MATLAB仿真在机器人技术中的应用:赋能智能机器的利器
发布时间: 2024-07-09 17:05:03 阅读量: 75 订阅数: 50 


用matlab仿真机器人系统
# 1. MATLAB简介**
MATLAB(Matrix Laboratory)是一种用于数值计算、可视化和编程的高级语言和交互式环境。它由 MathWorks 公司开发,广泛应用于科学、工程和金融等领域。MATLAB 以其强大的矩阵操作功能、丰富的工具箱和易于使用的图形用户界面而闻名。
MATLAB 的核心优势之一是其矩阵操作能力。它提供了一系列用于矩阵创建、操作和分析的函数。这些函数使研究人员和工程师能够高效地处理和分析大型数据集。此外,MATLAB 还提供了广泛的工具箱,涵盖了从信号处理到图像处理等各种领域。这些工具箱提供了预先构建的函数和算法,简化了复杂任务的实现。
# 2. MATLAB在机器人技术中的理论基础
### 2.1 机器人动力学和运动学建模
机器人动力学和运动学是机器人技术的基础,分别描述了机器人的运动特性和力学特性。
**机器人动力学**
机器人动力学描述了机器人的运动与作用在其上的力之间的关系。它涉及到牛顿第二定律和拉格朗日方程等基本物理原理。通过动力学建模,可以计算机器人的加速度、速度和位置等运动状态。
**机器人运动学**
机器人运动学描述了机器人的运动与关节变量之间的关系。它涉及到几何变换、齐次变换矩阵和欧拉角等数学工具。通过运动学建模,可以计算机器人的末端执行器的位姿和轨迹。
### 2.2 MATLAB中的机器人仿真建模
MATLAB提供了丰富的工具箱和函数库,可以方便地进行机器人仿真建模。
**机器人动力学仿真**
```matlab
% 创建机器人模型
robot = robotics.RigidBodyTree('DataFormat','column');
% 添加关节
joint1 = robotics.Joint('j1', 'revolute', 'X', [0, 0, 0]);
joint2 = robotics.Joint('j2', 'revolute', 'Y', [0, 0, 0]);
% 添加连杆
link1 = robotics.RigidBody('link1');
link2 = robotics.RigidBody('link2');
% 组装机器人
robot.addBody(link1, joint1);
robot.addBody(link2, joint2);
% 定义重力
gravity = [0; 0; -9.81];
% 定义关节角
q = [pi/4; pi/3];
% 计算机器人加速度
a = rigidBodyDynamics(robot, q, zeros(size(q)), gravity);
```
**机器人运动学仿真**
```matlab
% 创建机器人模型
robot = robotics.RigidBodyTree('DataFormat','column');
% 添加关节
joint1 = robotics.Joint('j1', 'revolute', 'X', [0, 0, 0]);
joint2 = robotics.Joint('j2', 'revolute', 'Y', [0, 0, 0]);
% 添加连杆
link1 = robotics.RigidBody('link1');
link2 = robotics.RigidBody('link2');
% 组装机器人
robot.addBody(link1, joint1);
robot.addBody(link2, joint2);
% 定义关节角
q = [pi/4; pi/3];
% 计算机器人末端执行器位姿
T = getTransform(robot, q, 'link2');
```
通过MATLAB中的仿真建模,可以直观地分析机器人运动的规律,并为机器人的控制和规划提供基础。
# 3.1 机器人轨迹规划和控制
### 轨迹规划
轨迹规划是指为机器人确定一条从起始位置到目标位置的路径,同时满足运动学和动力学约束。MATLAB中提供了丰富的工具箱和函数库,可以高效地完成机器人轨迹规划任务。
**基于样条曲线的轨迹规划**
样条曲线是一种分段多项式函数,可以平滑地连接一系列控制点。MATLAB中的`spline`函数可以生成样条曲线,并用于规划机器人的轨迹。
```matlab
% 定义控制点
control_points = [0, 0; 1, 1; 2, 2];
% 生成样条曲线
spline_curve = spline(control_points(:, 1), control_points(:, 2));
% 评估轨迹点
t = linspace(0, 1, 100); % 时间参数
trajectory = ppval(spline_curve, t);
```
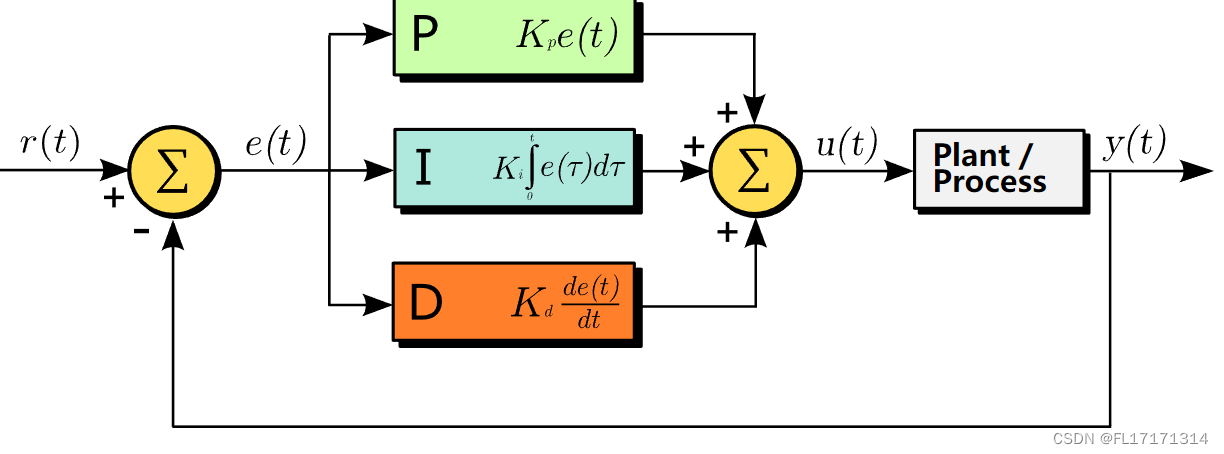
### 运动控制
运动控制是指根据轨迹规划的路径,控制机器人的运动,使其沿着路径平稳、准确地移动。MATLAB中提供了`controlSystemDesigner`工具箱,可以设计和仿真各种运动控制器
0
0





