COL 10(10), 100602(2012) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS October 10, 2012
Theoretical analysis of polarization control for the stable
output of multi-carrier source based on a re-circulating
frequency shifter
Hao Zhou (
±±±
ÓÓÓ
), Lixia Xi (
RRR
www
___
), Jianping Li (
ooo
ïïï
²²²
), Xiaoguang Zhang (
ÜÜÜ
¡¡¡
111
)
∗
, and Na Liu (
444
AAA
)
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications,
Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
∗
Corresponding author: xgzhang@bupt.edu.cn
Received Janu ary 13, 2012; accepted April 13, 2012; posted online August 3, 2012
Fluctuating polarization state-of-light in the optical loop is an important factor that seriously influences
the output performance of a multi-carrier source based on re-circulating frequency shifter (RFS). The
reason for outpu t spectrum instability when n o polarization controller (PC) is present in the loop is
analyzed theoretically. Numerical simulations for the output spectra of the multi-carrier source with and
without PC are conducted, and the trajectories of the several frequency components polarization states
on the Poincare sphere with and without PC are compared. The results show that the performance of
multi-carrier source based on a RFS can be improved effectively by adjusting the PC in the configuration
properly.
OCIS codes: 060.2330, 060.2630, 230.5440.
doi: 10.3788/COL201210.100602.
In order to meet increasing demand for the capac-
ity and transmission efficiency of the co mmunica-
tion system, many frontier studies on single-source
Tb/s transmission have bee n conducted
[1−5]
. Coher-
ent optical orthogonal-frequency-division-multiplexing
(CO-OFDM)
[1−3]
and coherent wavelength-division-
multiplexing (CO-WDM)
[4,5]
systems based on a single-
laser source have been widely applied in several Tb/s rate
transmission experiments wherein a multi-carrier source
is required. Several structures of multi-carrier sources
have been identified, including the optical frequency
comb technique
[6]
, the multi-wavelength erbium-doped
fiber laser (EDFL)
[7]
, the cascaded phase modulator and
the intensity modulator
[8]
, two cascaded phase modula-
tors based on re-cir culating frequency shifter (RFS)
[9]
,
the multi-frequency phase modulator
[10]
, and single-
sideband (SSB) modulator based on RFS
[11]
. Compared
with other methods, the SSB modulator based on RFS
has many advantages, such as low driving voltage and
controllable output frequency range, carrier interval, and
carrier numbers. However, because of the pola rization
sensitive characteristics of the I/Q modulator, the SSB
multi-carrier source is easily influenced by changes in
the laser polarization state
[12]
. Therefore, determining
how the polarization state-of-light influences the output
of multi-carrier source and how to control the polariza-
tion state to realize output stability is important.
In this letter, we theoretically analy z e the change of
the polariza tion state when optical signa ls pass thr ough
I/Q modulator, as well as the reason for the output in-
stability of the multi-ca rrier source. Numerical simula-
tions on the output spectra of multi-carrier genera tio n
system with and without a polarization controller (PC)
are conducted, and the polarization states of each fre-
quency component after every circulation are shown us-
ing a Poincare s phere. Stable output of the multi-carrier
source can be realized by adjusting PC properly.
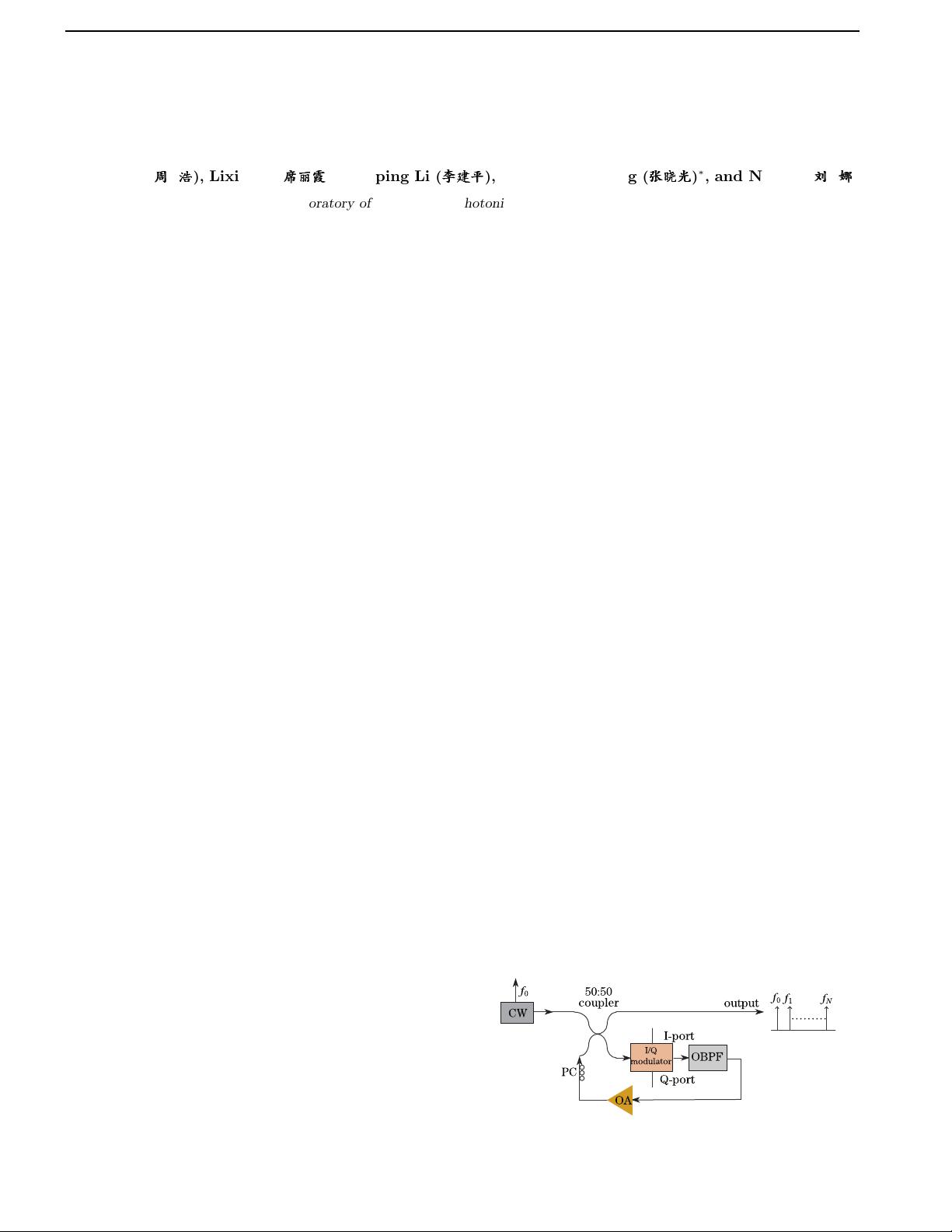
The diagram of the multi-carrier generator based on
RFS is shown in Fig. 1. This generator is a closed-loop
system that consists of a CW laser, a 50:50 coupler, an
I/Q modulator, an o ptical ba nd- pass filter (OBPF), an
optical amplifier (OA), and a PC. In this structure, the
CW laser is used as the see d lig ht source, the OBPF is
used to control the number of carriers, the OA is to com-
pens ate for the modulation and ins e rtion los ses, and the
PC is used to control p olarization s tate of the lig ht.
The I/Q modulator consists of two Mach-Zenhder mod-
ulators (MZMs) placed parallel in two arms, and a π/2-
phase shifter in one arm. The I/Q modulator is driven
by three DC voltages and two equal-amplitude but π/2-
phase shifted radio frequency (RF) clock signals through
the I and Q ports. The I/Q modulator is a polarization-
sensitive device; thus, it will modulate light oriented
along one polarization while leaving the light polarized
orthogonal to this orientation unchanged
[13]
. The polar-
ization state of the output light of the I/Q modulator will
exp erience random changes when the light is transmitted
into the cir c ulation loop. Thus, each time the light passes
the I/Q modula tor, some light components will not be
modulated. These unmodulated c omponents finally de-
stroy the stability of the output spectrum. Next, the the-
oretical derivation based on one component is discussed.
Assuming one component of input light of the I/Q mod-
ulator, e xpressed as a Jo nes vector, is
E
in
=
E
x
e
j(ω
n
t)
E
y
e
j(ω
n
t+∆θ
xy
)
, (1)
Fig. 1. Diagram of the multi-carrier generator based on RFS.
1671-7694/2012/100602(4) 100602-1
c
2012 Chinese Optics Letters









