1
1
Introduction of DNA Computing in Cryptography
Suyel Namasudra and Ganesh Chandra Deka
1.1 Introduction
The security of data has become more and more important as data are shared through the
cloud in heterogeneous devices (Deka and Das, 2014; Namasudra, 2017, 2018; Namasudra
et al., 2017a; Namasudra et al., 2014). Cryptography is the technique of secret writing
(Willett, 1982; Lin, 1998). The main goal of cryptography is to transmit data or messages
(les) between the sender and receiver over an untrusted medium in such a manner that an
attacker or malicious user is unable to read the original data content. It can also be used for
the authentication of customers and users.
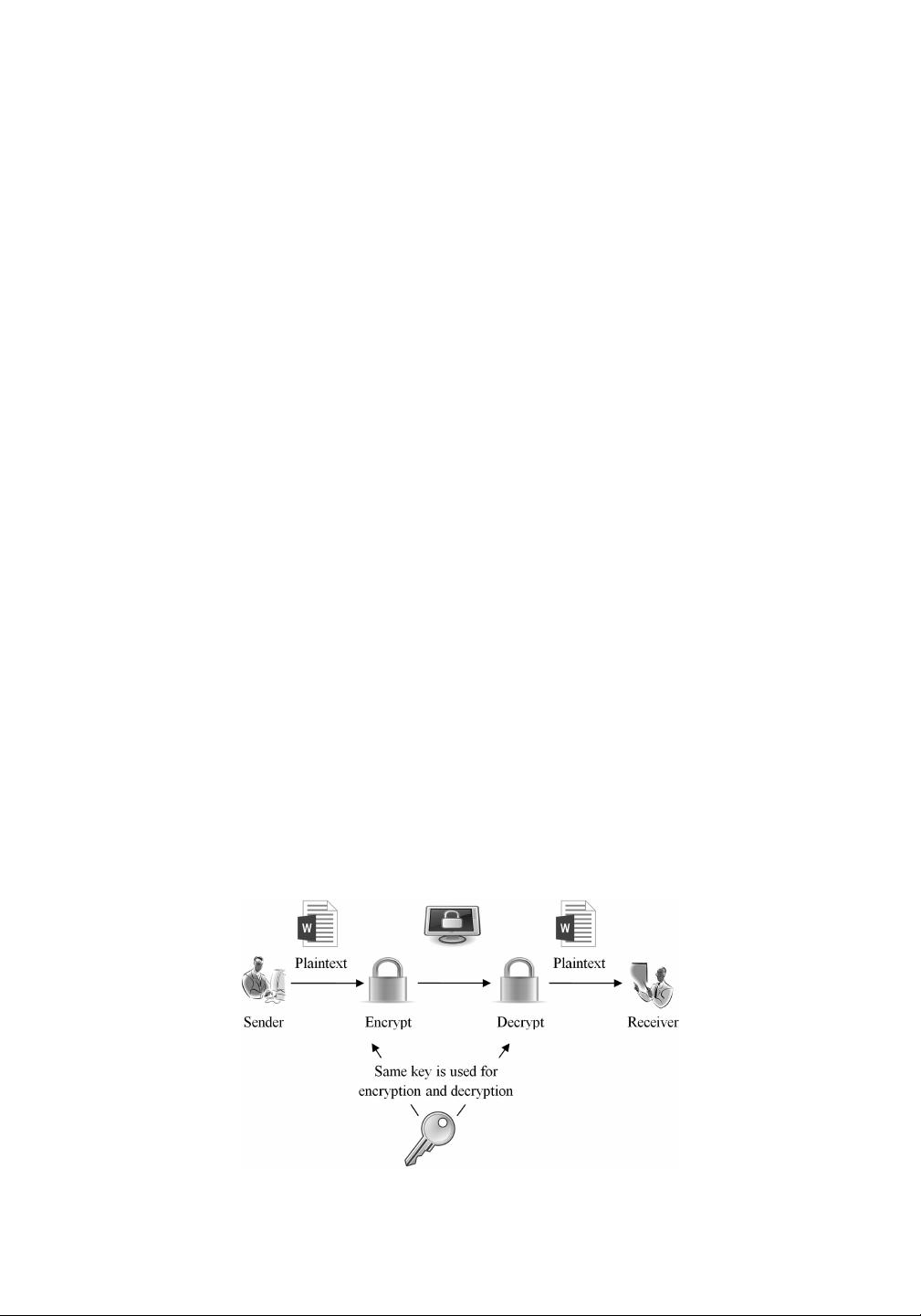
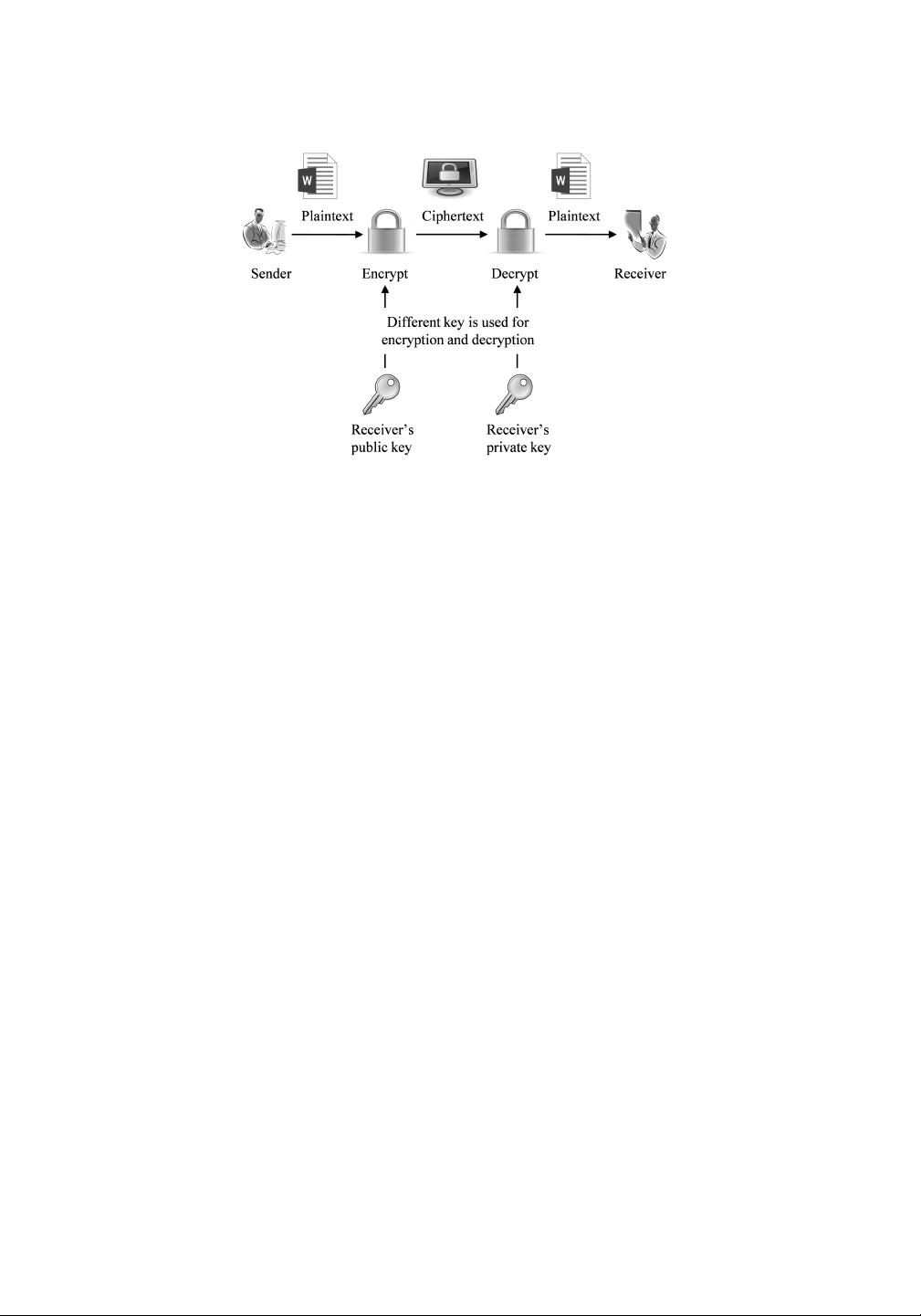
In cryptography, the plaintext refers to an ordinary readable data or message. The encryp-
tion process takes plaintext as input and generates ciphertext as output by using a secret key
and encryption algorithm. The process of recovering the plaintext from the ciphertext by
using the secret key is known as decryption. Fundamentally, there are two types of crypto-
systems, based on how the encryption and decryption processes are carried out:
1. Symmetric key encryption
2. Asymmetric key encryption
The main dissimilarity between these two cryptographic systems is the use of the decryp-
tion and encryption keys. Both these keys are strongly associated in any cryptosystem.
Advances of DNA Computing in Cryptography
Introduction of DNA Computing in Cryptography
CONTENTS
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1.1 Key Management in Cryptography ........................................................................3
1.2 Steganography ........................................................................................................................4
1.3 Background Studies of DNA ................................................................................................5
1.4 DNA Computing ....................................................................................................................7
1.4.1 Why DNA Computing?.............................................................................................8
1.5 DNA Computing in Cryptography ..................................................................................... 9
1.5.1 Polymerase Chain Reaction .................................................................................... 10
1.5.2 DNA-Based Steganography .................................................................................... 11
1.5.3 DNA-Based Chip Technology ................................................................................12
1.6 Future Research Work Directions ..................................................................................... 13
1.7 Conclusions ........................................................................................................................... 15
Key Terms and Denitions .......................................................................................................... 15
References ....................................................................................................................................... 16
References for Advanced/Further Reading .............................................................................. 18