IEEE SIGNAL PROCESSING LETTERS, VOL. 19, NO. 5, MAY 2012 295
Cross-View Down/Up-Sampling Method for
Multiview Depth Video Coding
Qiong Liu, Member, IEEE, You Yang, Member, IEEE, Rongrong Ji, Yue Gao, and Li Yu
Abstract—In this letter, we propose a cross-view down/up-sam-
pling (CDU) method for the framework of reduced resolution mul-
tiview depth video coding, which exploits cross-view information to
assist the up-sampling at the decoder. In the dow n-samp ling pro-
cedure of CDU, the odd-even interlaced extraction is employed to
preserve more confident information of the original depth vid eo
with reduced resolution. In the d ec oder, the cross-view information
is exploited for up-sampling the reconstructed d epth video. An it-
erative interpolation process is proposed to eliminate the effect of
compression distortion on this up-sampling. Experimental results
demonstrate the gains of up to 3.88 dB for the proposed algorithm
and better quality of synthesized views.
Index Terms—Cross-view, down/up-sampling, multiview d epth
video, view synthesis.
I. INTRODUCTION
F
REE view video (FVV) represented by Multi -vi e w p lus
Depth (MVD) is an att
ractive future video application
characterized by enabling users to freely select their desired
viewpoint [1]. MVD is a data forma t consisting of multi-
view texture v ide
o and associated depth video. Depth video
records the scene and represents the relative distance from
camera to objects in 3-D space, and is widely used in depth
image-based r
endering (DIBR), which can be also further ap-
plied in multiple-view based object retrieval [2], [3] and video
summarization [4]. With DIBR methods, arbitrary viewpoint
can be synth
esized for FVV realization. Different from other
3-D video application s, FVV usually requires a wide range of
viewing angles for user interaction. Therefore, multiview depth
video (MD
V) is required for high quality DIBR . Besides the
multiview texture videos, the hug e v olu me of MDV causes a
vital problem for data storage and transmission. High perfor-
mance
compression techniques for M DV are urgently in n eed
to make FVV practical in the near futur e.
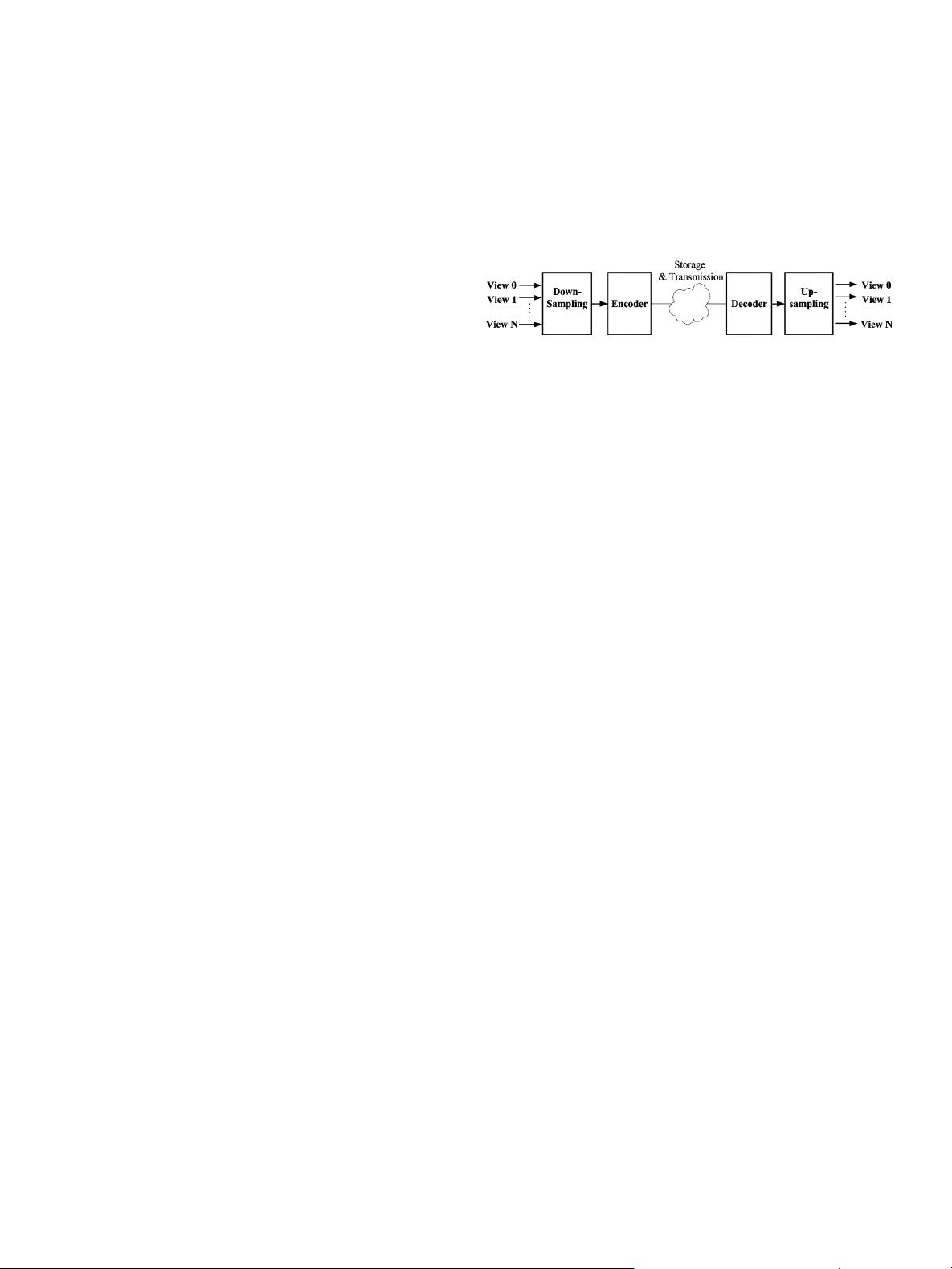
Resolution red ucti on was proposed as an efficient approach
for MD
V compression recently [5], [6]. As illustrated in Fig. 1,
MDVs are down-sampled firstly and then encoded in reduced
resolution with much lower bit-rate compared with that encoded
Manuscript received January 04, 2012; revised March 02, 2012; accepted
March 02, 2012. Date of publication March 14, 2012; date of current version
April 03, 2012. This work was supported by the NSFC under Grant 61170194.
The associate editor coordinating the review of this manuscript and approving
it for publication was Dr. Ali Bilgin.
Q. Liu and L. Yu are with the Department of Electronic and Information En-
gineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
Y. Yang and Y. Gao are with the Department of Automation, Tsinghua Uni-
versity, Beijing, China (e-mail: yangyou@ieee.org).
R. Ji is with the Department of Electrical Engineeri ng , Columbia University,
New York, NY 10027 USA.
Color versions of one or more of the figures in this paper are available online
at http://ieeexplore.i eee.org.
Dig
ital Object Identifier 10.1109/LSP.2012.2190060
Fig. 1. Framework of multiview depth video cod ing.
in full resoluti on. In the decoder side, the M DV is firstly re-
constructedfrombitstreamandthenup-sampledtohighresolu-
tion. With the advantag e of bit-rate saving, down/up-samplin g
on MDV in this framework will lead to quality losses, espe-
cially for sharp boundaries of objects. Therefore, an effective
down/up-sampling method is needed for the reduced resolution
framework of M DV coding.
Traditional filters, including linear and uniform up-sampling
filters [7], are not specified for MDV. Distortions in MDV
caused by compression quantization and up-sampling filter will
result in visual artifacts in DIBR, such as boundary crackles.
In order to handle the distortions, a joint trilateral filter [8] and
adaptive bilateral filter [9] were proposed for in-loop filtering
and post-filtering on reconstructed d epth images. Besides that,
a Joint Bilateral U p-sam pling (JBU) filter [10] was propo sed by
using auxiliary information from hig h resolution images. T his
filter extends the concept of Gaussian smoothing by w eighting
the filter coefficients with their corresponding relative pix e l
intensities, and it is benefit for edge-preserving. The texture
informatio n from color im age can be used in JBU for high
quality MD V up-sampling, as the fact that each depth image
has a corresponding color image in MVD data format.
However, the texture-assisted JBU filter for depth image suf-
fers from the texture copy problem. M ore accurate and confident
depth values are needed to im prov e the quality of up-sampled
MDV. In this letter, we propose a cross-view do wn/up-samp lin g
(CDU) method for MDV coding. In this method, the confident
depth value o f neighbo r views is preserved by odd-even inter-
laced extraction for down-sampling in the encoder side. This
confident depth value from the n eigh bor view is projected to
the current view to improve the quality of up-sampling in the
decoder side.
II. P
ROPOSED ALGORITHM
In this section, we first introduce our way on odd-even inter-
laced extraction for down-sampling. Then we define the cross-
view iterative interpolation for up-sampling. Finally, the con-
vergence analysis for up-sampling is given.
A. The Odd-Even Interlaced Extraction for Down-Samplin g
In the framework of depth video coding depicted by Fig. 1, a
down-sampling procedure is performed before encoding. There-
for
e,thedown-samplinginthisframeworkshouldbedesigned
1070-9908/$31.00 © 2012 IEEE









