GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW3122
utilize devices that require multiple transitions
from recessive to dominant to recognize a valid
wakeup event within a single bus frame;
however, the device shall not require more
than two recessive to dominant or dominant to
recessive transitions.
c. When the bus is in dominant state at the point
in time when the ECU attempts to enter a low
power mode, then the ECU shall enter the low
power mode and shall remain in the low power
mode until there is a valid wakeup condition. In
this case a valid wakeup condition requires at
least one recessive to dominant transition on
the bus, unless otherwise explicitly specified
for a particular ECU.
3.3.2.1 Requirements On Valid Wakeup Request
Messages. It is important to note a bus frame must
meet certain characteristics in order to enable
reliable wakeup request functionality. The frame
that is used for the purpose of bus wakeup request
must contain the pattern as specified below:
3.3.2.1.1 The frame must contain at least 2
instances consisting of at least 3 consecutive
dominant bits separated by a pattern that includes
at least one phase consisting of at least 3
consecutive recessive bits. At data rates higher
than 500 kbit/s the specified phases have to
contain more than the above described number of
consecutive bits.
3.3.2.1.2 The frame must not contain any data
bytes. Exception: If an ECU-specific frame header
is utilized for the purpose to facilitate bus wakeup
requests, then presence of data bytes is permitted.
Note: The above described pattern may be located
anywhere in the transmitted bus frame, e.g.,
including ID field, DLC, fixed form bits, CRC, SOF
and stuff bits:
3.3.3 Wake Up on Continuous High Level
Discrete Input. This approach foresees that ECUs
shall enable/disable the communication function of
the primary HS-GMLAN interface based on the
voltage level of a dedicated input. There is (at
least) one ECU which controls the voltage on this
dedicated wake up line. Devices which provide
output control capability for the dedicated wakeup
line shall also provide the input function specified
in this section. Note it is possible that only a subset
of ECUs of a subnet is connected to the wake up
line. The Component Technical Specification
specifies whether the ECU shall have a wake up
output function and/or whether it shall have a wake
up detection input function. For ESD protection
requirements refer to GMW3097. Wake up outputs
and inputs shall be proof against short circuits to
any voltage between –3 V and +26.5 V.
ECUs which shall be able to request wake up of
the network shall meet the following requirements
at the particular output:
In principle the wake up wire output shall provide
open collector characteristic. When asserted the
ECU shall typically output battery voltage level.
When not asserted the ECU shall exhibit a weak
low state.
Note: Parameter specifications apply over
operating conditions and aging, e.g. temperature,
supply voltage and age drift over specified vehicle
temperature and component life time unless
otherwise noted.
ECUs which shall provide wake up input detection
capability shall meet the following requirements at
this particular input:
The ECU shall have a logic input that connects to
the continuous high level signal. This input shall be
used for detecting presence of a wake up request.
In principle the wake up wire input shall provide
weak pull down to ground potential characteristic.
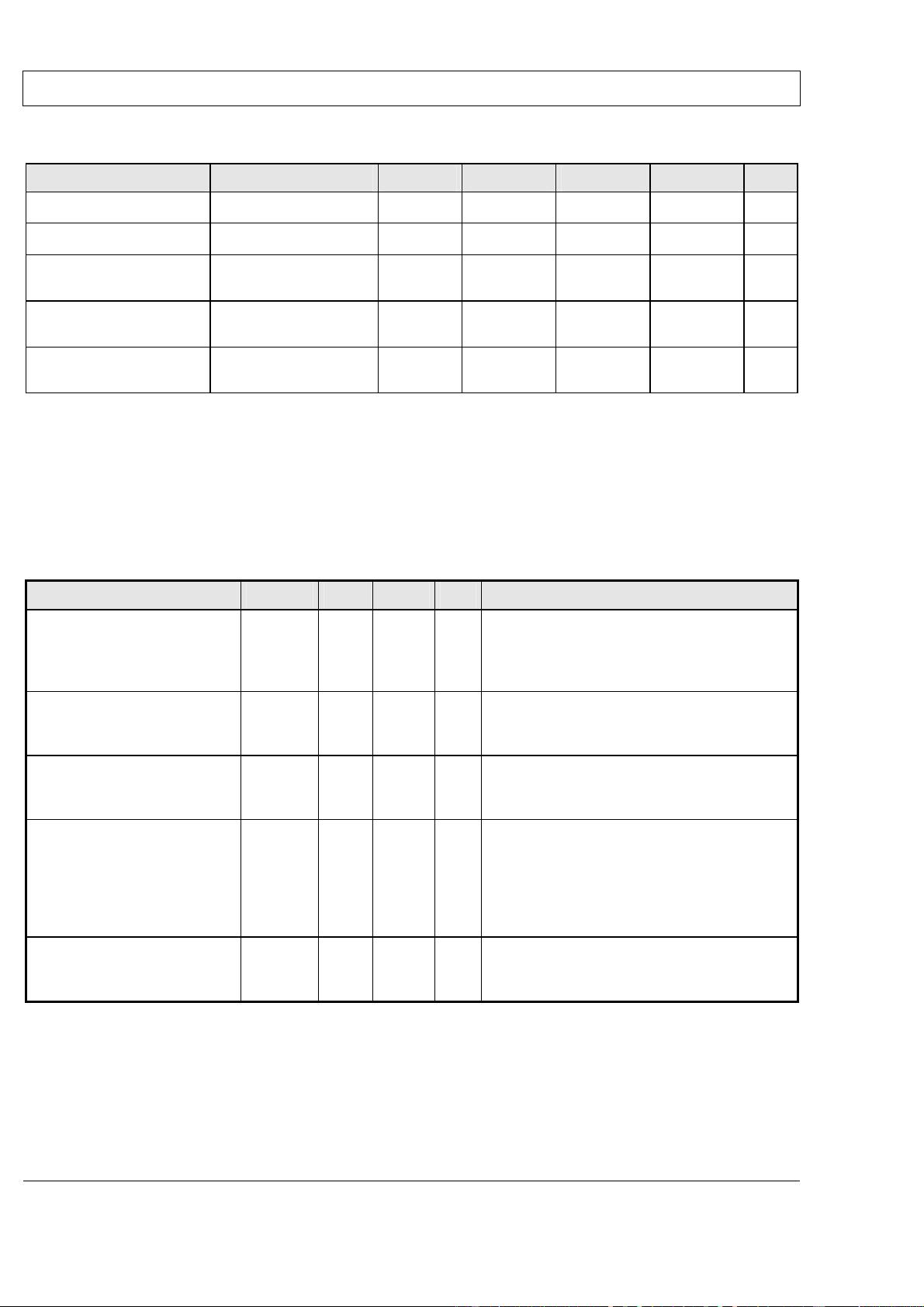
Table 4: Wake up line output requirements
Parameter Conditions Symbol Min. Nom. Max. Unit
Active State Output
Voltage
R
L
= 240 Ω
V
wuoh
Min {9,
(V
s
– 1.7)}
V
s
Max {26.5,
(V
s
+ 0.3)}
V
Active State Output
Current
V
s
≥ 9 V
I
Oh
50 200 mA
Active State Short-Circuit
Output Current
V
wu
= 0 V and/or
V
wu
= 26.5 V
V
wuohsc
-
250
mA
Inactive State Output
Leakage Current
V
wu
= +12 V I
LEAKmax
-10
0 +10 uA
Conditions: 6.0 V ≤ V
s
≤ 26.5 V, -40
o
C < T
amb
< T
ambMax
unless otherwise noted. T
ambMax
shall be specified in the CTS.
V
wu
corresponds to the voltage at the Communication Enable I/O pin of the ECU.
© Copyright 2005 General Motors Corporation All Rights Reserved
April 2005 Page 7 of 37
Reproduced by IHS under license with GMW
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
--`,,`,,`-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---