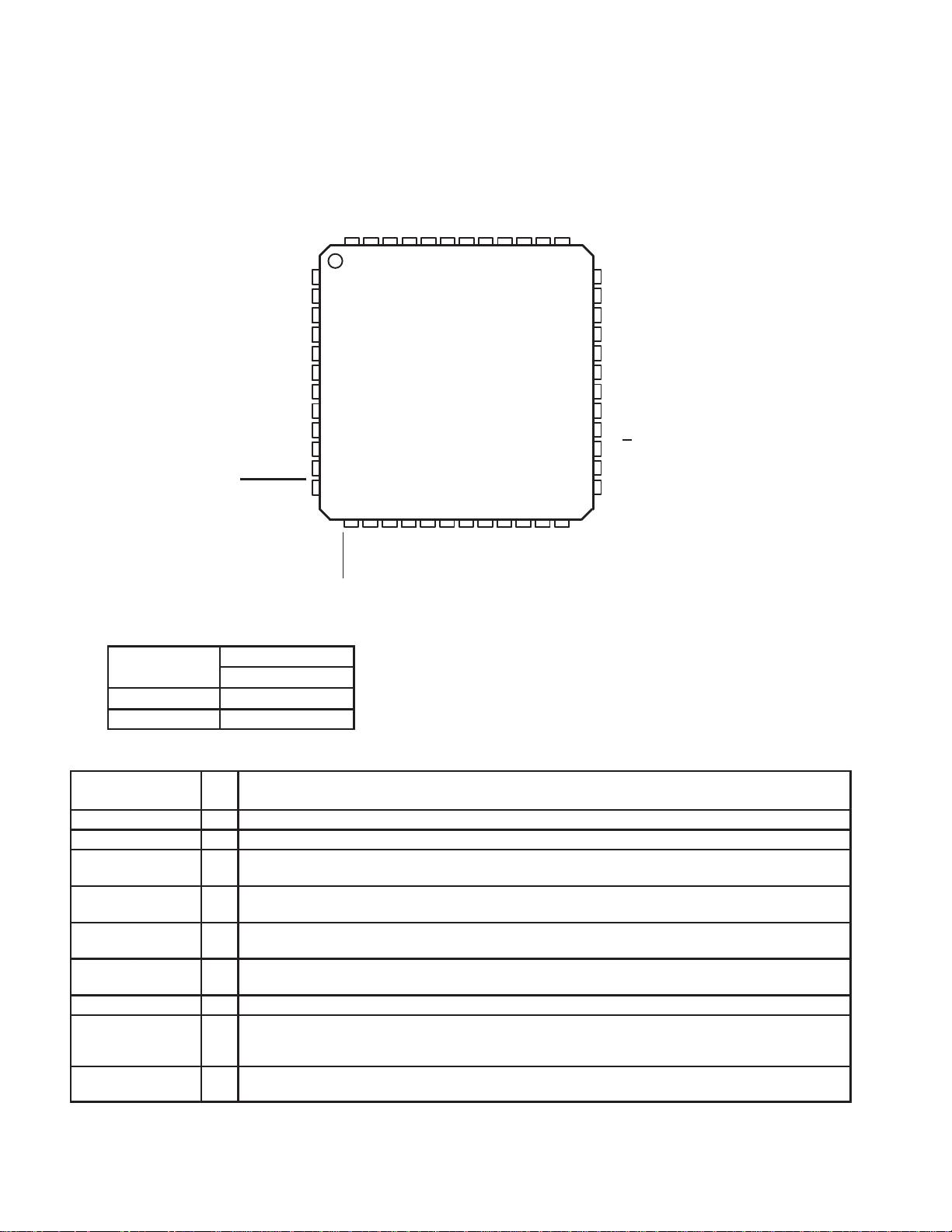
1–5
1.5 Terminal Functions (Continued)
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
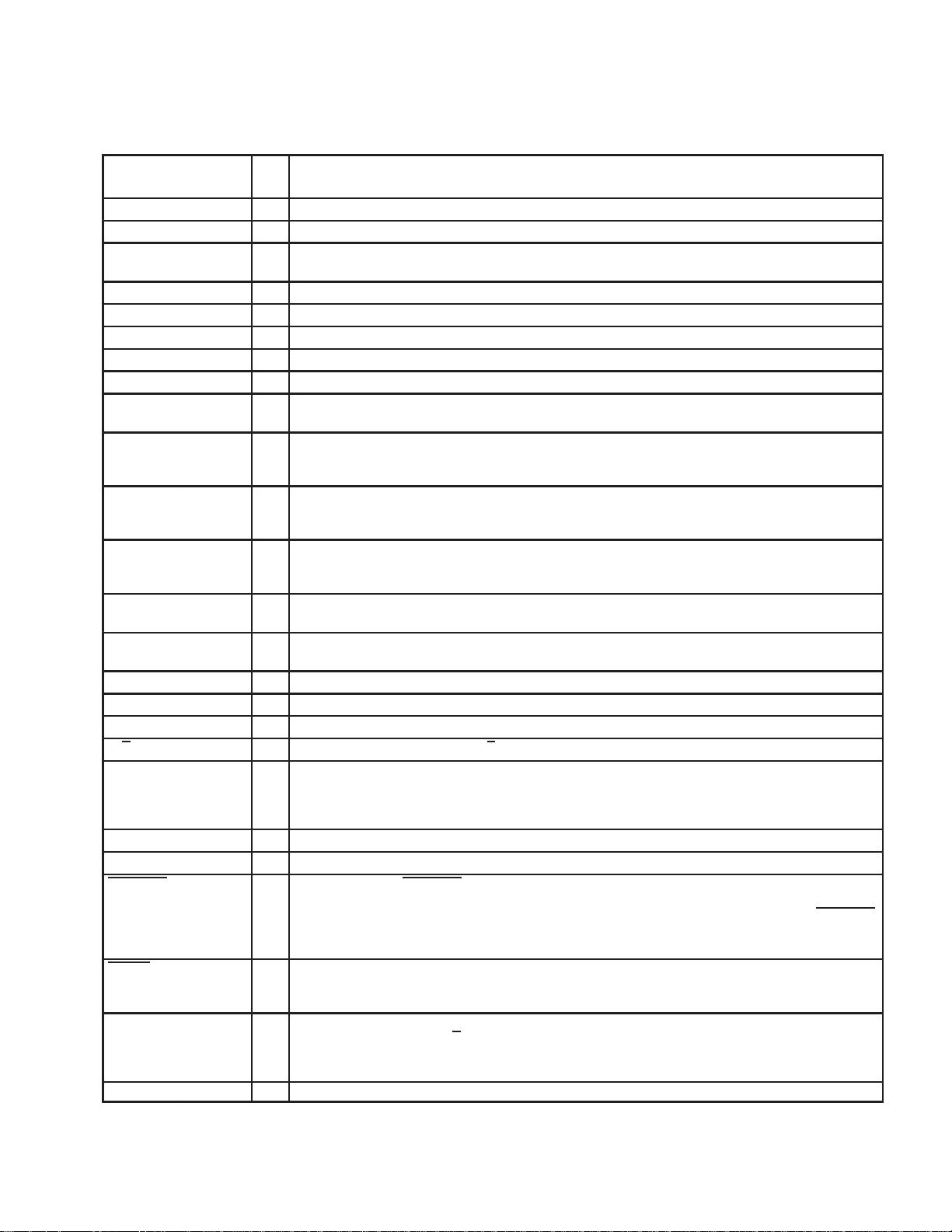
DTXIM 7 I Transmitter-path amplifier A3 analog inverting input. Can also be used for general-purpose amplification.
DTXIP 6 I Transmitter-path amplifier A4 analog noninverting input. Can also be used for general-purpose amplification.
DTXOM 5 O Transmitter path amplifier A4 feedback for negative output. Can also be used for general-purpose
amplification.
DTXOP 4 O Transmitter path amplifier A3 feedback for positive output. Can also be used for negative output.
DV
DD1
15 I Digital power supply
DV
DD2
30 I Digital power supply
DV
SS
14, 29 I Digital ground
FC 24 I Hardware request for secondary communication
FILT 38 O Bandgap filter. FILT is provided for decoupling of the bandgap reference, and provides 2.5 V. The optimal
capacitor value is 0.1 µF (ceramic). This voltage node should be loaded only with a high-impedance dc load.
FLAG 23 O Controlled by bit D4 of control register 3. If D4=0 (default), the FLAG pin outputs the communication flag that
goes low/high to indicate primary-communication/secondary-communication interval, respectively. If D4=1,
the FLAG pin outputs the value of D3.
FS 22 I/O Frame sync. When FS goes low, DIN begins receiving data bits and DOUT begins transmitting data bits. In
master mode, FS is internally generated and is low during data transmission to DIN and from DOUT. In slave
mode, FS is externally generated.
FSD 21 O Frame-sync delayed output. The FSD output synchronizes a slave device to the frame sync of the master
device. FSD is applied to the slave FS input and has the same duration as the master FS signal. Requires a
pullup resistor if not used.
INM 48 I Inverting input to analog modulator. INM requires an external R-C antialias filter with low output impedance if
the internal antialias filter is bypassed.
INP 47 I Noninverting input to analog modulator. INP requires an external R-C antialias filter with low output impedance
if the internal antialias filter is bypassed.
M0 10 I Combine with M1 to select serial interface mode (frame-sync mode)
M1 11 I Combine with M0 to select serial interface mode (frame-sync mode)
MCLK 20 I Master clock. MCLK derives the internal clocks of the sigma-delta analog interface circuit.
M/S 27 I Master/slave select input. When M/S is high, the device is the master, and when is low, it is a slave.
NC 18, 28, 31,
32, 35, 36,
37, 39, 41,
44
No connection
OUTM 9 O DAC’s inverting output. OUTM is functionally identical with and complementary to OUTP.
OUTP 8 O DAC’s noninverting output. OUTP can also be used alone for single-ended operation.
PWRDWN 12 I Power down. When PWRDWN is pulled low, the device goes into a power-down mode, the serial interface is
disabled, and most of the high-speed clocks are disabled. However, all register values are sustained and the
device resumes full-power operation without reinitialization when PWRDWN is pulled high again. PWRDWN
resets the counters only and preserves the programmed register contents. See paragraph 2.2.2 for more
information.
RESET 13 I Reset. The reset function is provided to initialize all the internal registers to their default values. The serial port
can be configured to the default state accordingly. See Appendix A,
Register Set
, and Subsection 2.2.1,
Reset
and Power-Down Functions
for detailed descriptions.
SCLK 19 I/O Shift clock. SCLK signal clocks serial data into DIN and out of DOUT during the frame-sync interval. When
configured as an output (M/S
high), SCLK is generated internally by multiplying the frame-sync signal
frequency by 256 (cascade devices < 5) or 512 (cascade devices > 4). When configured as an input (M/S low),
SCLK is generated externally and must be synchronous with the master clock and frame sync.
VMID 43 O Reference voltage output at AVDD/2