Control Systems: Plant Level Controls (i)
Source: Credit Suisse research, Company data
Slide 13
Overview of Plant-Level Control Systems
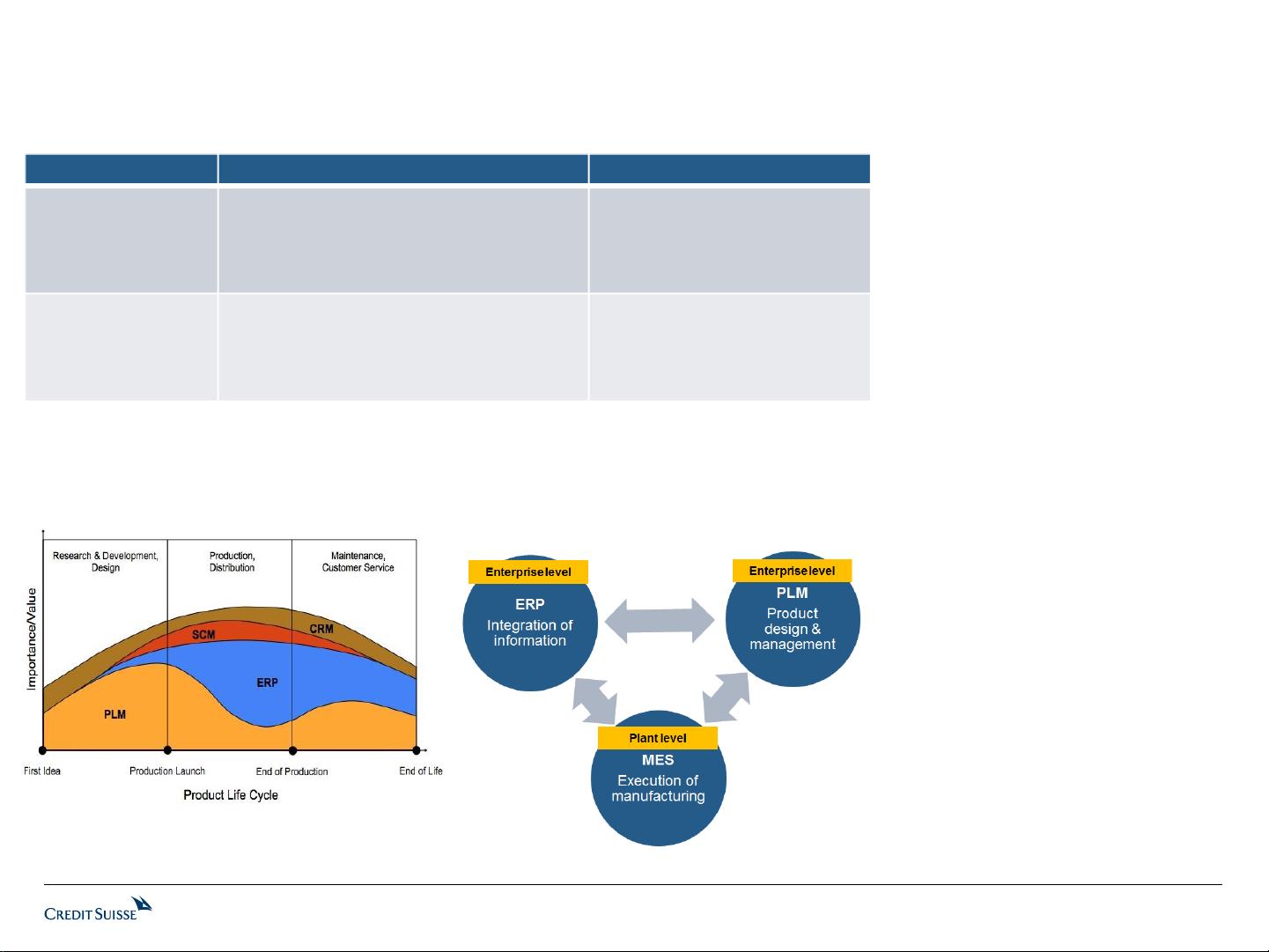
MES was developed much later as
compared to ERP and PLM, and only
first reached maturity in the 90s.
The MES receives product definitions,
electronic work instructions, and
equipment settings from the PLM and
production planning / order
requirements from the ERP.
The MES then reports production
performance results, produced, and
consumed materials to the ERP.
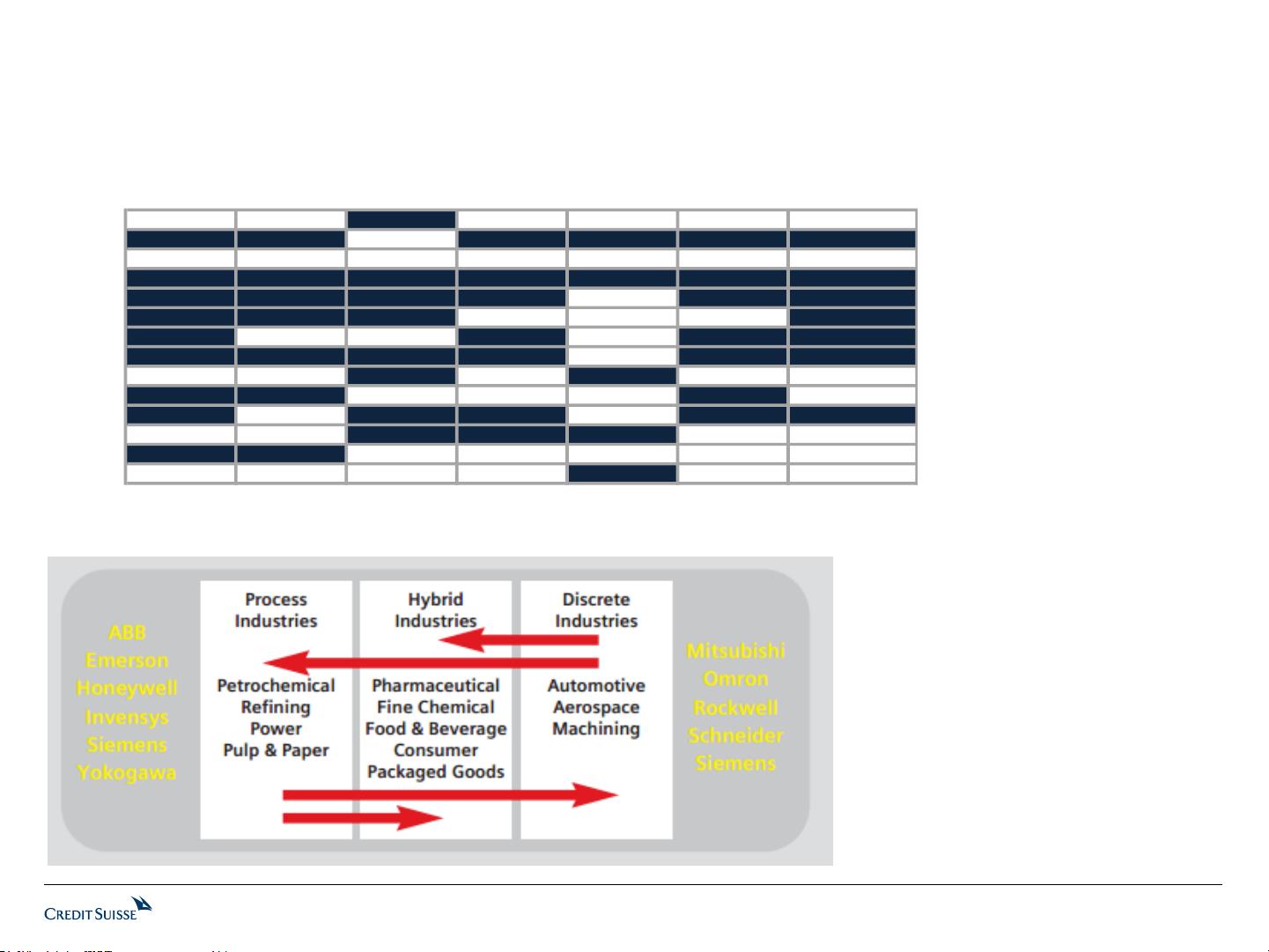
As MES is usually highly specific to a
particular industry, it is generally
difficult to give an estimate of overall
market share.
Each player has its niche end-market
with a high level of engineering
speciality, and market share can be as
high as 50-70% for the leading players
in their core end-markets.
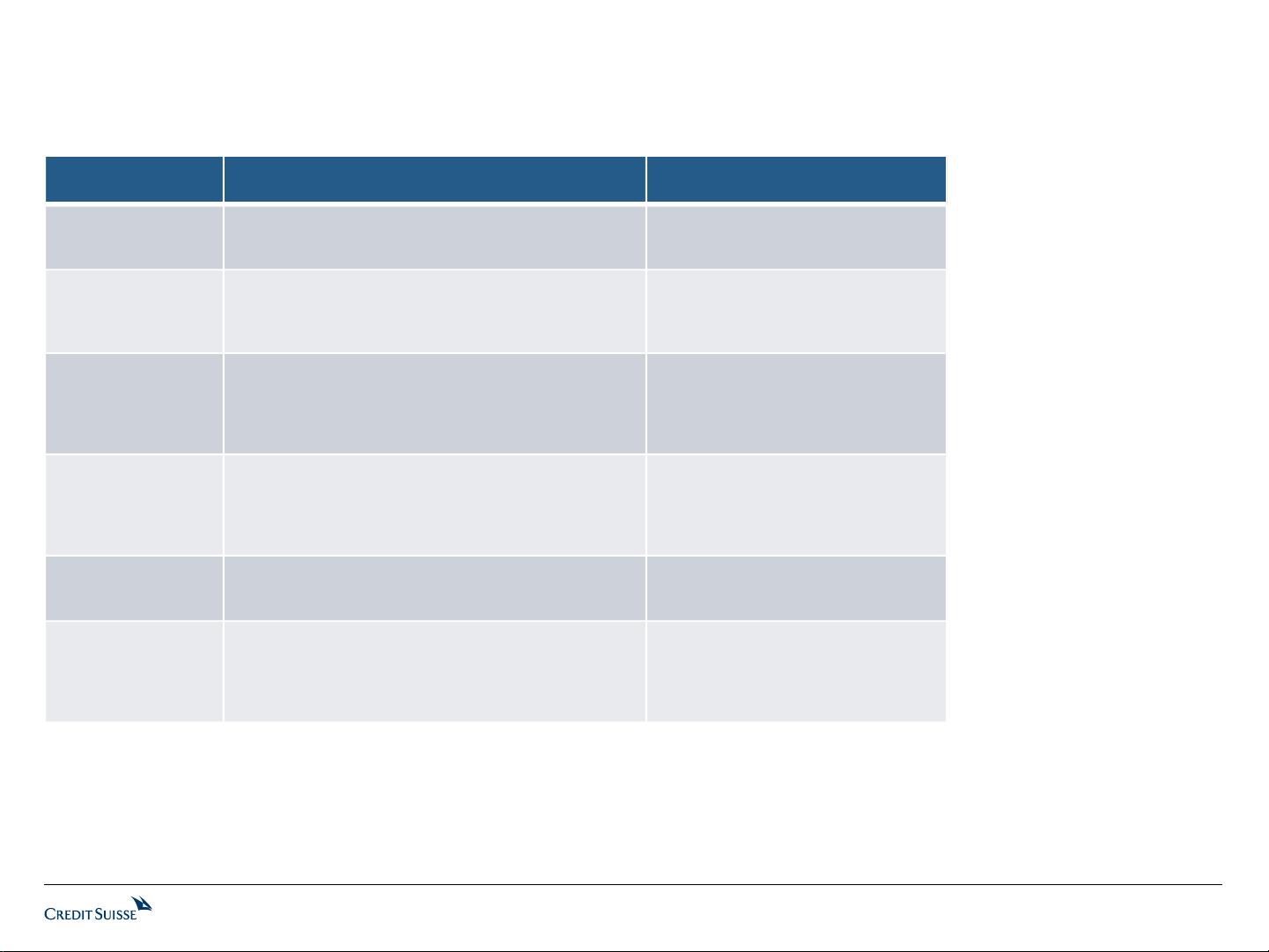
Description Major vendors
MES (Manufacturing
execution system)
A software system that manages manufacturing operations
within a factory.
Schneider (Invensys), ABB, Siemens,
Rockwell, Honeywell, Dassault, SAP,
Yokogawa, GE Aspen Technology
SCADA (Supervisory
control and data
acquisition)
An industrial control software that monitors and controls
industrial (manufacturing and flow - process or factory), and
facility-based (HVAC control, access, and energy
consumption) processes.
Yokogawa, GE, ABB, Siemens,
Schneider/ Invensys
Optimization
Software
A production process analysis program that utilizes
algorithms in order to provide the user with efficiency and
cost reduction solutions. The software provides a bridge for
the gap between ERP and DCS systems.
AspenTech, ABB, Honeywell, Invensys,
KBC Advanced Technology Plc., OSIsoft,
Inc., Rockwell, Siemens, Yokogawa
Electric, JDA Software Group, Inc.,
Oracle, SAP.
DCS (Distributed
control system)
A control system, typically applied in process applications, in
which the controller elements are not in a central location
but are distributed throughout the system with each
component sub-system controlled by one or more
controllers.
ABB, Siemens, Emerson, and Invensys
PLC (Programmable
logic controller)
A digital computer used to direct automation processes,
including the control of machinery, robots, and factory
assembly lines.
Siemens, Rockwell Automation,
Mitsubishi, Omron, and Schneider.
CNC (Computer
Numerical Control)
A computer that converts the design produced by Computer
Aided Design (CAD) software into numbers. The numbers
can be considered to be the coordinates of a graph and they
control the movement of the cutter. In this way the computer
controls the cutting and shaping of the material.
Siemens, Mitsubishi Electric, FANUC,
Huanzhong CNC