字符数组与字符串的终极对比:深入解析本质差异和应用场景
发布时间: 2024-07-13 00:56:42 阅读量: 71 订阅数: 50 


深入解析C++中的字符数组和处理字符串的方法
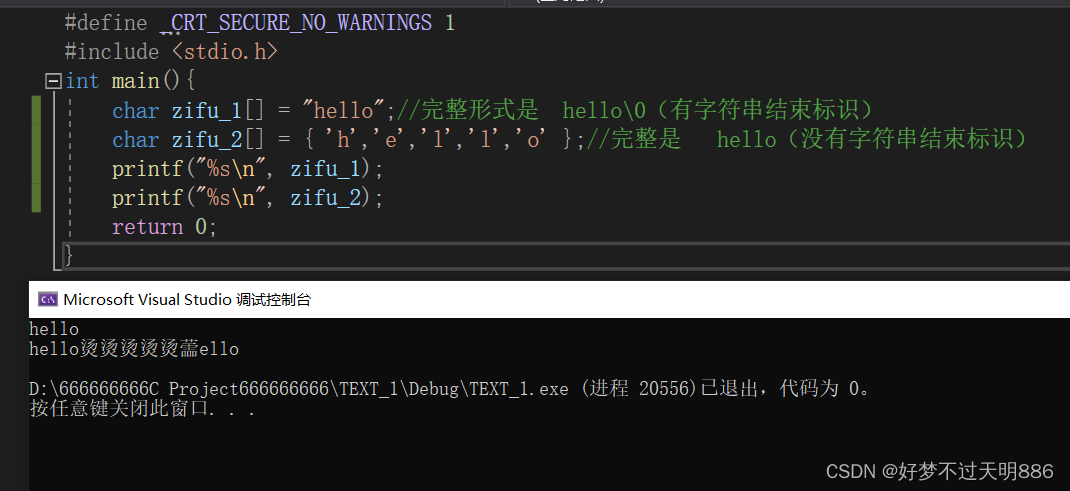
# 1. 字符数组与字符串的本质差异
字符数组和字符串都是用于存储和操作文本数据的两种基本数据结构,但它们在本质上存在着一些关键差异。
**字符数组**本质上是一个固定大小的字符序列,每个字符占用一个字节。它可以存储任何类型的字符数据,包括空字符('\0'),并且可以被直接访问和修改。
**字符串**本质上是一个以空字符结尾的字符序列。它提供了比字符数组更高级别的抽象,具有自动内存管理和字符串操作函数等特性。字符串在内存中以一个指针的形式存储,该指针指向字符序列的第一个字符。
# 2. 字符数组与字符串的应用场景
### 2.1 字符数组的优势和应用
字符数组是一种用于存储和处理原始字符数据的低级数据结构。它在以下场景中具有优势:
#### 2.1.1 存储和处理原始数据
字符数组可以存储和处理二进制数据、图像数据或其他非文本数据。这些数据通常以字节或字符的形式存储,需要使用低级操作来处理。
**代码块:**
```c
char data[100];
fread(data, sizeof(char), 100, file);
```
**逻辑分析:**
此代码从文件中读取 100 个字符并将其存储在字符数组 `data` 中。
#### 2.1.2 灵活控制字符操作
字符数组允许对单个字符进行精确控制。开发人员可以遍历数组、比较字符、修改字符或执行其他低级操作。
**代码块:**
```c
char str[] = "Hello";
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++) {
printf("%c", str[i]);
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
此代码遍历字符串 "Hello" 中的每个字符并打印它们。
### 2.2 字符串的优势和应用
字符串是一种高级数据结构,它存储和处理文本数据。它在以下场景中具有优势:
#### 2.2.1 便捷的文本处理
字符串提供了一组丰富的函数和操作符,用于处理文本数据。这些函数包括连接、比较、搜索和替换。
**代码块:**
```c
char str1[] = "Hello";
char str2[] = "World";
char str3[20];
strcpy(str3, str1);
strcat(str3, " ");
strcat(str3, str2);
printf("%s", str3);
```
**逻辑分析:**
此代码将字符串 "Hello" 和 "World" 连接到字符串 `str3` 中,并打印结果 "Hello World"。
#### 2.2.2 高效的字符串操作
字符串在底层使用优化算法来执行字符串操作。这些算法可以提高字符串比较、搜索和替换等操作的效率。
**代码块:**
```c
char str[] = "Hello World";
int index = strstr(str, "World");
if (index != NULL) {
printf("Found 'World' at index %d", index);
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
此代码使用 `strstr` 函数在字符串 `str` 中搜索子字符串 "World"。如果找到,它会打印子字符串的索引。
# 3.1 从字符数组转换为字符串
#### 3.1.1 使用连接符(+)
连接符(+)可以将两个字符串或字符数组连接起来,生成一个新的字符串。
```c
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char char_array[] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
char *string = " World!";
// 使用连接符连接字符数组和字符串
char *new_string = char_array + string;
// 打印新字符串
printf("%s\n", new_string);
return 0;
}
```
**代码逻辑逐行解读:**
1. 定义一个字符数组 `char_array`,并初始化为字符串 "Hello"。
2. 定义一个字符串指针 `string`,并指向字符串 " World!"。
3. 使用连接符 `+` 将 `char_array` 和 `string` 连接起来,生成一个新的字符串 `new_string`。
4. 打印 `new_string`。
**参数说明:**
* `char_array`:要转换的字符数组。
* `string`:要连接的字符串。
* `new_string`:连接后的新字符串。
#### 3.1.2 使用字符串函数(strcpy)
`strcpy` 函数可以将一个字符串复制到另一个字符串中。它也可以用于将字符数组转换为字符串。
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char char_array[] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
char string[20];
// 使用 strcpy 函数将字符数组复制到字符串中
strcpy(string, char_array);
// 打印字符串
printf("%s\n", string);
return 0;
}
```
**代码逻辑逐行解读:**
1. 定义一个字符数组 `char_array`,并初始化为字符串 "Hello"。
2. 定义一个字符串 `string`,大小为 20 个字符。
3. 使用 `strcpy` 函数将 `char_array` 复制到 `string` 中。
4. 打印 `string`。
**参数说明:**
* `string`:要复制到的字符串。
* `char_array`:要复制的字符数组。
# 4. 字符数组与字符串的优化技巧
### 4.1 字符数组的优化
#### 4.1.1 合理分配内存
字符数组在声明时需要指定大小,如果分配的内存过小,可能会导致数组越界错误;如果分配的内存过大,则会浪费内存空间。因此,合理分配内存非常重要。
**优化建议:**
* 根据实际需要确定字符数组的大小,避免分配过大或过小的内存。
* 使用动态内存分配(如 `malloc` 和 `realloc`)来动态调整字符数组的大小,以满足不断变化的需求。
#### 4.1.2 避免越界访问
字符数组的越界访问会导致未定义的行为,甚至程序崩溃。因此,在使用字符数组时,必须确保访问的索引始终在数组的有效范围内。
**优化建议:**
* 在访问字符数组元素之前,检查索引是否有效。
* 使用边界检查函数(如 `strnlen` 和 `strncpy`)来限制访问范围。
* 考虑使用字符串(`char *`)代替字符数组(`char[]`),因为字符串会自动处理边界检查。
### 4.2 字符串的优化
#### 4.2.1 使用字符串常量
字符串常量存储在程序的只读内存区域中,不可修改。使用字符串常量可以提高代码的安全性,因为它们不会被意外修改。
**优化建议:**
* 对于不会改变的字符串,使用字符串常量代替字符数组。
* 使用 `const` 关键字将字符串声明为常量,以防止意外修改。
#### 4.2.2 优化字符串比较
字符串比较是字符串处理中常见的操作。优化字符串比较可以提高程序的性能。
**优化建议:**
* 使用 `strcmp` 函数进行字符串比较,该函数比 `==` 运算符更有效。
* 对于短字符串,使用 `memcmp` 函数进行字节比较,该函数比 `strcmp` 函数更快。
* 对于相等的字符串,使用 `==` 运算符进行比较。
* 对于不相等的字符串,使用 `strcmp` 函数进行比较。
**优化示例:**
```c
// 使用 strcmp 函数比较字符串
if (strcmp(str1, str2) == 0) {
// 字符串相等
} else {
// 字符串不相等
}
// 使用 memcmp 函数比较短字符串
if (memcmp(str1, str2, strlen(str1)) == 0) {
// 字符串相等
} else {
// 字符串不相等
}
```
# 5. 字符数组与字符串的综合应用
### 5.1 字符数组与字符串在数据结构中的应用
#### 5.1.1 栈和队列的实现
栈和队列是两种重要的数据结构,它们可以使用字符数组或字符串来实现。
**栈**
栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构。使用字符数组实现栈时,可以将数组的最后一个元素作为栈顶。入栈操作将元素压入数组末尾,出栈操作将数组末尾的元素弹出。
**代码块**
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
char stack[MAX_SIZE];
int top = -1;
void push(char element) {
if (top == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Stack overflow\n");
return;
}
stack[++top] = element;
}
char pop() {
if (top == -1) {
printf("Stack underflow\n");
return '\0';
}
return stack[top--];
}
int main() {
push('a');
push('b');
push('c');
printf("%c\n", pop());
printf("%c\n", pop());
printf("%c\n", pop());
return 0;
}
```
**队列**
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构。使用字符数组实现队列时,可以将数组的第一个元素作为队头,最后一个元素作为队尾。入队操作将元素添加到数组末尾,出队操作将数组第一个元素删除。
**代码块**
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
char queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front = 0, rear = -1;
void enqueue(char element) {
if (rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Queue overflow\n");
return;
}
queue[++rear] = element;
}
char dequeue() {
if (front > rear) {
printf("Queue underflow\n");
return '\0';
}
return queue[front++];
}
int main() {
enqueue('a');
enqueue('b');
enqueue('c');
printf("%c\n", dequeue());
printf("%c\n", dequeue());
printf("%c\n", dequeue());
return 0;
}
```
#### 5.1.2 哈希表的实现
哈希表是一种基于哈希函数的数据结构,它可以快速查找和插入元素。使用字符数组或字符串作为哈希表中的键可以提高效率。
**代码块**
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TABLE_SIZE 100
struct hash_table {
char *key;
int value;
};
struct hash_table table[TABLE_SIZE];
int hash_function(char *key) {
int hash = 0;
for (int i = 0; key[i] != '\0'; i++) {
hash += key[i];
}
return hash % TABLE_SIZE;
}
void insert(char *key, int value) {
int index = hash_function(key);
table[index].key = key;
table[index].value = value;
}
int search(char *key) {
int index = hash_function(key);
if (table[index].key == NULL) {
return -1;
}
return table[index].value;
}
int main() {
insert("apple", 10);
insert("banana", 20);
insert("cherry", 30);
printf("%d\n", search("apple"));
printf("%d\n", search("banana"));
printf("%d\n", search("cherry"));
return 0;
}
```
### 5.2 字符数组与字符串在文本处理中的应用
#### 5.2.1 文本搜索和替换
字符数组和字符串在文本搜索和替换中扮演着重要的角色。可以使用字符串函数(如 strstr() 和 strcpy())来查找和替换文本中的特定子串。
**代码块**
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char text[] = "This is a sample text.";
char search_string[] = "sample";
char replace_string[] = "example";
int main() {
char *result = strstr(text, search_string);
if (result != NULL) {
strcpy(result, replace_string);
printf("%s\n", text);
} else {
printf("Substring not found\n");
}
return 0;
}
```
#### 5.2.2 文本解析和格式化
字符数组和字符串还可以用于文本解析和格式化。可以使用字符串函数(如 strtok() 和 sprintf())来解析文本并将其格式化为所需的格式。
**代码块**
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char text[] = "name: John Doe, age: 30, city: New York";
char delimiter[] = ", ";
int main() {
char *token = strtok(text, delimiter);
while (token != NULL) {
printf("%s\n", token);
token = strtok(NULL, delimiter);
}
return 0;
}
```
0
0





