W25Q128FV
- 15 -
6.2 Write Protection
Applications that use non-volatile memory must take into consideration the possibility of noise and other
adverse system conditions that may compromise data integrity. To address this concern, the
W25Q128FV provides several means to protect the data from inadvertent writes.
6.2.1 Write Protect Features
Device resets when VCC is below threshold
Time delay write disable after Power-up
Write enable/disable instructions and automatic write disable after erase or program
Software and Hardware (/WP pin) write protection using Status Registers
Additional Individual Block/Sector Locks for array protection
Write Protection using Power-down instruction
Lock Down write protection for Status Register until the next power-up
One Time Program (OTP) write protection for array and Security Registers using Status Register
*
* Note: This feature is available upon special order. Please contact Winbond for details.
Upon power-up or at power-down, the W25Q128FV will maintain a reset condition while VCC is below
the threshold value of VWI, (See Power-up Timing and Voltage Levels and Figure 43). While reset, all
operations are disabled and no instructions are recognized. During power-up and after the VCC voltage
exceeds VWI, all program and erase related instructions are further disabled for a time delay of tPUW.
This includes the Write Enable, Page Program, Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase and the Write
Status Register instructions. Note that the chip select pin (/CS) must track the VCC supply level at
power-up until the VCC-min level and tVSL time delay is reached, and it must also track the VCC supply
level at power-down to prevent adverse command sequence. If needed a pull-up resister on /CS can be
used to accomplish this.
After power-up the device is automatically placed in a write-disabled state with the Status Register Write
Enable Latch (WEL) set to a 0. A Write Enable instruction must be issued before a Page Program,
Sector Erase, Block Erase, Chip Erase or Write Status Register instruction will be accepted. After
completing a program, erase or write instruction the Write Enable Latch (WEL) is automatically cleared
to a write-disabled state of 0.
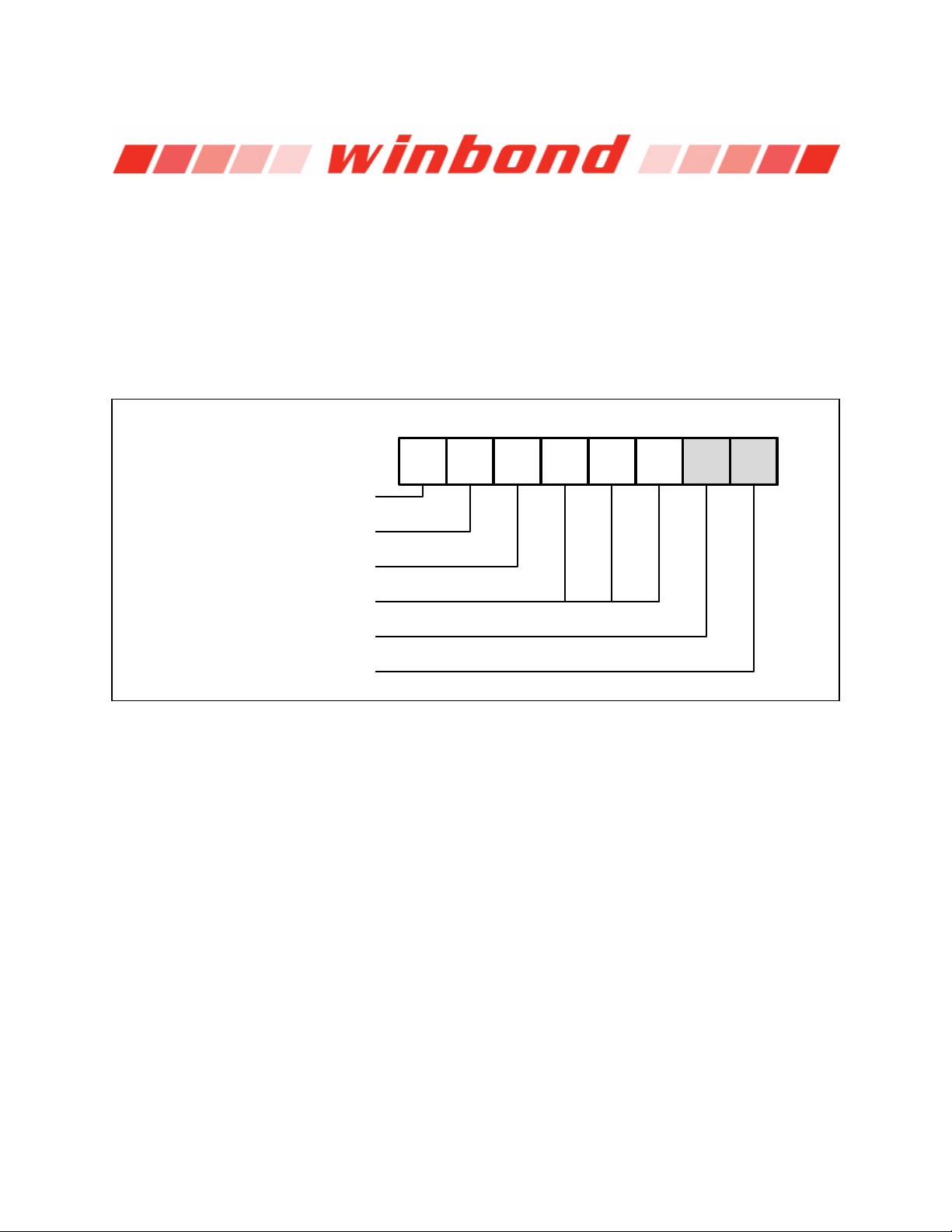
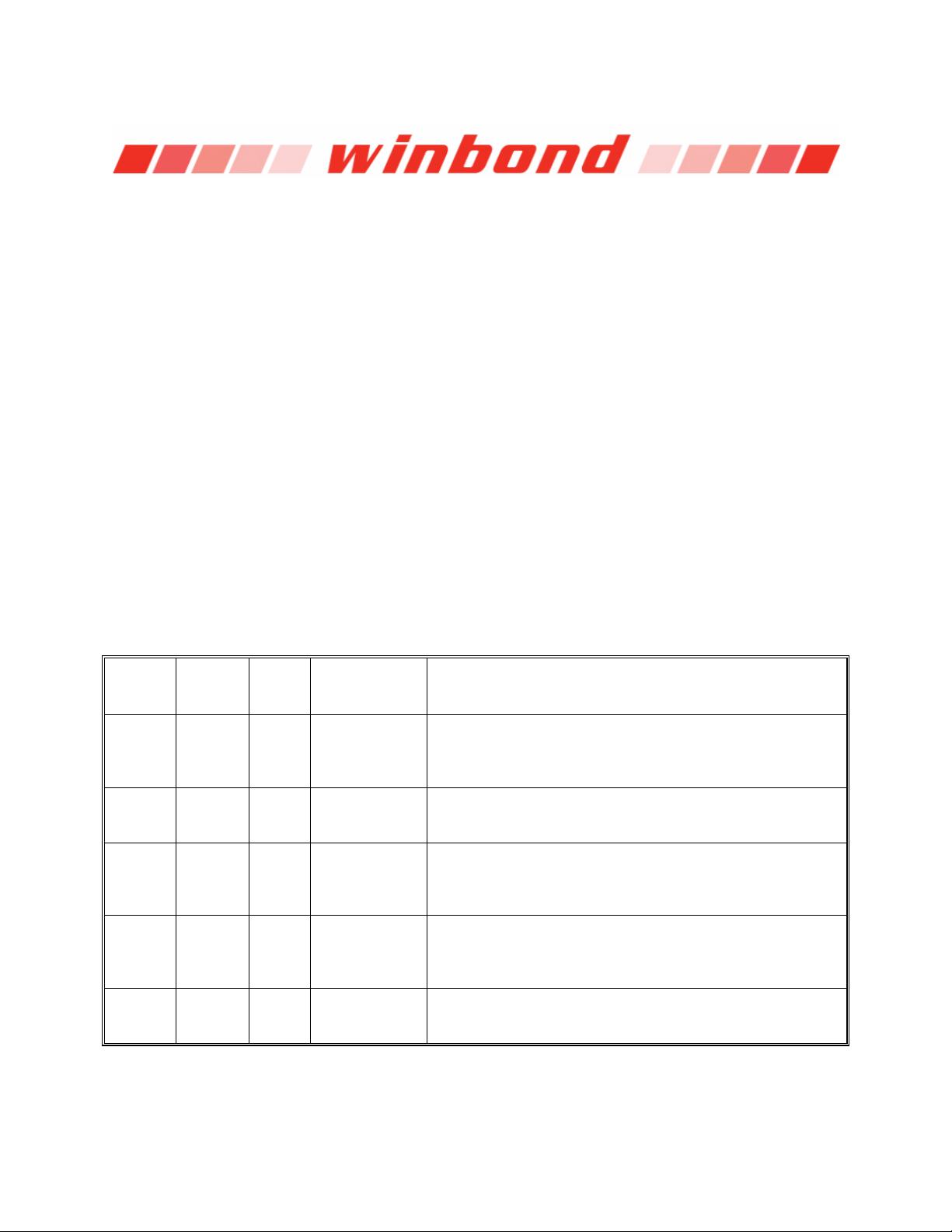
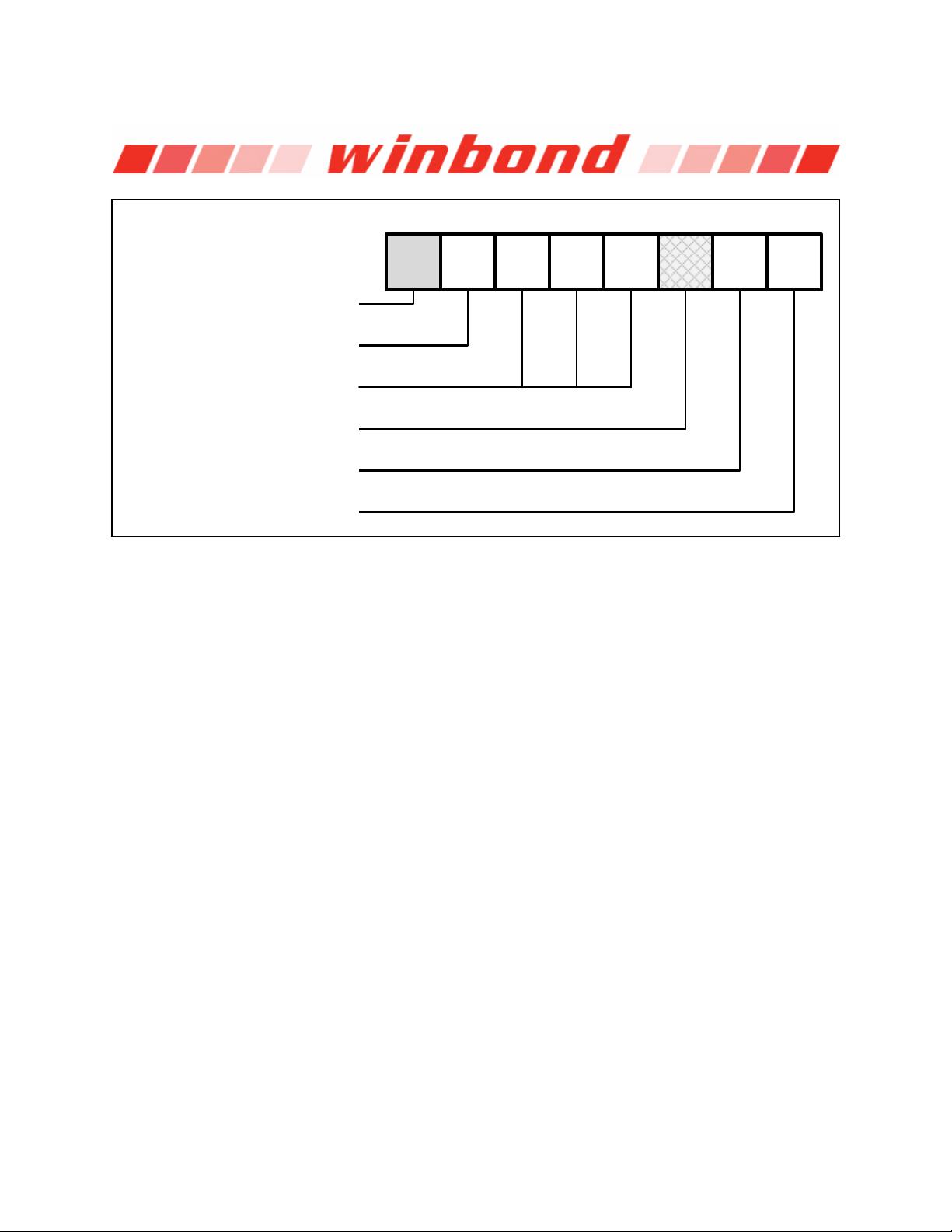
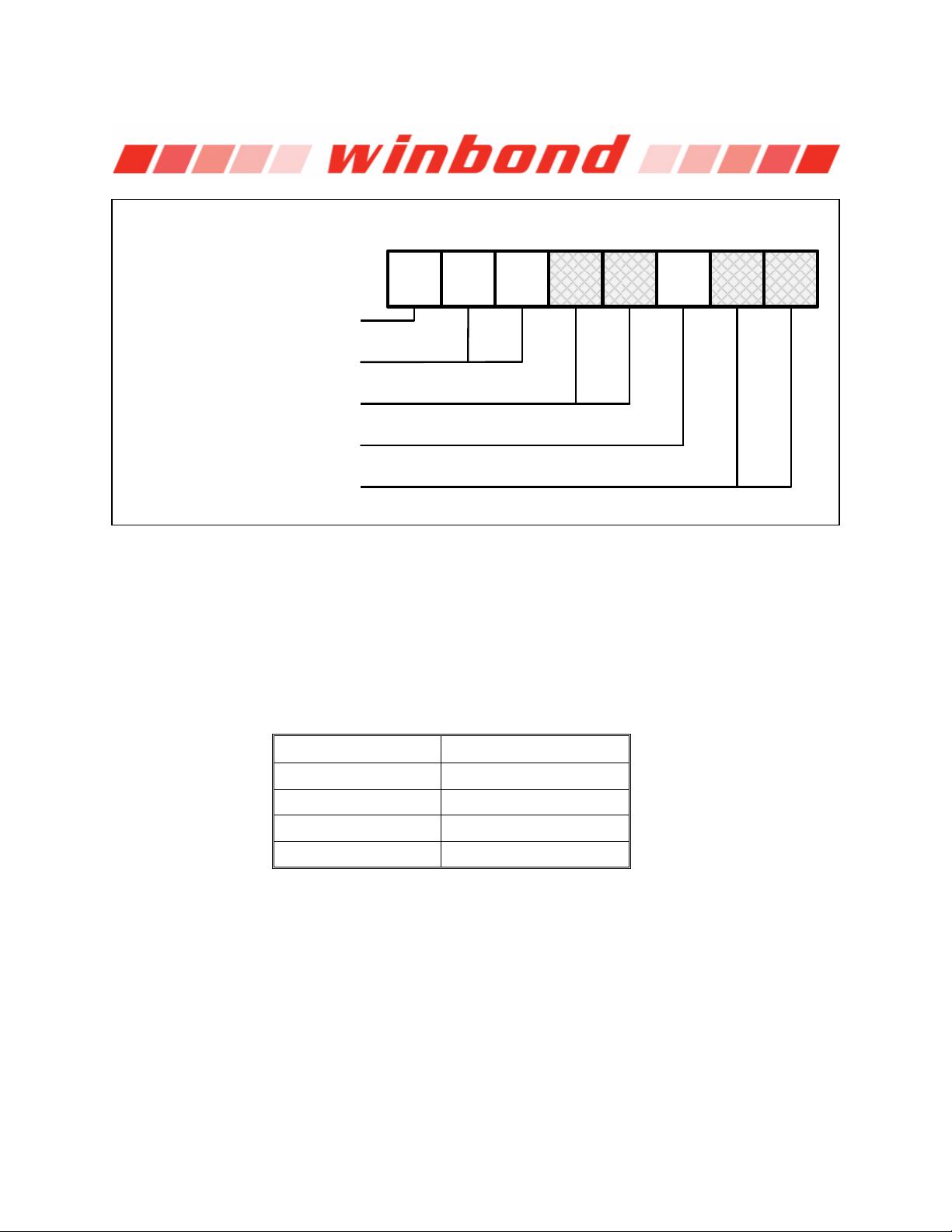
Software controlled write protection is facilitated using the Write Status Register instruction and setting
the Status Register Protect (SRP0, SRP1) and Block Protect (CMP, SEC, TB, BP[2:0]) bits. These
settings allow a portion or the entire memory array to be configured as read only. Used in conjunction
with the Write Protect (/WP) pin, changes to the Status Register can be enabled or disabled under
hardware control. See Status Register section for further information. Additionally, the Power-down
instruction offers an extra level of write protection as all instructions are ignored except for the Release
Power-down instruction.
The W25Q128FV also provides another Write Protect method using the Individual Block Locks. Each
64KB block (except the top and bottom blocks, total of 510 blocks) and each 4KB sector within the
top/bottom blocks (total of 32 sectors) are equipped with an Individual Block Lock bit. When the lock bit
is 0, the corresponding sector or block can be erased or programmed; when the lock bit is set to 1,
Erase or Program commands issued to the corresponding sector or block will be ignored. When the
device is powered on, all Individual Block Lock bits will be 1, so the entire memory array is protected
from Erase/Program. An “Individual Block Unlock (39h)” instruction must be issued to unlock any
specific sector or block.
The WPS bit in Status Register-3 is used to decide which Write Protect scheme should be used. When
WPS=0 (factory default), the device will only utilize CMP, SEC, TB, BP[2:0] bits to protect specific areas
of the array; when WPS=1, the device will utilize the Individual Block Locks for write protection.