LTE物理层详解:FDD模式的关键参数与多载波技术
需积分: 10 50 浏览量
更新于2024-09-17
收藏 1.15MB PDF 举报
本文档深入探讨了长期演进(LTE)物理层(PHY)的概述,特别关注了在广泛采用的频分双工(FDD)模式中的关键要素。针对那些参与设计基于LTE的网络和系统实践者,这是一份实用指南。文章首先介绍了多址接入技术和物理层参数,强调了LTE PHY设计的挑战,包括对高速数据传输(下行100Mbps,上行50Mbps)的需求,以及对高谱效率和宽频带(1.25-20MHz)的支持。
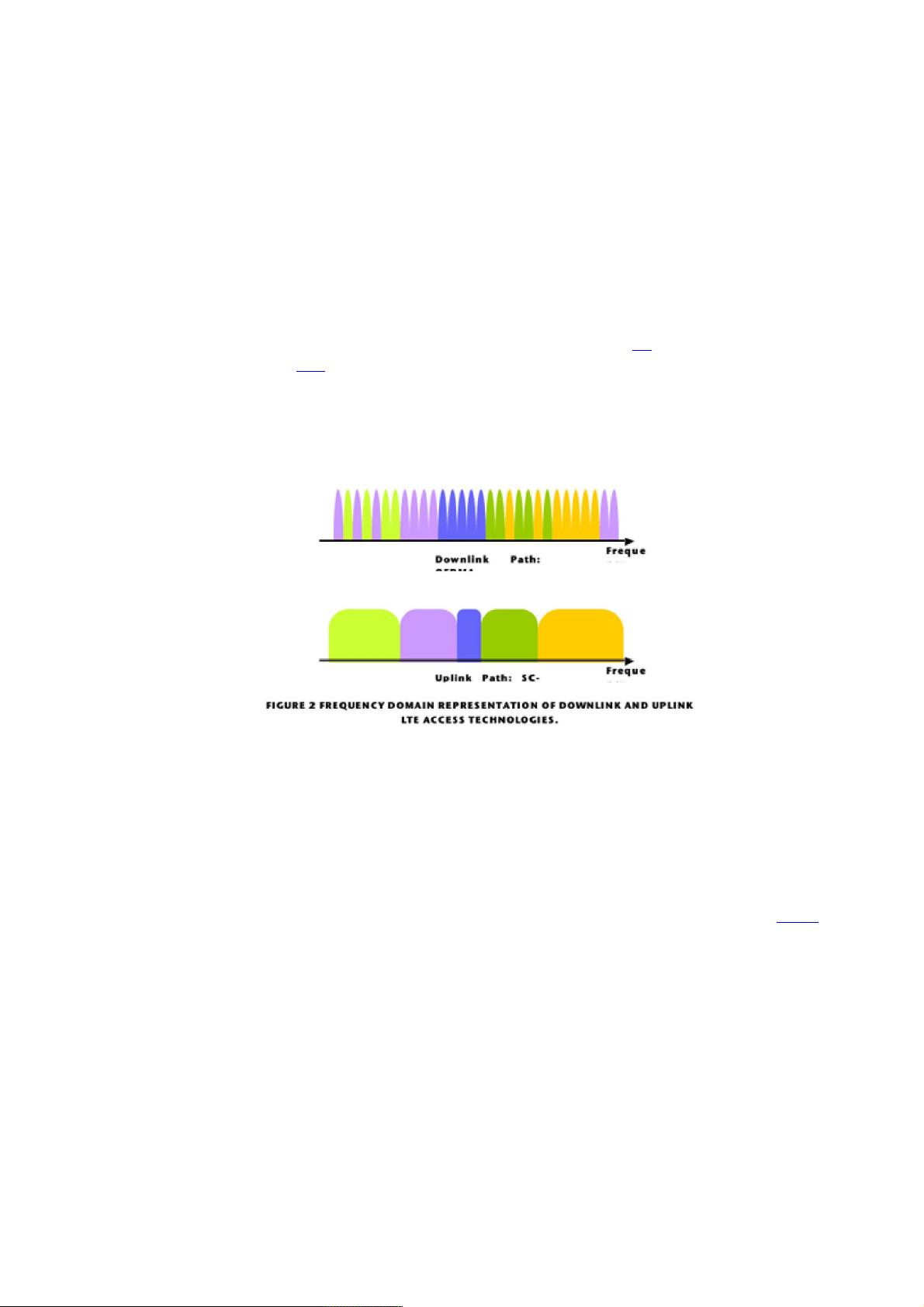
为了实现这些性能指标,文章指出正交频分复用(OFDM)技术被选为LTE物理层的基础。OFDM并非新概念,起源于20世纪60年代,曾在20世纪90年代中期的3G系统讨论中考虑过,但由于当时的技术不成熟而未被采纳。然而,随着电子设备和信号处理技术的显著进步,OFDM已成为Wi-Fi(802.11)、WiMAX(802.16)等无线接入系统以及数字音频/视频广播(DAB/DVB)等广播系统的标准技术,证明了其成熟度。
在LTE PHY设计中,OFDM的优势在于它能够有效应对多径传播环境,通过将数据分割到多个子载波上进行并行传输,从而提高了抗多径干扰的能力。此外,OFDM还允许灵活地调整子载波数量和带宽分配,适应不同场景下的网络需求。在FDD模式下,上行和下行信道通过不同的频率分配进行通信,这要求在物理层设计中考虑到信道编码、调制方式、以及功率控制等关键元素,以确保在频谱资源的有效利用和用户吞吐量的平衡。
本文后续可能还会深入讲解以下部分:
1. LTE物理层的帧结构,包括时隙结构、子帧划分和特殊子帧的作用。
2. 频域资源分配,如资源块(RBs)和上下行链路的资源分布。
3. 调制和解调技术,如QPSK、16QAM和64QAM,以及它们在不同信道条件下的性能。
4. 前向纠错编码(FEC)和信道编码,如Turbo编码和卷积码。
5. MIMO技术的应用,如何提高数据传输的容量和可靠性。
6. 小区间的同步和参考信号(RS)的部署,用于时间和频率同步以及测量目的。
通过学习这篇文档,读者将对LTE物理层的设计原理有更深入的理解,有助于他们在实际网络规划和优化中做出明智决策。
2010-03-15 上传
2012-12-29 上传
2016-05-13 上传
2023-07-22 上传
2023-07-25 上传
2023-11-18 上传
2023-03-26 上传
2023-05-24 上传
2023-04-18 上传
2023-06-08 上传
wangdaqi
- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 10
最新资源
- NIST REFPROP问题反馈与解决方案存储库
- 掌握LeetCode习题的系统开源答案
- ctop:实现汉字按首字母拼音分类排序的PHP工具
- 微信小程序课程学习——投资融资类产品说明
- Matlab犯罪模拟器开发:探索《当蛮力失败》犯罪惩罚模型
- Java网上招聘系统实战项目源码及部署教程
- OneSky APIPHP5库:PHP5.1及以上版本的API集成
- 实时监控MySQL导入进度的bash脚本技巧
- 使用MATLAB开发交流电压脉冲生成控制系统
- ESP32安全OTA更新:原生API与WebSocket加密传输
- Sonic-Sharp: 基于《刺猬索尼克》的开源C#游戏引擎
- Java文章发布系统源码及部署教程
- CQUPT Python课程代码资源完整分享
- 易语言实现获取目录尺寸的Scripting.FileSystemObject对象方法
- Excel宾果卡生成器:自定义和打印多张卡片
- 使用HALCON实现图像二维码自动读取与解码