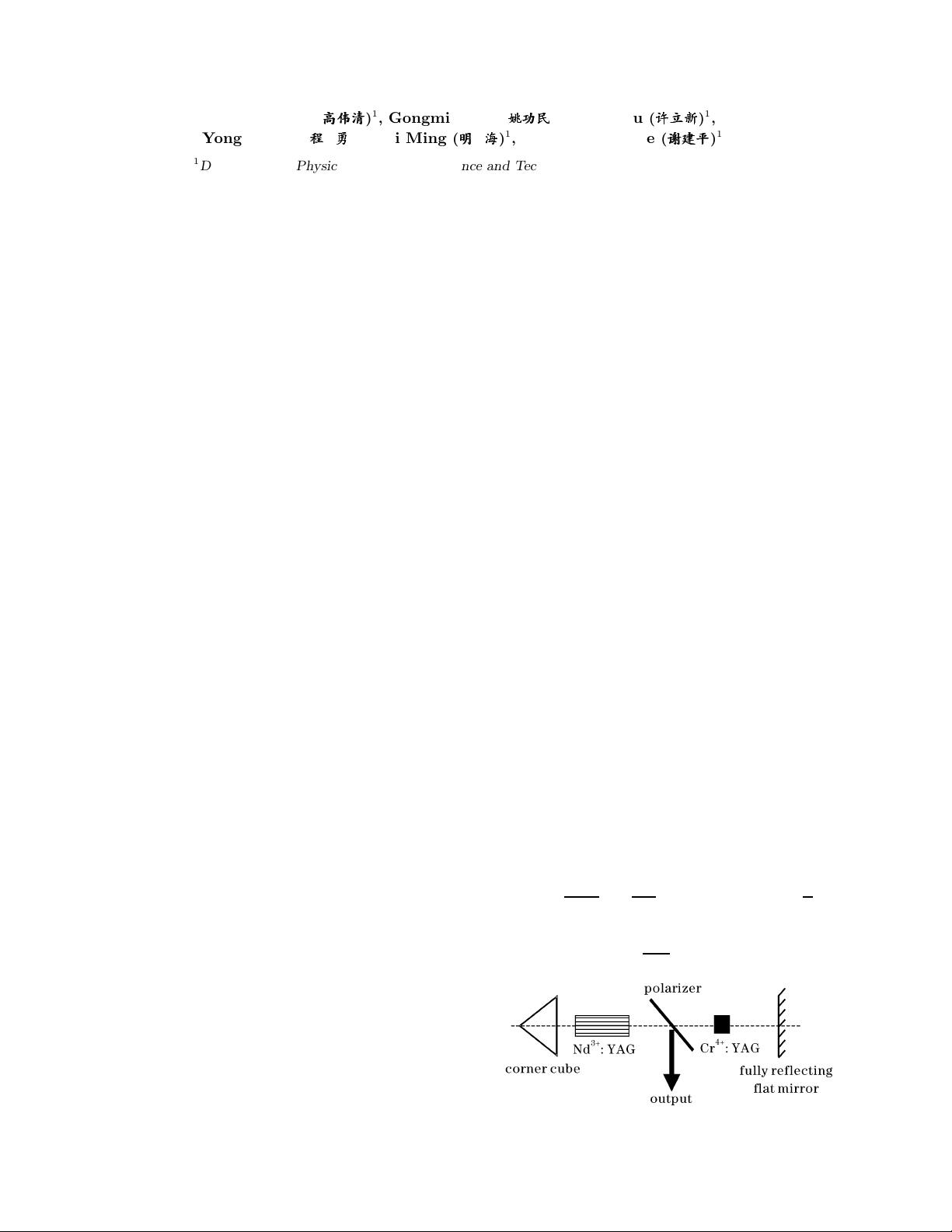
Our theoretical model is shown in Fig. 1. Resonant cav-
ity is formed by corner cube and fully reflecting flat mir-
ror. The gain material is Nd
3+
:YAG and the Q-switch is
Cr
4+
:YAG. The polarizer in the resonant cavity can pro-
vide the output beam of linear polarization. The cross
section of light beam in cavity is divided into six sym-
metric faculas (three pairs of conjugate faculas) because
of the diffraction of three edges of corner cube. Because
corner cube has the function of exchanging the situation
of light beam on space, the cavity is equivalent to three
sub-cavities. The three pairs of conjugate faculas enter
into Nd
3+
:YAG and Cr
4+
:YAG at different situations,
and pass through them four times each round trip (only
twice in flat-mirror cavity). This increases the gain of
cavity. Referring to the Refs. [16]—[18], we can deduce
the peak power and pulse energy of three sub-cavities as
P
m
(α) =
hνAl
γt
r
ln
1
R
m
(n
im
− n
tm
)
1 −
1
κ
× −n
t0m
ln
n
im
n
tm
, m = 1, 2, 3, (2)
Fig. 1. Theoretical model of passive Q-switched Nd
3+
:YAG
laser with corner cube.
1671-7694/2006/060332-04 http://www.col.org.cn









