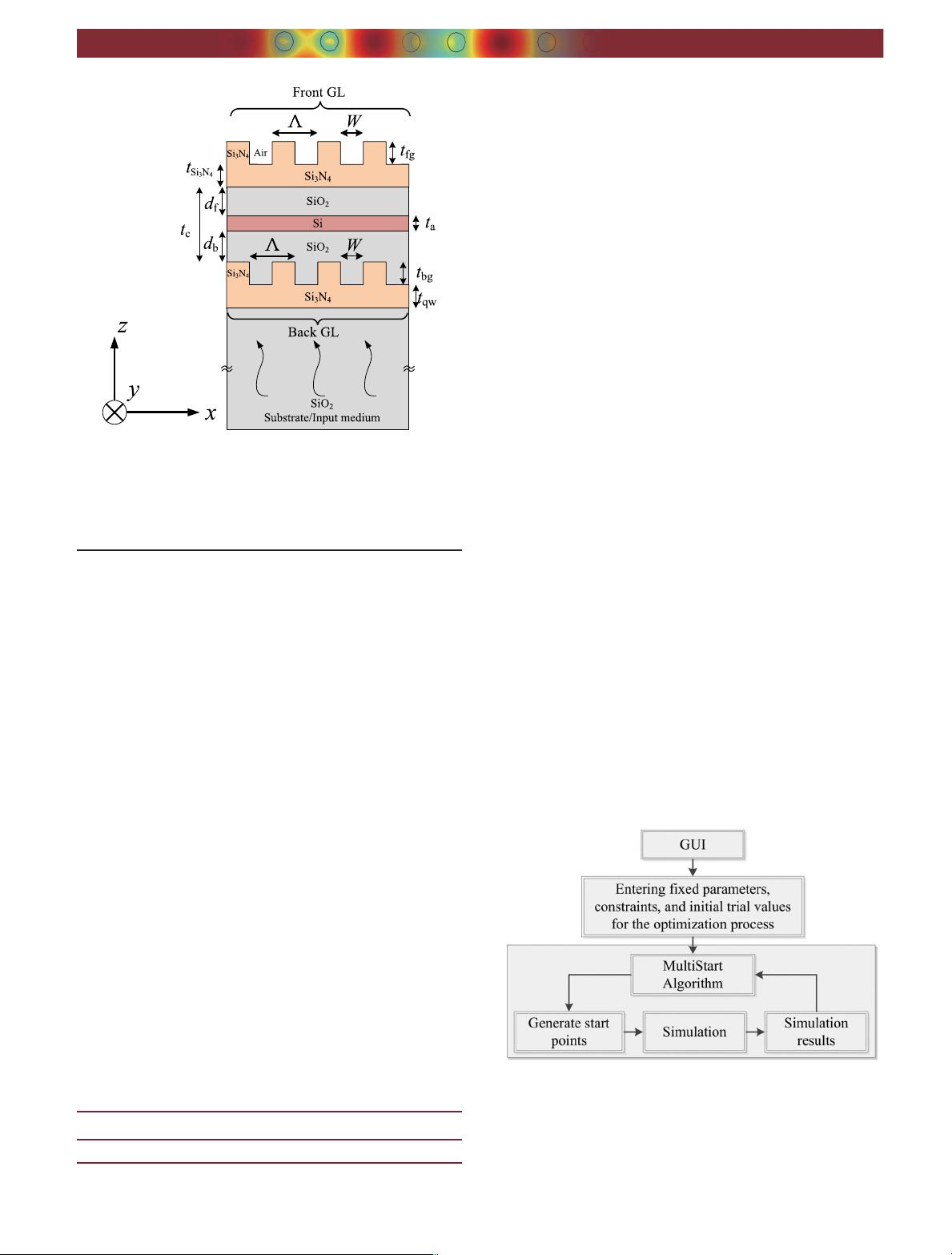
front air–Si
3
N
4
∕Si
3
N
4
with the back SiO
2
−Si
3
N
4
∕Si
3
N
4
GL
encloses the cavity. As shown in Fig. 1, we consider the
through-substrate backside illumination (BSI) at normal inci-
dence. Benefiting from the absence of the backside electrical
contacts, BSI has the essential advantage of reducing the PD
pixel size without decreasing the amount of input light power
[26], which is desirable for on-chip applications.
In this paper, we adopt the η A modeling, which simpli-
fies the design to one in which only the optics need to be con-
sidered. Herewith, rather than being restricted to a specific PD
technology, we analyze the structures optically, characterizing
the constitutive layers by complex RIs n ik, where n are
the real RIs and k ≪ n are the extinction coefficients. This
modeling still has widespread use for initial designs of the elec-
tronic PDs [16,18,21,22,26,27]. In such cases, optical model-
ing can be complemented and refined by an electron-device
simulation [18,28,29]; however, it is not expected to disprove
the optical modeling outcomes. The n and k spectra for the
involved materials are found in Refs. [30–32]; their values
at the CDW are given in Table 1.
Here, the design emphasis is put on obtaining the maximal
CDW efficiency η
max
max ηλ
0
, while maintaining t
a
con-
stant per design, and keeping the back-GL cladding’s thickness
(similarly to the DBR layers’ thicknesses) fixed at the quarter-
wave value t
qw
≈ 100.2nm. Such dimensions as Λ and the
groove width W (constrained for simplicity to be the same
for both GLs), etch depths t
fg
and t
bg
, as well as the thicknesses
of the front-grating cladding t
Si
3
N
4
and front and back cavities,
d
f
and d
b
, respectively, are the design variables. We observe the
SW regime, limiting ab initio the operation wavelengths from
below by the Rayleigh wavelength λ
R
Λn
SiO
2
, which sup-
presses the non-specular orders of the grating diffraction into
the cavity and so prevents losses due to light escaping from the
structure’s sides. Note that this is not compulsory since the
non-specular orders can be suppressed with extra constraints;
see, e.g., Refs. [21,33].
3. DESIGN PROCEDURE, OPTIMAL
STRUCTURES, AND THEIR EFFICIENCY
SPECTRA
We perform the computer-aided designs with an in-house soft-
ware run in MATLAB environment. The software consists of
two modules: “Simulation,” which contains the codes of an in-
house recast rigorous coupled-wave analysis (RCWA) for sim-
ulations of the structures merging smooth and grating-pat-
terned layers as described in detail elsewhere (see Ref. [21] and
references therein); and “Optimization,” which calls a multi-
start optimization algorithm from MATLAB Optimization
Toolbox [34–36] and a graphical user interface (GUI), which
forces the modules to interact and thus drives the simulations
and designs as shown in Fig. 2.
In order that the optimization would not be blind, we are
guided by an approach to obtaining initial (start, trial) design
parameters that, in modern terms, are geometric-phase control
[20]. Homogenizing the gratings as described in Appendix A,
we first design the front and back GLs to be standalone and to
be highly and lowly reflective (subsections A and B), respec-
tively, at a normal CDW incidence from a semi-infinite
SiO
2
. In this way, we assess trial values Λ
, W
, t
fg
, t
bg
,
t
Si
3
N
4
for the GLs’ parameters shown in Fig. 1. With these,
our RCWA code returns the GLs’ reflection-amplitudes’ phases
φ
f
and φ
b
, the sum of which Φ gives a rough idea on the
geometric phase of an unloaded dual-GL cavity. Φ leads
Fig. 1. Sketch of the enhanced light-absorption structure that com-
prises a cavity-embedding Si layer, two GLs enclosing the cavity, and a
substrate. The coordinate system is shown, where the grating perio-
dicity and grooves/lines are along the x and y axes, respectively,
and the layer stacking and light impinging directions are along the
z axis.
Table 1. RIs at the CDW of the Materials that Are Set in
the Text
λ
0
[μm] Si
3
N
4
SiO
2
Si
0.8 1.9962 i0 1.4533 i0 3.6925 i0.0065
Fig. 2. Sketchy flowchart of the optimization process. The GUI
Module inputs the trial parameters, assessed as described in the text,
fixed parameters, and constraints to the Optimization Module. There,
the trial-and-error multi-start algorithm generates the next start points
and inputs them into the Simulation Module, which feeds the algo-
rithm back and loops until attaining an optimum.
Research Article
Vol. 8, No. 3 / March 2020 / Photonics Research 383









