Java课程设计:简易计算器功能详解
版权申诉
110 浏览量
更新于2024-07-01
收藏 1.26MB DOCX 举报
本资源是一份关于Java课程设计的计算器程序文档,旨在帮助学生深入理解和应用Java语言编程技术。课程的主要目标是通过实践项目,让学生掌握面向对象的软件设计思想,包括类的声明、对象的使用、继承、接口以及变量和数组的应用。具体任务是设计并实现一个功能丰富的简单计算器,具备基本数学运算(0~9数字、π、加、减、乘、除、开根号、三角函数、指数、对数、双曲正切、角度和弧度转换等)以及清除和清零功能。
设计过程中,关键部分包括:
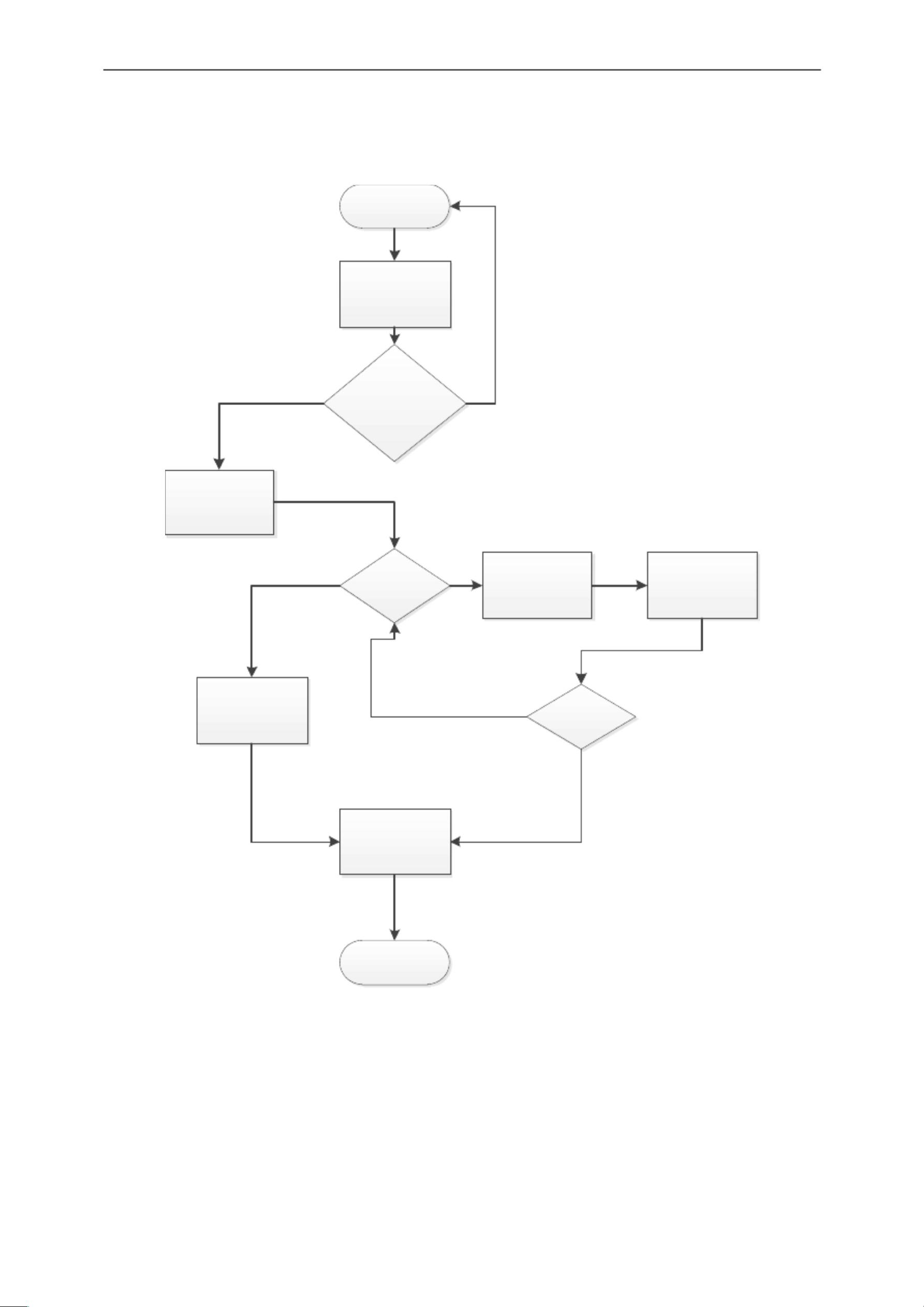
1. **问题分析**:设计目标明确,要求创建一个具有用户界面的计算器,支持各种数学操作和特殊函数,考虑了用户交互逻辑,比如在加减乘除运算时处理连续输入数字的情况。
2. **总体设计**:采用Java GUI编程,利用`BorderLayout`布局管理器构建界面,分为三个主要面板:
- `Panel1`用于放置数字和小数点按钮,采用`GridLayout`布局。
- `Panel2`包含加减乘除等基本运算按钮,同样用`GridLayout`,字体设为蓝色。
- `Panel3`集中放置特殊函数按钮,如三角函数和指数运算,采用蓝色字体。
- 文本框置于`NORTH`,整个布局结构清晰,便于用户操作。
3. **编程环境**:选择JCreatorPro作为开发工具,这是一款流行的Java集成开发环境,能够提供良好的代码编辑和调试功能。
4. **事件处理**:关注用户体验,设计了智能的按钮事件处理机制,确保当用户连续点击数字按钮或在进行运算前选择运算符时,能够正确处理输入。
5. **编程实现**:基于以上设计,学生需要运用Java语法编写代码,实现各个功能模块,包括按钮的响应逻辑和数据处理,最终形成一个可运行的计算器程序。
这份文档不仅提供了Java编程基础的巩固,还涵盖了GUI编程、事件驱动编程以及实际问题的解决策略,对于提升学生的实践能力和编程技巧具有重要作用。
2022-07-09 上传
2022-07-09 上传
2012-10-10 上传
2022-07-08 上传
2021-10-05 上传
2022-07-08 上传
2021-12-16 上传
2022-07-08 上传
2022-07-09 上传
G11176593
- 粉丝: 6917
- 资源: 3万+
最新资源
- vcworks 5.4 技术文档
- TCP-IP Sockets in Java - Practical Guide for Programmers [Academic-Press 2002, Scan].pdf
- PHP实战(英文高清版)
- 大型网站架构演变和知识体系.pdf
- PHP面向对象编程(英文原版高清)
- C语言设计.第三版.谭浩强.
- IT 管理需求分析说明书
- flex 中文开发文档,基本原理和应用
- 网络教程(服务器)服务器
- Keil实例教程.pdf
- Linux内核结构详解教程.pdf
- CSS+DIV布局大全
- DWR基本原理、编程方法和例子
- 报表工具 xx x
- MYSQL中文乱码 xx
- 基于数码相机的三维物体空间几何位置的摄影测量