Kintinuous: Spatially Extended KinectFusion
Thomas Whelan, John McDonald
Departmen t of Computer Science, National of Ireland Mayn ooth, Co. Kildare, Ireland.
Email: Thomas.J.Whelan@nuim.ie
Michael Kaess, Maurice Fallon, H ordur Johannsson, John J. Leo nard
Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL),
Massachusetts Institute of Technolo gy (MIT), Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
Abstract—In this paper we present an extension to the
KinectFusion algorithm that permits dense mesh-based mapping
of extended scale environments in real-time. This is achieved
through (i) altering the original algorithm such that the region
of space being mapped by the KinectFusion algorithm can vary
dynamically, (ii) extracting a dense point cloud from the regions
that leave the KinectFusion volume due to this variation, and, (iii)
incrementally adding the resulting points to a triangular mesh
representation of the environment. The system is implemented
as a set of hierarchical multi-threaded components which are
capable of operating in real-time. The architecture facilitates
the creation and integration of new modules with minimal
impact on the performance on the dense volume tracking and
surface reconstruction modules. We provide experimental results
demonstrating the system’s ability to map areas considerably
beyond the scale of the original KinectFusion algorithm including
a two story apartment and an extended sequence taken from a
car at night. In order to overcome failure of the iterative closest
point (ICP) based odometry in areas of low geometric features we
have evaluated the Fast Odometry from Vision (FOVIS) system
as an alternative. We provide a comparison between the two
approaches where we show a trade off between the reduced
drift of the visual odometry approach and the higher local
mesh quality of the ICP-based approach. Finally we present
ongoing work on incorporating full simultaneous localisation and
mapping (SLAM) pose-graph optimisation.
I. INTRODUCTION
In rec e nt years visual SLAM has reached a significan t level
of maturity with a number of robust real-time so lutions being
reported in the literature [9]. Altho ugh th e se techniques permit
the construction of an acc urate map of an enviro nment, the fact
that they are feature-based means that they result in sparse
point cloud maps that ca nnot be used directly or have limited
utility in many robotic tasks (e.g. obstacle avoidance, path
planning, manipulation, etc.). This issue has motivated th e
development of dense mapping approaches that aim to use
informa tion from every pixel from the input video frames to
create 3D surface models of the environment [12, 15]. The
emergence of RGB-D cameras, and in par ticular the Microsoft
Kinect
R
, has seen this work being taken a step f urther. New-
combe et al. introduced the KinectFusion algorithm [11] which
uses a volumetric representation of the scene, known as the
truncated signed distance function (TSDF), in conjunction with
fast iterative closest point (ICP) pose estimation to provide a
real-time fused dense model of the scene at an un precedented
level of accuracy.
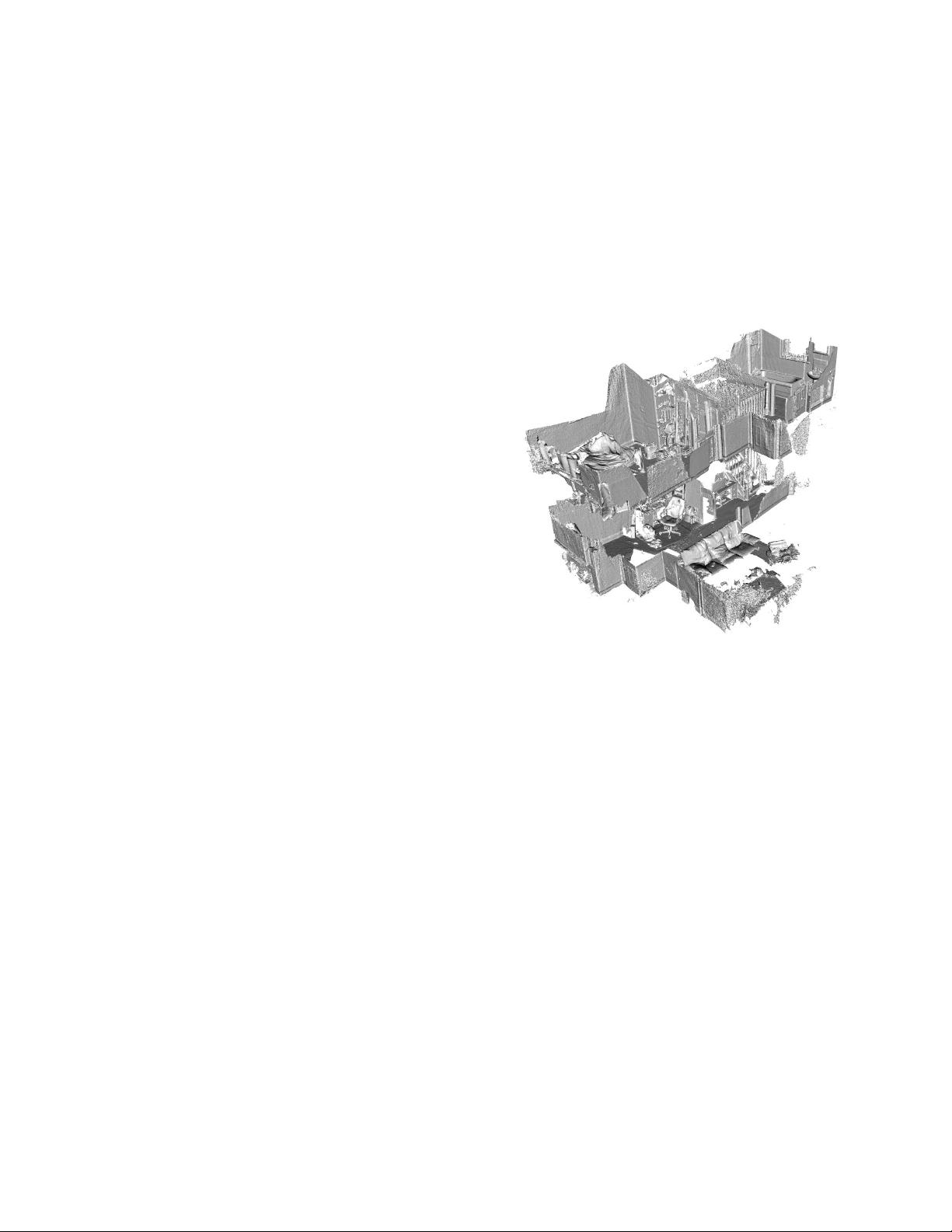
Fig. 1. Real-time 6DOF extended scale map reconstruction of a dataset
captured using a handheld Kinect traversing multiple rooms over two floors
of an apartment. (see Section V-B)
However this algorithm does suffer from a number of
limitations in part derived from the chosen unde rlying TSDF
voxel model. These limitations include an inflexible sur face
model that cannot properly model d e formation s, the ina bility
to use the system in an unbounded extend ed area and tracking
failures in env ironments with poor 3D geometry.
In this paper we present ongoing research to extend the work
of Newcombe et al. to permit KinectFusion style mapping
in an unbounded environment in r eal-time. At any point in
time our system maintains a TSDF of the region of spac e that
is currently being map ped. The region of space represented
by this TSDF varies dynamically during pr ocessing. As new
regions o f spac e enter the TSDF, previously mapped regions
are extracted into a more parsimonious triangular mesh r epre-
sentation.
We present results that demonstrate the techniqu e ’s ability
to create highly de ta iled maps of extended scale environments.
We also present some early stage work which allows the
KinectFusion tracking and surface r econstruction algorithm to
function correctly in areas with few 3 D features.









