机器学习实战:Scikit-Learn, Keras, TensorFlow 2nd Edition 概览
"《Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, TensorFlow, 2nd Edition》是关于机器学习实践的一本经典书籍,涵盖了Scikit-Learn、Keras和TensorFlow等工具的使用,特别指出该版本仅包含第一部分的前九章,并新增了无监督学习等内容。"
在机器学习领域,这本书首先介绍了什么是机器学习(Machine Learning),它是一种让计算机通过数据学习并改进的方法,而不是硬编码规则。机器学习的主要应用在于它能解决复杂问题,例如模式识别、预测分析等。
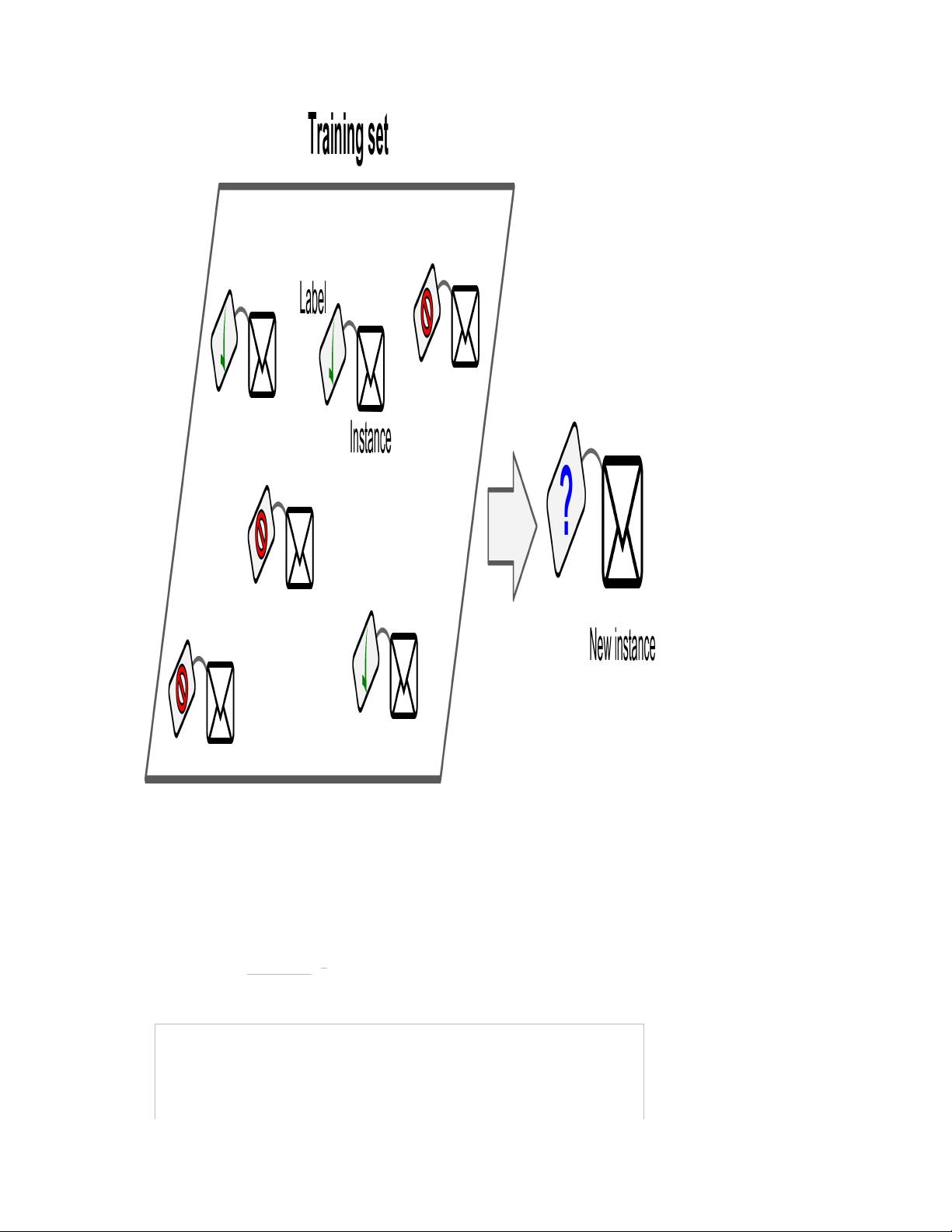
接着,书中阐述了为何使用机器学习。这是因为机器学习能够处理大量数据,自动发现规律,适应不断变化的环境,以及进行预测和决策。机器学习系统分为监督学习和无监督学习两大类。监督学习是指有标签的数据集,模型通过学习输入与输出之间的关系来预测新数据;而无监督学习则在没有标签的情况下,尝试找出数据中的内在结构或群组。
书中还讨论了不同类型的机器学习系统,如批处理学习和在线学习。批处理学习一次性处理所有数据,适合离线场景;在线学习则逐个或小批量处理数据,适用于实时或流式数据。此外,还有基于实例的学习与模型驱动的学习,前者依赖于已知的案例,后者则构建全局模型。
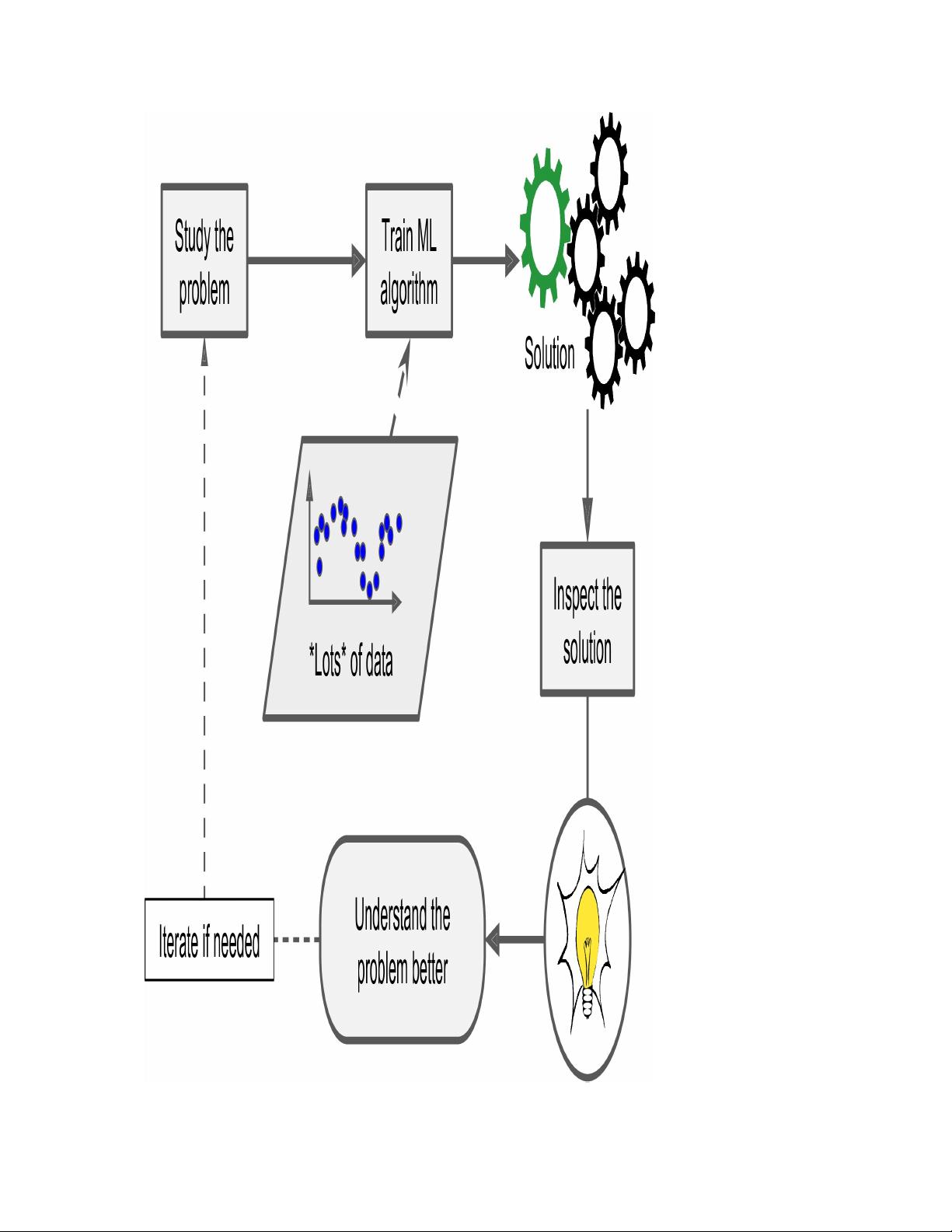
机器学习面临的挑战包括:训练数据不足、训练数据不具代表性、数据质量差、特征不相关、过拟合(模型过度复杂,对训练数据过适应)、欠拟合(模型过于简单,无法捕捉数据模式)等问题。为了解决这些问题,书中的"Stepping Back"部分可能涉及了反思和调整模型策略的重要性。
测试和验证是机器学习项目的关键环节。在实际项目中,我们需要先定义问题,选择合适的性能指标,检查假设,获取数据并创建工作空间。数据预处理包括清洗、处理文本和分类属性,以及自定义转换,这些都是为了使数据更适合机器学习算法。
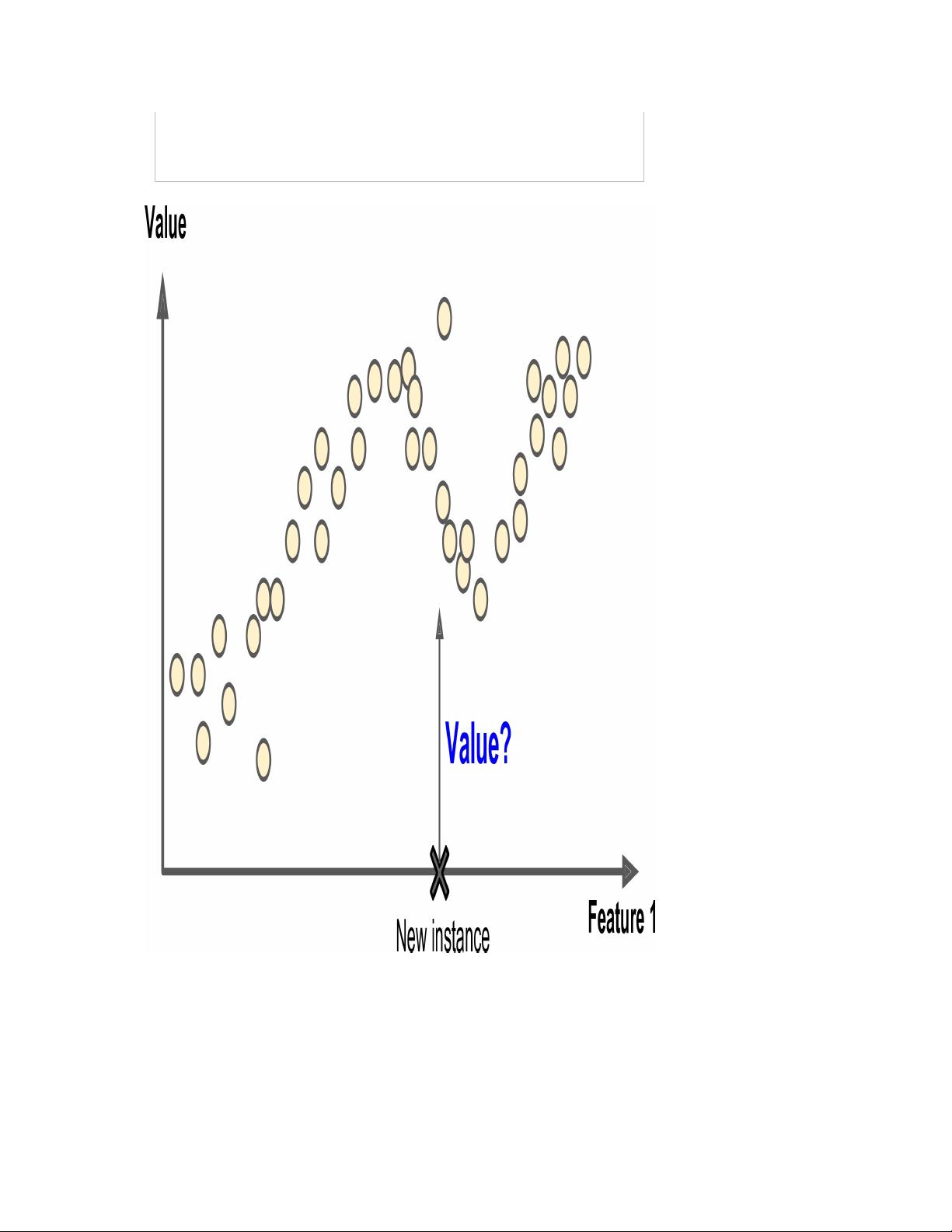
通过真实数据的工作流程,可以深入理解数据,例如可视化地理数据以揭示空间模式,寻找特征间的相关性,试验不同特征组合。数据预处理步骤中的数据清洗是去除噪声和异常值,处理文本数据通常涉及分词和向量化,而分类属性的处理可能需要用到独热编码等技术。
这本书为读者提供了一个全面的机器学习实践指南,涵盖从项目规划到数据准备,再到模型训练和评估的全过程,特别是对于初学者,这是一个极好的起点,帮助他们掌握Scikit-Learn、Keras和TensorFlow等工具,以及如何解决实际的机器学习问题。
2018-02-01 上传
2019-10-07 上传
2017-12-23 上传
2018-02-07 上传
2018-09-01 上传
2022-04-02 上传
点击了解资源详情
2017-11-16 上传
2019-09-20 上传
gudong321
- 粉丝: 1
- 资源: 6
最新资源
- IETI-LAB7-2021
- emd.rar_matlab例程_matlab_
- Xbee-boss:使用Paul Malmstem的python xbee库
- ETL_Project:GWU Bootcamp ETL项目
- OpenCV-MinGW-Build::eyes:MinGW在Windows上编译的OpenCV32位和64位版本。 包括OpenCV 3.3.1、3.4.1、3.4.1-x64、3.4.5、3.4.6、3.4.7、3.4.8-x64、3.4.9、4.0.0-alpha-x64、4.0.0- rc-x64、4.0.1-x64、4.1.0、4.1.0-x64、4.1.1-x64、4.5.0-with-contrib
- data-structures-and-algorithms
- contentful.swift:与Contentful的内容交付API的令人愉快的Swift接口
- StackStockRouter
- speaker_recognition.rar_语音合成_matlab_
- Allow CORS: Access-Control-Allow-Origin-crx插件
- pairgame-heroku
- 参考资料-WI-NK0103公司会议制度管理规定(09.04.30改).zip
- Golang_Homework
- TopAnimes是一个示例动漫Android应用程序-Android开发
- Landing-Page:我的编程产品组合的目标页面
- 快车时间