Electronic copy available at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3166188
3rd International Conference on Internet of Things and Connected Technologies (ICIoTCT), 2018
ELSEVIER-SSRN INFORMATION SYSTEMS & EBUSINESS NETWORK ISSN: 1556-5068
HTTPS://WWW.ELSEVIER.COM/SOLUTIONS/SSRN HTTPS://WWW.SSRN.COM/LINK/3RD-ICIOTCT-2018.HTML
An Improved Approach in Core Point Detection Algorithm for
Fingerprint Recognition
Meghna Patel
a
, Satyen M. Parikh
b
, Ashok R. Patel
c
a
AMPICS, Ganpat University, Gujarat, India
b
AMPICS, Ganpat University, Gujarat, India
c
Florida Polytechnic University, Lakeland, Florida, USA
Abstract:
Core Point Detection is used when comparison of two fingerprint based on alignment is done. To extract the core point is still open issue in fingerprint
recognition. The success rate of fingerprint recognition as well as to speed up the process core point is used. The proposed core point detection algorithm
follows four steps: normalization, ridge orientation estimation, smoothing and core point detection. To test the experimental result and performance of
proposed algorithm carried out using FVC2000 and FingerDOS databases and prove that, the FMR and FNMR for FVC2000 is 2 and 1.2 and for
FingerDOS is 0 and 1.67 respectively. The accuracy of FVC2000 is 98.4% and FingerDOS is 99.16%. The average execution time of FVC2000 is less
than 0.72 and for FingerDOS is 0.25 second.
Keywords: normalization, ridge orientation estimation, smoothing and core point detection, fingerprint recognition
1. Introduction
In the era of information security biometric is the most secure and
appropriate method for encouraging the person recognition and
identification. It authenticates an user based on physiological (material or
behavioral) characteristics of the person.
Fingerprint authentication is the most famous and widely adopted
biometric over a century because it remains unique and consistent over
time. It is popular because implanted in many commercial systems like
mobile and laptops. It is also used in worldwide airport countries as well
as used in forensic arena to recognize the crime scene for national and
international security. Now a day the government, and law enforcement
agencies are also used fingerprint authentication for making safe and
secure world. These types of real time applications require less than one
second for executing the authentication process. During fingerprint
recognition two types of features are acquired: 1) Global and 2) Local
Features. Ridge ending, ridge bifurcation, spike, island etc. are known as
local features while core and delta points (singular points) are known as
global features. To compare alignment between two fingerprints, singular
points are used [1] [2] [3]. For all types of fingerprint core point is
reliable. In the conventional techniques, minutiae feature set is used for
comparing two fingerprints without checking alignment. Extensively, to
reduce the computational time feature set of minutiae is aligned in relation
with core point [4].
Every person’s fingerprint contains unique structure with ridges and
valleys. The parallel line pattern in fingerprint is called ridges. It contains
high curvature in singular regions [5]. This high curvature singular
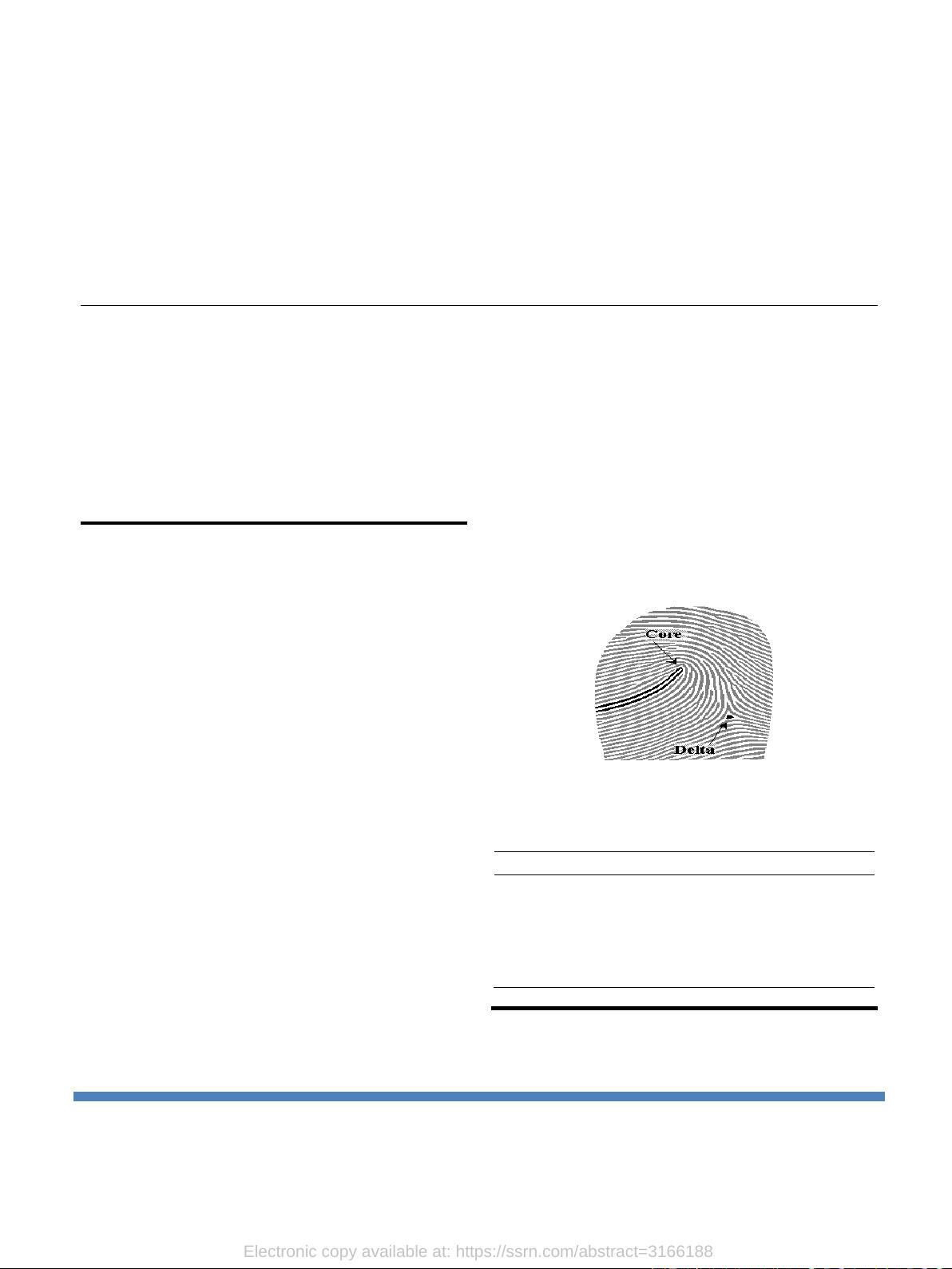
regions contains two types of global features core and delta displayed in
Fig. 1. Center point in fingerprint image is called as core point while flow
of ridges diverts in two different directions is called as delta points [1, 6].
According to the presence of singular points the fingerprint images are
categorized into five classes [5] like arch, tented arch, whorl, left loop,
right loop, The below Table 1. show the details of core and delta points.
Fig. 1. Singular Points
Table 1. Core and Delta points required in classification types of
fingerprint
2. Literature Survey
Singular point detection can be done using several categories [5], and
Core point is one type of singular point. The Poincare Index based









