没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
首页2018年802.3标准:200Gbps和400Gbps Ethernet物理层规格概述
2018年802.3标准:200Gbps和400Gbps Ethernet物理层规格概述
需积分: 14 5 下载量 43 浏览量
更新于2024-07-17
收藏 7.86MB PDF 举报
本篇文档是IEEE 802.3标准的第八部分,涵盖了Clause 116至Clause 126以及Annex 119A至Annex 120E。主要内容聚焦于200 Gb/s和400 Gb/s网络技术,以及与之相关的物理层规格,同时包括了对2.5 Gb/s和5 Gb/s操作的概述。
在Clause 116(200 Gb/s和400 Gb/s网络介绍)中,首先阐述了该标准的适用范围,明确了与ISO/OSI参考模型的关系,介绍了术语定义,如物理层信号系统。这部分详细解释了不同的子层,如Reconciliation Sublayer (RS) 和 Media Independent Interface (MII),以及其扩展版本如200 GMII和400 GMII。PCS(Physical Coding Sublayer,物理编码子层)负责数据的编码和解码,PMA(Physical Medium Attachment,物理介质接入)子层处理与传输媒介的交互,而PMD(Physical Medium Dependent,物理介质依赖)子层确保与特定物理介质的兼容性。
接着,Clause 116.2进一步描述了管理接口(MDIO/MDC),包括如何进行设备管理和数据通信。这部分强调了服务接口规范方法和符号表示,定义了不同子层间的交互和服务接口实例,以及接口原语的语义。
Clause 116.3专门讨论服务接口的规范,如何定义子层之间的服务接口,以及实例化这些接口时的含义。这部分对于理解和设计实现高效、兼容的网络架构至关重要。
此外,文档还包含了针对2.5 Gb/s和5 Gb/s速率的通用信息,尽管这部分的详细程度可能不如200 Gb/s和400 Gb/s那样深入。这部分内容同样关注物理层规范,确保了标准的全面性和适用性。
整个Section 8的内容不仅深入剖析了高速以太网技术的底层细节,也涉及了管理和维护方面的要求,为工程师提供了设计和实施高带宽网络的完整指导。通过阅读和理解这部分内容,技术人员可以掌握最新的以太网标准,从而优化网络性能并确保设备间的兼容性。

16
Copyright © 2018 IEEE. All rights reserved.
126.12.3.3 Other PCS functions ............................................................................................... 333
126.12.4 Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) ............................................................................. 333
126.12.5 PMA Electrical Specifications.........................................................................................335
126.12.6 PMA Management Interface............................................................................................ 336
126.12.7 Characteristics of the link segment.................................................................................. 337
126.12.8 MDI requirements............................................................................................................ 338
126.12.9 General safety and environmental requirements ............................................................. 339
126.12.10 Timing requirements...................................................................................................... 339
Annex 119A (informative) 200GBASE-R and 400GBASE-R PCS FEC codeword examples ................. 340
Annex 120A (informative) 200 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s PMA sublayer partitioning examples........................ 346
120A.1 Partitioning example supporting 400GBASE-SR16................................................................ 346
120A.2 Partitioning examples supporting 200GBASE-DR4/FR4/LR4 and 400GBASE-FR8/LR8 .... 347
120A.3 Partitioning examples supporting 400GBASE-DR4................................................................ 349
120A.4 Partitioning example using 200GXS and 400GXS.................................................................. 350
Annex 120B (normative) Chip-to-chip 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-8
C2C) and 400 Gb/s sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-16 C2C)......................... 351
120B.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................. 351
120B.2 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 chip-to-chip compliance point definition ............................... 353
120B.3 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 chip-to-chip electrical characteristics ..................................... 354
120B.3.1 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2C transmitter characteristics ..................................... 354
120B.3.2 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2C receiver characteristics .......................................... 354
120B.4 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 chip-to-chip channel characteristics ....................................... 355
120B.5 Protocol implementation conformance statement (PICS) proforma for Annex 120B, Chip-
to-chip 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-8 C2C) and 400 Gb/s
sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-16 C2C) .................................................. 356
120B.5.1 Introduction..................................................................................................................... 356
120B.5.2 Identification................................................................................................................... 356
120B.5.2.1 Implementation identification.............................................................................. 356
120B.5.2.2 Protocol summary ................................................................................................. 356
120B.5.3 Major capabilities/options............................................................................................... 357
120B.5.4 PICS proforma tables for Chip-to-chip 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit
Interface (200GAUI-8 C2C) and 400 Gb/s sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface
(400GAUI-16 C2C) ........................................................................................................ 357
120B.5.4.1 Transmitter............................................................................................................ 357
120B.5.4.2 Receiver ............................................................................................................
.... 358
120B.5.4.3 Channel ................................................................................................................. 358
Annex 120C (normative) Chip-to-module 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-
8 C2M) and 400 Gb/s sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-16 C2M) .................... 359
120C.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................. 359
120C.1.1 Bit error ratio .................................................................................................................. 361
120C.2 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 chip-to-module compliance point definitions......................... 361
120C.3 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 chip-to-module electrical characteristics ................................ 361
120C.3.1 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2M host output characteristics .................................... 361
120C.3.2 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2M module output characteristics............................... 361
120C.3.3 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2M host input characteristics ...................................... 361
120C.3.4 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2M module input characteristics................................. 362
120C.4 200GAUI-8 and 400GAUI-16 C2M measurement methodology............................................ 362
Authorized licensed use limited to: Dalian University of Technology. Downloaded on December 18,2018 at 05:21:38 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.

17
Copyright © 2018 IEEE. All rights reserved.
120C.5 Protocol implementation conformance statement (PICS) proforma for Annex 120C, Chip-
to-module 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-8 C2M) and
400 Gb/s sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-16 C2M).................................. 363
120C.5.1 Introduction..................................................................................................................... 363
120C.5.2 Identification................................................................................................................... 363
120C.5.2.1 Implementation identification.............................................................................. 363
120C.5.2.2 Protocol summary ................................................................................................. 363
120C.5.3 Major capabilities/options............................................................................................... 364
120C.5.4 PICS proforma tables for Chip-to-module 200 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit
Interface (200GAUI-8 C2M) and 400 Gb/s sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface
(400GAUI-16 C2M) ....................................................................................................... 364
120C.5.4.1 Host output............................................................................................................ 364
120C.5.4.2 Module output....................................................................................................... 365
120C.5.4.3 Host input.............................................................................................................. 365
120C.5.4.4 Module input.........................................................................................................365
Annex 120D (normative) Chip-to-chip 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-4
C2C) and 400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-8 C2C) .............................. 366
120D.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................. 366
120D.2 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 chip-to-chip compliance point definition ................................. 369
120D.3 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 chip-to-chip electrical characteristics ....................................... 369
120D.3.1 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2C transmitter characteristics ....................................... 369
120D.3.1.1 Transmitter differential output return loss ............................................................ 370
120D.3.1.2 Transmitter linearity ............................................................................................. 371
120D.3.1.2.1 Measurement of mean signal levels.............................................................. 371
120D.3.1.3 Linear fit to the measured waveform .................................................................... 372
120D.3.1.4 Steady-state voltage and linear fit pulse peak....................................................... 372
120D.3.1.5 Transmitter equalization settings .......................................................................... 372
120D.3.1.6 Transmitter output noise and distortion ................................................................ 374
120D.3.1.7 Transmitter output residual ISI ............................................................................. 374
120D.3.1.8 Output jitter........................................................................................................... 374
120D.3.1.8.1 J4u and JRMS jitter....................................................................................... 375
120D.3.1.8.2 Even-odd Jitter.............................................................................................. 376
120D.3.2 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2C receiver characteristics ............................................ 376
120D.3.2.1 Receiver interference tolerance ............................................................................ 376
120D.3.2.2 Receiver jitter tolerance ............................
............................................................ 378
120D.3.2.3 Transmitter equalization feedback (optional) ....................................................... 378
120D.4 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 chip-to-chip channel characteristics ......................................... 379
120D.4.1 Channel Operating Margin ............................................................................................. 379
120D.4.2 Channel return loss ......................................................................................................... 380
120D.5 Protocol implementation conformance statement (PICS) proforma for Annex 120D, Chip-
to-chip 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-4 C2C) and 400 Gb/s
eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-8 C2C) ....................................................... 382
120D.5.1 Introduction..................................................................................................................... 382
120D.5.2 Identification................................................................................................................... 382
120D.5.2.1 Implementation identification.............................................................................. 382
120D.5.2.2 Protocol summary ................................................................................................. 382
120D.5.3 Major capabilities/options............................................................................................... 383
120D.5.4 PICS proforma tables for Chip-to-chip 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit
Interface (200GAUI-4 C2C) and 400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface
(400GAUI-8 C2C) .......................................................................................................... 383
120D.5.4.1 Transmitter............................................................................................................ 383
120D.5.4.2 Receiver ................................................................................................................ 384
Authorized licensed use limited to: Dalian University of Technology. Downloaded on December 18,2018 at 05:21:38 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.

18
Copyright © 2018 IEEE. All rights reserved.
120D.5.4.3 Channel ................................................................................................................. 384
Annex 120E (normative) Chip-to-module 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-4
C2M) and 400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-8 C2M) ............................ 385
120E.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................. 385
120E.1.1 Bit error ratio .................................................................................................................. 387
120E.2 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 chip-to-module compliance point definitions........................... 387
120E.3 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 chip-to-module electrical characteristics .................................. 388
120E.3.1 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2M host output characteristics ...................................... 388
120E.3.1.1 Signaling rate and range ....................................................................................... 389
120E.3.1.2 Signal levels.......................................................................................................... 389
120E.3.1.3 Output return loss.................................................................................................. 390
120E.3.1.4 Differential termination mismatch........................................................................ 390
120E.3.1.5 Transition time......................................................................................................390
120E.3.1.6 Host output eye width and eye height................................................................... 390
120E.3.1.7 Reference receiver for eye width and eye height evaluation ................................ 391
120E.3.2 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2M module output characteristics................................. 393
120E.3.2.1 Module output eye width, eye height, and pre-cursor ISI ratio ............................ 394
120E.3.2.1.1 Reference receiver for module output evaluation......................................... 395
120E.3.2.1.2 Far-end pre-cursor ISI ratio .......................................................................... 395
120E.3.3 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2M host input characteristics ........................................ 395
120E.3.3.1 Input return loss ....................................................................................................395
120E.3.3.2 Host stressed input test ......................................................................................... 396
120E.3.3.2.1 Host stressed input test procedure ................................................................ 396
120E.3.4 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2M module input characteristics................................... 398
120E.3.4.1 Module stressed input test..................................................................................... 398
120E.3.4.1.1 Module stressed input test procedure............................................................ 398
120E.4 200GAUI-4 and 400GAUI-8 C2M measurement methodology.............................................. 400
120E.4.1 HCB/MCB characteristics .............................................................................................. 400
120E.4.2 Eye width and eye height measurement method ............................................................ 401
120E.4.3 Vertical eye closure ........................................................................................................ 403
120E.5 Protocol implementation conformance statement (PICS) proforma for Annex 120E, Chip-
to-module 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit Interface (200GAUI-4 C2M) and
400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface (400GAUI-8 C2M) ....................................... 405
120E.5.1 Introduction..................................................................................................................... 405
120E.5.2 Identification........................................................................................................
........... 405
120E.5.2.1 Implementation identification.............................................................................. 405
120E.5.2.2 Protocol summary ................................................................................................. 405
120E.5.3 Major capabilities/options............................................................................................... 406
120E.5.4 PICS proforma tables for Chip-to-module 200 Gb/s four-lane Attachment Unit
Interface (200GAUI-4 C2M) and 400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface
(400GAUI-8 C2M) ......................................................................................................... 406
120E.5.4.1 Host output............................................................................................................ 406
120E.5.4.2 Module output....................................................................................................... 407
120E.5.4.3 Host input.............................................................................................................. 407
120E.5.4.4 Module input.........................................................................................................407
Authorized licensed use limited to: Dalian University of Technology. Downloaded on December 18,2018 at 05:21:38 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
IEEE Std 802.3-2018, IEEE Standard for Ethernet
SECTION EIGHT
19
Copyright © 2018 IEEE. All rights reserved.
116. Introduction to 200 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s networks
116.1 Overview
116.1.1 Scope
This clause describes the general requirements for 200 Gigabit and 400 Gigabit Ethernet.
200 Gigabit Ethernet uses the IEEE 802.3 MAC sublayer operating at a data rate of 200 Gb/s, coupled with
any IEEE 802.3 200GBASE Physical Layer implementation and is defined for full duplex operation only.
400 Gigabit Ethernet uses the IEEE 802.3 MAC sublayer operating at a data rate of 400 Gb/s, coupled
with any IEEE 802.3 400GBASE Physical Layer implementation and is defined for full duplex operation
only.
116.1.2 Relationship of 200 Gigabit and 400 Gigabit Ethernet to the ISO OSI reference
model
200 Gigabit and 400 Gigabit Ethernet couples the IEEE 802.3 MAC to a family of 200 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s
Physical Layers. The relationships among 200 Gigabit and 400 Gigabit Ethernet, the IEEE 802.3 MAC, and
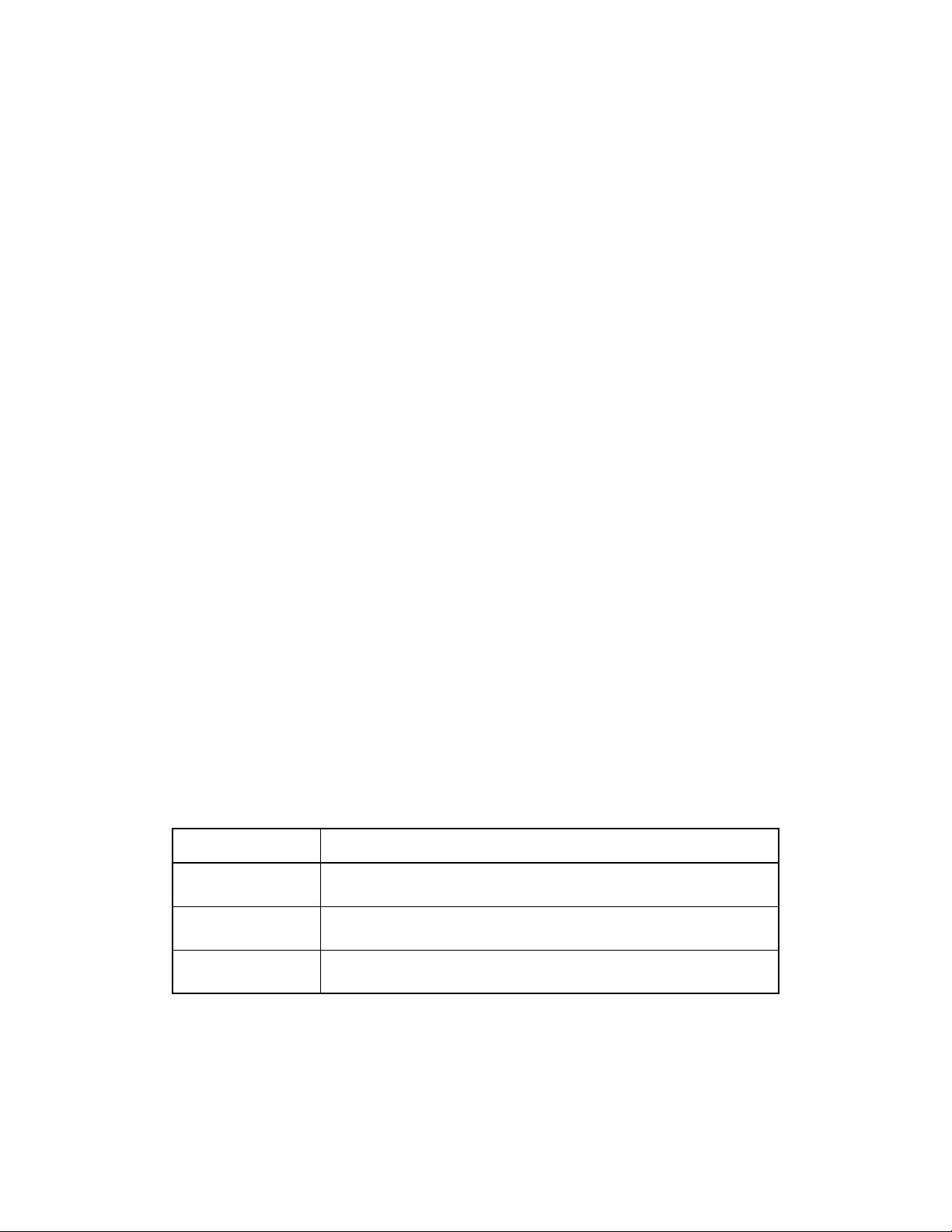
the ISO Open System Interconnection (OSI) reference model are shown in Figure 116–1.
While this specification defines interfaces in terms of bits, octets, and frames, implementations may choose
other data-path widths for implementation convenience. The only exceptions are as follows:
Figure 116–1—Architectural positioning of 200 Gigabit and 400 Gigabit Ethernet
ETHERNET
LAYERS
LLC OR OTHER MAC CLIENT
MAC
HIGHER LAYERS
MAC CONTROL (OPTIONAL)
PRESENTATION
APPLICATION
SESSION
TRANSPORT
NETWORK
DATA LINK
PHYSICAL
OSI
REFERENCE
MODEL
LAYERS
PCS = PHYSICAL CODING SUBLAYER
PHY = PHYSICAL LAYER DEVICE
PMA = PHYSICAL MEDIUM ATTACHMENT
PMD = PHYSICAL MEDIUM DEPENDENT
RECONCILIATION
PMD
400GBASE-R PCS
400GBASE-R
PHY
MEDIUM
MDI
400GMII
PMA
200GMII = 200 Gb/s MEDIA INDEPENDENT INTERFACE
400GMII = 400 Gb/s MEDIA INDEPENDENT INTERFACE
LLC = LOGICAL LINK CONTROL
MAC = MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL
MDI = MEDIUM DEPENDENT INTERFACE
PMD
200GBASE-R PCS
200GBASE-R
PHY
MEDIUM
MDI
200GMII
PMA
Authorized licensed use limited to: Dalian University of Technology. Downloaded on December 18,2018 at 05:21:38 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
IEEE Std 802.3-2018, IEEE Standard for Ethernet
SECTION EIGHT
20
Copyright © 2018 IEEE. All rights reserved.
a) The 200GMII and 400GMII, which, when implemented as logical interconnection points between
the MAC sublayer and the Physical Layer (PHY), use a 64-bit wide data path as specified in
Clause 117. Physical instantiations of this interface may use other data-path widths.
b) The management interface, which, when physically implemented as the MDIO/MDC (Management
Data Input/Output and Management Data Clock) at an observable interconnection port, uses a bit-
wide data path as specified in Clause 45.
c) The PMA service interface, which, when physically implemented as 400GAUI-16 (400 Gb/s
sixteen-lane Attachment Unit Interface) at an observable interconnection port, uses a 16-lane data
path as specified in Annex 120B or Annex 120C.
d) The PMA service interface, which, when physically implemented as 200GAUI-8 (200 Gb/s
eight-lane Attachment Unit Interface) or 400GAUI-8 (400 Gb/s eight-lane Attachment Unit
Interface) at an observable interconnection port, uses an 8-lane data path as specified in
Annex 120B, Annex 120C, Annex 120D, or Annex 120E.
e) The PMA service interface, which, when physically implemented as 200GAUI-4 (200 Gb/s
four-lane Attachment Unit Interface) at an observable interconnection port, uses a 4-lane data path
as specified in Annex 120D or Annex 120E.
f) The MDI as specified in Clause 123 for 400GBASE-SR16 uses a 16-lane data path.
g) The MDI as specified in Clause 122 for 400GBASE-FR8 and 400GBASE-LR8 uses an 8-lane data
path.
h) The MDIs as specified in Clause 121 for 200GBASE-DR4, in Clause 122 for 200GBASE-FR4 and
200GBASE-LR4, and in Clause 124 for 400GBASE-DR4, all use a 4-lane data path.
116.1.3 Nomenclature
The nomenclature employed by the 200 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s Physical Layer is explained as follows.
The alpha-numeric prefix 200GBASE in the port type (e.g., 200GBASE-R) represents a family of Physical
Layer devices operating at a speed of 200 Gb/s. The alpha-numeric prefix 400GBASE in the port type (e.g.,
400GBASE-R) represents a family of Physical Layer devices operating at a speed of 400 Gb/s.
200GBASE-R represents a family of Physical Layer devices using the Physical Coding Sublayer for
200 Gb/s operation over multiple PCS lanes (see Clause 119). Physical Layer devices listed in Table 116–1
are defined for operation at 200 Gb/s.
400GBASE-R represents a family of Physical Layer devices using the Physical Coding Sublayer for
400 Gb/s operation over multiple PCS lanes (see Clause 119). Physical Layer devices listed in Table 116–2
are defined for operation at 400 Gb/s.
Table 116–1—200 Gb/s PHYs
Name Description
200GBASE-DR4 200 Gb/s PHY using 200GBASE-R encoding over four lanes of single-mode
fiber, with reach up to at least 500 m (see Clause 121)
200GBASE-FR4 200 Gb/s PHY using 200GBASE-R encoding over four WDM lanes on single-
mode fiber, with reach up to at least 2 km (see Clause 122)
200GBASE-LR4 200 Gb/s PHY using 200GBASE-R encoding over four WDM lanes on single-
mode fiber, with reach up to at least 10 km (see Clause 122)
Authorized licensed use limited to: Dalian University of Technology. Downloaded on December 18,2018 at 05:21:38 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
剩余407页未读,继续阅读
2019-07-07 上传
2014-09-15 上传
2019-07-07 上传
2013-03-11 上传
2014-09-15 上传
2013-03-11 上传
2022-09-23 上传
124 浏览量
kaka2007f1
- 粉丝: 3
- 资源: 7
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

最新资源
- 探索数据转换实验平台在设备装置中的应用
- 使用git-log-to-tikz.py将Git日志转换为TIKZ图形
- 小栗子源码2.9.3版本发布
- 使用Tinder-Hack-Client实现Tinder API交互
- Android Studio新模板:个性化Material Design导航抽屉
- React API分页模块:数据获取与页面管理
- C语言实现顺序表的动态分配方法
- 光催化分解水产氢固溶体催化剂制备技术揭秘
- VS2013环境下tinyxml库的32位与64位编译指南
- 网易云歌词情感分析系统实现与架构
- React应用展示GitHub用户详细信息及项目分析
- LayUI2.1.6帮助文档API功能详解
- 全栈开发实现的chatgpt应用可打包小程序/H5/App
- C++实现顺序表的动态内存分配技术
- Java制作水果格斗游戏:策略与随机性的结合
- 基于若依框架的后台管理系统开发实例解析
安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功