Zhu et al. 2023 | https://doi.org/10.34133/icomputing.0006 8
ability that simulates the evolutionary process of organisms
in nature, where the machines learn from the environment
and subsequently make self- adjustments to adapt to the
environment.
· High computing capability and high energy efficiency.
Aiming to exceed the traditional von Neumann’s architecture,
intelligent computing evolves to new computing architectures
concerning processing-in-memory, heterogeneous integration,
and wide-area collaboration. High computing power refers to the
computing capability that meets the needs of an intelligent society
and serves as infrastructures like water and electricity. Moreover,
high energy eciency aims to maximize computing eciency and
reduce energy consumption as much as possible to ensure ecient
processing of big data with large-scale characteristics, complex
structure, and sparse value.
· Security and reliability. Intelligent computing supports
cross-domain trust and security protection for large-scale
ubiquitous interconnected computing systems. It establishes
independent and controllable trusted security technology
and support systems, realizing data fusion, sharing, and opening.
High trust refers to the trust of identity, data, computing
process, and computing environment through trusted hardware,
operating system, soware, network, and private computing.
Particularly, high security means network security, storage
security, content security, and circulation security of computing
systems that can be guaranteed by integrating various privacy
protection technologies.
· Automation and precision. Intelligent computing is task
oriented; it matches computing resources and realizes automatic
demand calculation and precise system reconstruction. e
system architecture is constantly adjusted to the task execution.
Directed coupling reconstruction is performed at the soware
and hardware levels. Automation of the computing process
includes automatic resource management and scheduling,
automatic service creation and provision, and automatic
management of the task life cycle, which is the key to evaluating
the friendliness, availability, and service of intelligent
computing. e precision of computing results anchors
computing services; besides, it solves diculties, including
fast processing of computing tasks and timely matching of
computing resources.
· Collaboration and ubiquity. Intelligent computing integrates
existing techno logies to promote the penetration and integration
of the physical, information, and social space using the various
perception ability of heterogeneous elements, complementary
computational resources, and the collaboration and competition
of computational node functions. Cooperation between humans
and machines improves intelligence levels in intelligent tasks,
and ubiquity enables computing to be conducted everywhere by
combining intelligent computing theoretical methods, architectural
systems, and technical approaches.
Fusion of intelligence and computation
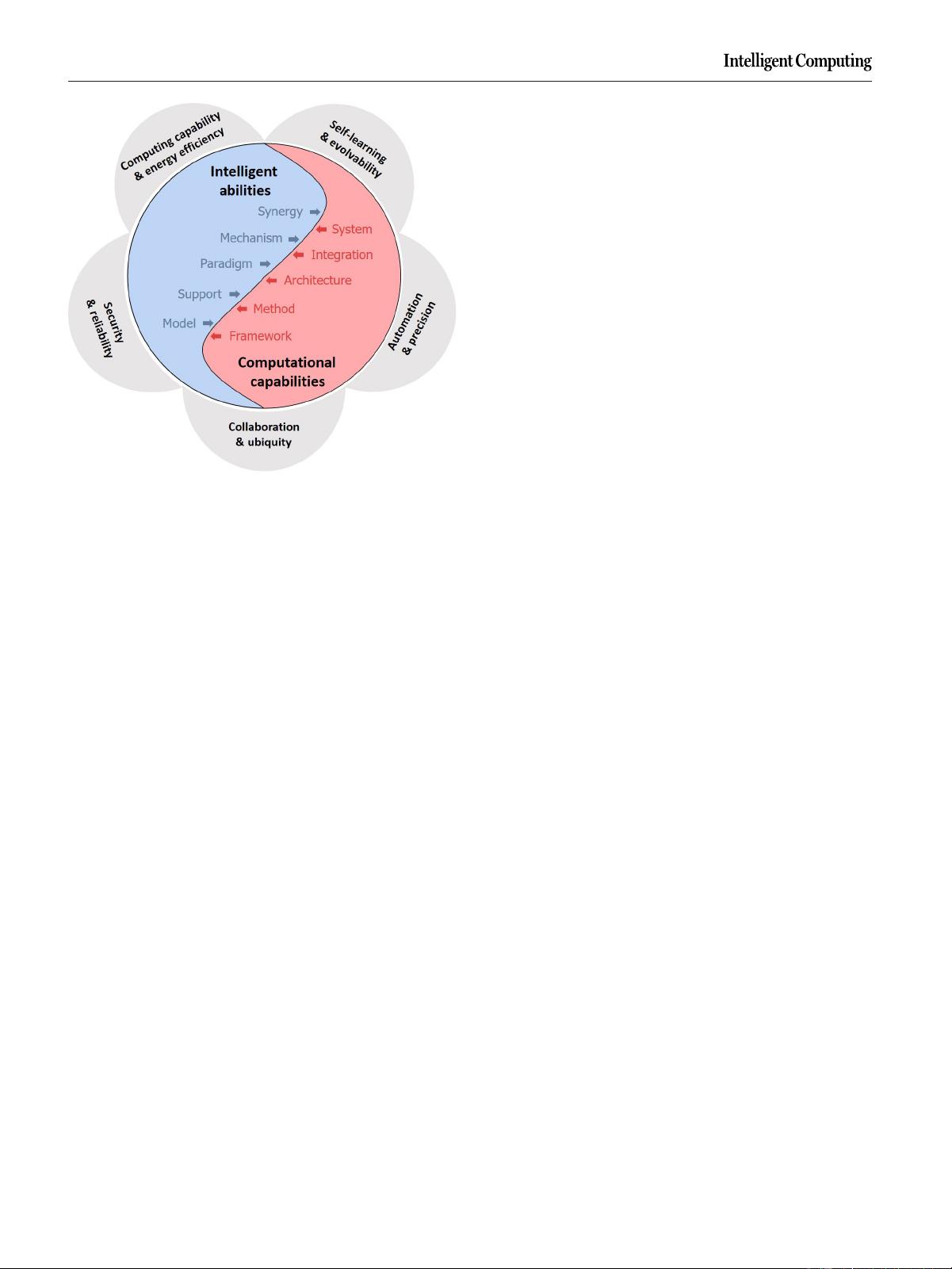
Intelligent computing includes 2 essential aspects: intelligence
and computation, which complement each other. Intelligence
facilitates the development of computing technologies, while
computation is the foundation of intelligence. e paradigm
of high-level intelligence technologies that improve the perform-
ance and eciency of computing systems is “computing by
intelligence.” e paradigm of ecient and powerful compu-
tational technologies that support the development of com-
puter intelligence is “computing for intelligence.” e 2 basic
paradigms are innovated from 5 aspects to improve computing
power, energy eciency, data usage, knowledge expression,
and algorithm capabilities and achieve ubiquitous, transparent,
reliable, real-time, and automatic services.
· The paradigm of computing by intelligence. e computing
power demand of complex models has exceeded that of
general computers by 1 or 2 orders of magnitude. Moreover,
there is a considerable gap between the underlying computing
mechanism of traditional computers and the computing mode
of intelligent models, resulting in low computing eciency.
e paradigm of computing by intelligence includes new
models, support, paradigms, mechanisms, and synergy that
utilize intelligent approaches to improve computing capability
and eciency.
Currently, intelligent systems can only handle specic tasks
in a closed environment since they lack common sense, intui-
tion, and imagination. Research on neuromorphic computing,
graph computing, biological computing, and other new com-
puting models is conducted to analyze the human brain, biolog-
ical, and knowledge computing mechanisms. ese new models
can eectively improve cognitive understanding and reasoning
learning abilities, adaptability, and the generalization eect for
intelligent algorithms.
Due to the limitations of computing system architecture and
lack of end-to-end computational capacity, the computing and
response speed of the current computing system needs further
improvement. Intelligent computing can improve the real-time
performance of the computing system by utilizing new computing
Fig.5.Features of intelligent computing.
Downloaded from https://spj.science.org on April 10, 2024