OpenCV轮廓识别实战指南:识别复杂形状和物体
发布时间: 2024-08-10 11:30:13 阅读量: 57 订阅数: 33 


PaddleTS 是一个易用的深度时序建模的Python库,它基于飞桨深度学习框架PaddlePaddle,专注业界领先的深度模型,旨在为领域专家和行业用户提供可扩展的时序建模能力和便捷易用的用户体验
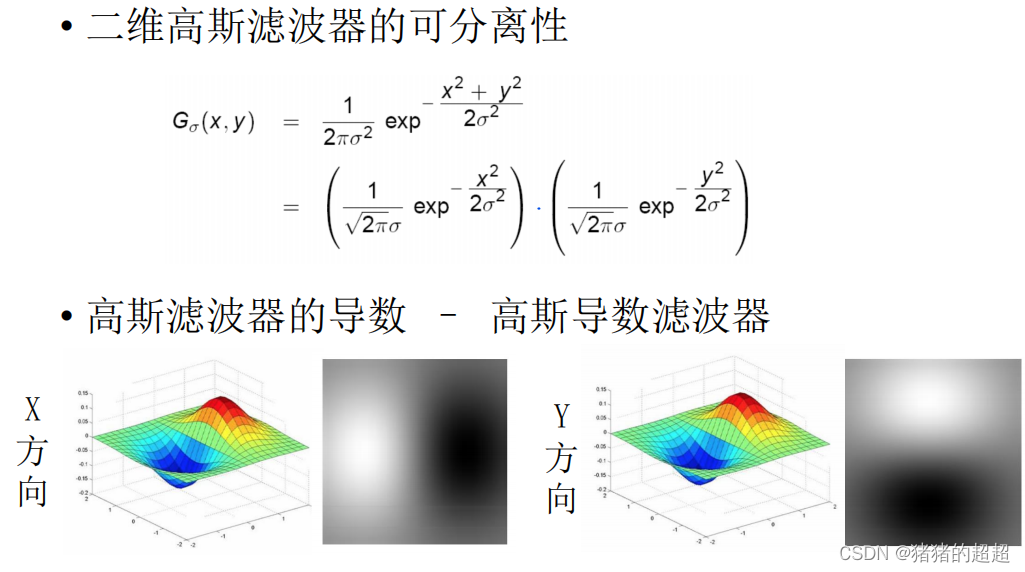
# 1. OpenCV轮廓识别的基础**
轮廓识别是计算机视觉中的一项基本技术,用于从图像中提取物体的形状信息。OpenCV(Open Source Computer Vision Library)是一个流行的计算机视觉库,提供了强大的轮廓识别功能。
OpenCV的轮廓识别算法基于图像处理和数学形态学原理。它通过一系列图像预处理步骤,如灰度化、二值化和降噪,将图像简化为二值图像,其中物体以白色像素表示,背景以黑色像素表示。然后,OpenCV使用轮廓提取算法,如Canny边缘检测和轮廓追踪,来识别图像中的轮廓。
# 2. OpenCV轮廓识别算法
### 2.1 图像预处理技术
图像预处理是轮廓识别中的关键步骤,它可以有效去除图像噪声,增强图像特征,为后续的轮廓提取做好准备。常用的图像预处理技术包括:
#### 2.1.1 图像灰度化
图像灰度化是指将彩色图像转换为灰度图像,即将图像中的每个像素点的颜色信息转换为亮度值。灰度化可以简化图像数据,减少计算量,同时保留图像中的大部分信息。
**代码示例:**
```python
import cv2
# 读取彩色图像
image = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
# 转换为灰度图像
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 显示灰度图像
cv2.imshow('Gray Image', gray_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.cvtColor()` 函数将彩色图像 `image` 转换为灰度图像 `gray_image`。
* `cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY` 参数指定将图像从 BGR 颜色空间(蓝色、绿色、红色)转换为灰度空间。
#### 2.1.2 图像二值化
图像二值化是指将灰度图像转换为二值图像,即将图像中的每个像素点的亮度值转换为 0(黑色)或 255(白色)。二值化可以进一步简化图像数据,突出图像中的主要特征。
**代码示例:**
```python
import cv2
# 读取灰度图像
gray_image = cv2.imread('gray_image.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 阈值二值化
thresh_image = cv2.threshold(gray_image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
# 显示二值图像
cv2.imshow('Thresholded Image', thresh_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.threshold()` 函数将灰度图像 `gray_image` 转换为二值图像 `thresh_image`。
* `127` 是阈值,将亮度值小于 127 的像素点转换为 0,大于 127 的像素点转换为 255。
* `cv2.THRESH_BINARY` 参数指定使用二进制阈值化方法。
#### 2.1.3 图像降噪
图像降噪是指去除图像中的噪声,例如椒盐噪声、高斯噪声等。降噪可以提高图像质量,为后续的轮廓提取提供更清晰的图像数据。
**代码示例:**
```python
import cv2
# 读取灰度图像
gray_image = cv2.imread('gray_image.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 高斯滤波降噪
denoised_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_image, (5, 5), 0)
# 显示降噪图像
cv2.imshow('Denoised Image', denoised_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.GaussianBlur()` 函数使用高斯滤波器对灰度图像 `gray_image` 进行降噪,生成降噪图像 `denoised_image`。
* `(5, 5)` 参数指定高斯滤波器的核大小。
* `0` 参数指定高斯滤波器的标准差,设置为 0 表示使用图像的默认标准差。
# 3. OpenCV轮廓识别实战
### 3.1 复杂形状识别
复杂形状识别是指识别不规则或非标准形状的轮廓,例如多边形、圆形和椭圆。OpenCV提供了多种算法来处理这些复杂形状。
#### 3.1.1 多边形识别
多边形是一种具有多个直边的形状。OpenCV使用轮廓近似算法来识别多边形。该算法将轮廓近似为一组直线段,并根据这些直线段的长度和角度来确定多边形的类型。
```python
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread('polygon.jpg')
# 图像预处理
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 100, 200)
# 轮廓提取
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 多边形近似
approx_contours = []
for contour in contours:
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contour, 0.01 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True), True)
approx_contours.append(approx)
# 绘制多边形
cv2.drawContours(image, approx_contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 显示图像
cv2.imshow('Polygon Recognition', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.approxPolyDP()`函数使用道格拉斯-普克算法对轮廓进行近似,该算法将轮廓近似为一组直线段。
* `epsilon`参数指定了允许的近似误差,较小的`epsilon`值将产生更精确的近似,但计算成本更高。
* `True`参数指示算法是否闭合近似轮廓,即是否将最后一个点与第一个点连接起来。
#### 3.1.2 圆形识别
圆形是一种具有相同半径的闭合曲线。OpenCV使用霍夫变换算法来识别圆形。该算法通过在图像中搜索圆形边缘的交点来检测圆形。
```python
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread('circle.jpg')
# 图像预处理
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 100, 200)
# 霍夫变换圆形检测
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(edges, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1=100, param2=30, minRadius=0, maxRadius=0)
# 绘制圆形
if circles is not None:
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
for circle in circles[0, :]:
cv2.circle(image, (circle[0], circle[1]), circle[2], (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 显示图像
cv2.imshow('Circle Recognition', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.HoughCircles()`函数使用霍夫变换算法检测圆形。
* `param1`和`param2`参数分别指定了边缘检测阈值和圆形半径范围。
* `minRadius`和`maxRadius`参数指定了要检测的圆形的最小和最大半径。
#### 3.1.3 椭圆识别
椭圆是一种具有两个不同半径的闭合曲线。OpenCV使用拟合椭圆算法来识别椭圆。该算法通过最小化轮廓点到椭圆边缘的距离之和来拟合椭圆。
```python
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread('ellipse.jpg')
# 图像预处理
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 100, 200)
# 拟合椭圆
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[0])
# 绘制椭圆
cv2.ellipse(image, ellipse, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 显示图像
cv2.imshow('Ellipse Recognition', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
* `cv2.fitEllipse()`函数使用最小二乘法拟合椭圆。
* 返回的椭圆参数是一个元组,其中包含椭圆的中心、长轴、短轴和旋转角度。
# 4.1 轮廓特征分析
### 4.1.1 轮廓面积和周长计算
轮廓的面积和周长是两个重要的特征,可用于识别和分析形状。OpenCV提供了`cv2.contourArea()`和`cv2.arcLength()`函数来计算这些特征。
```python
import cv2
# 加载图像并灰度化
image = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 提取轮廓
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 计算面积和周长
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
perimeter = cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
print("Area:", area, "Perimeter:", perimeter)
```
### 4.1.2 轮廓凸包和凹陷点检测
轮廓的凸包是将其所有点包围的最小凸多边形。凹陷点是轮廓上向内弯曲的点。OpenCV提供了`cv2.convexHull()`和`cv2.convexityDefects()`函数来检测这些特征。
```python
import cv2
# 加载图像并灰度化
image = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 提取轮廓
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 计算凸包和凹陷点
for contour in contours:
hull = cv2.convexHull(contour)
defects = cv2.convexityDefects(contour, hull)
print("Hull points:", hull)
print("Defects:", defects)
```
### 4.1.3 轮廓矩计算
轮廓矩是描述轮廓形状的统计量。它们可以用于计算质心、方向和惯性矩。OpenCV提供了`cv2.moments()`函数来计算这些矩。
```python
import cv2
# 加载图像并灰度化
image = cv2.imread('image.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 提取轮廓
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 计算轮廓矩
for contour in contours:
moments = cv2.moments(contour)
print("Moments:", moments)
print("Centroid:", (moments['m10'] / moments['m00'], moments['m01'] / moments['m00']))
```
# 5.1 轮廓识别算法优化
### 5.1.1 并行处理
在轮廓识别过程中,图像处理和轮廓提取等操作可以并行化,以提高处理速度。OpenCV提供了多线程和多核处理支持,可以通过使用`OpenMP`或`TBB`等并行编程库来实现。
```cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <omp.h>
using namespace cv;
int main() {
Mat image = imread("image.jpg");
cvtColor(image, image, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(image, image, 127, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
std::vector<std::vector<Point>> contours;
std::vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < image.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < image.cols; j++) {
if (image.at<uchar>(i, j) == 255) {
findContours(image, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
```
### 5.1.2 GPU加速
对于大型图像或视频流处理,GPU加速可以显著提高轮廓识别的速度。OpenCV提供了`CUDA`和`OpenCL`支持,可以通过使用`cv::cuda::findContours`或`cv::ocl::findContours`函数来实现。
```cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/cudaarithm.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::cuda;
int main() {
Mat image = imread("image.jpg");
cvtColor(image, image, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(image, image, 127, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
GpuMat gpuImage(image);
GpuMat gpuContours;
findContours(gpuImage, gpuContours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
return 0;
}
```
0
0





