【语音识别技术研究前沿】:自然语言处理的最新突破
发布时间: 2024-09-06 13:29:33 阅读量: 63 订阅数: 77 


人工智能作业 -论文 - 领域:自然语言处理.docx
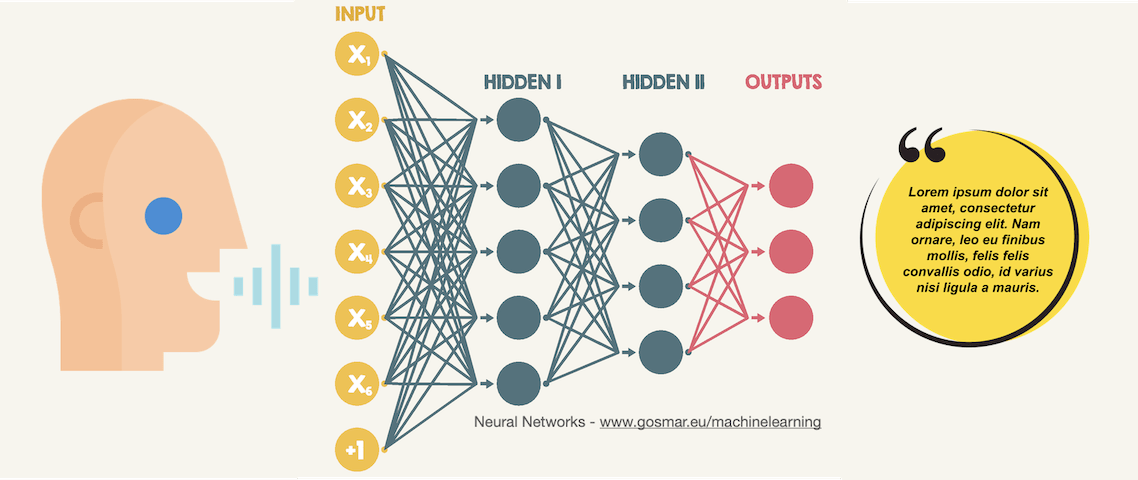
# 1. 语音识别技术概述
语音识别技术,作为人工智能领域的一个重要分支,正逐步渗透到我们的日常生活中。本章将为您提供一个关于语音识别技术的基础性介绍,包括它的定义、工作原理和应用领域。
## 1.1 语音识别技术的定义
语音识别技术,简而言之,是利用计算机技术将人类的语音信号转化为可读的文本信息。这项技术通过模拟人类的听觉感知过程,识别和处理语音信号,并将其转换成相应的文字信息。
## 1.2 语音识别技术的工作原理
语音识别技术的工作原理大体可以分为三个步骤:首先,它通过麦克风等设备捕捉到声音信号;其次,利用各种算法对声音信号进行处理,提取出有用的特征;最后,通过模式匹配等方法将这些特征转化为可识别的文字。
## 1.3 语音识别技术的应用领域
语音识别技术广泛应用于智能助手、语音输入法、智能家居控制、医疗健康、教育与辅助技术等多个领域。未来,随着技术的不断进步,语音识别的应用领域还将进一步扩大。
以上就是第一章关于语音识别技术的基本介绍,希望能帮助你对这项技术有一个初步的了解。接下来的章节,我们将深入探讨语音识别的理论基础、技术应用以及未来的发展方向。
# 2. 语音识别理论基础
语音识别技术的核心目标是使机器能够理解并转换人类的语音。为了达到这一目标,需要深入理解语音信号处理、语言模型与解码技术,以及端到端语音识别系统的设计。本章节将深入探讨这些理论基础,为读者构建一个坚实的语音识别知识基础。
## 2.1 语音信号处理
### 2.1.1 声学信号的基本特征
语音信号是一系列随时间变化的声波,它包含了丰富的信息,包括说话人的身份、情绪、意图等。在语音识别领域,我们通常关注以下几类声学特征:
- **频谱特征**:描述语音信号在不同频率上的能量分布,常用的频谱特征包括梅尔频率倒谱系数(MFCC),线性预测编码系数(LPC)。
- **时域特征**:描述信号随时间变化的特征,如零交叉率、短时能量等。
- **基音频率**:对于音高(音调)的感知,是区分不同语音和音乐音符的重要特征。
- **语音活动检测**(VAD):用于判断某一时刻是否有人在说话,这对于语音信号的分段和处理至关重要。
### 2.1.2 信号预处理与特征提取
在处理语音信号时,首先需要进行预处理,包括去除背景噪声、回声消除等,然后提取出对语音识别有用的特征。以下是一个简单示例,展示如何使用Python中的`librosa`库提取MFCC特征:
```python
import librosa
# 加载音频文件
y, sr = librosa.load('speech.wav')
# 提取MFCC特征
mfccs = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, n_mfcc=13)
# 打印MFCC特征
print(mfccs)
```
在上述代码中,`librosa.load`函数用于加载音频文件,返回音频样本和采样率。`librosa.feature.mfcc`用于计算MFCC特征,其中`n_mfcc`参数定义了要计算的MFCC系数的数量。提取出的MFCC特征能够用于后续的模型训练和识别。
## 2.2 语言模型与解码技术
### 2.2.1 统计语言模型的基本原理
统计语言模型为识别系统提供了一种评估不同词序列可能性的方法。语言模型能够根据前面的单词预测下一个单词出现的概率,这对于解决语音识别中的歧义问题至关重要。最简单的统计语言模型是基于n-gram的模型,它假设下一个词的出现仅依赖于前n-1个词。
例如,一个bigram模型会考虑所有可能的相邻词对出现的概率。这里是一个使用Python的`nltk`库来构建一个简单bigram语言模型的示例代码:
```python
import nltk
from nltk.util import ngrams
from nltk import FreqDist
from collections import defaultdict
# 示例句子
sent = ['the', 'dog', 'barks', 'at', 'the', 'mailman']
# 生成bigram
bigrams = ngrams(sent, 2)
# 统计bigram出现频率
fdist = FreqDist(bigrams)
# 获取bigram概率
probability = fdist['the', 'dog'] / fdist['the']
print(probability)
```
在该代码中,首先通过`ngrams`函数生成bigram,然后使用`FreqDist`计算各个bigram的频率。最后计算出“the dog”这个bigram的出现概率。
### 2.2.2 解码算法的演进与发展
解码算法在语音识别系统中负责根据语言模型和声学模型的联合概率,找出最可能的词序列。最初使用的是动态规划算法,如Viterbi算法,其在隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)中发挥关键作用。随着深度学习的发展,解码算法与端到端系统结合,使用神经网络直接预测字符或词序列。
解码过程的优化至关重要,因为它直接关联到识别的速度和准确率。以下是一个简单的基于Viterbi算法的解码流程示例:
```python
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
# 假设我们有以下的HMM参数
states = ['Rainy', 'Sunny']
start_probability = {'Rainy': 0.6, 'Sunny': 0.4}
transition_probability = {'Rainy': {'Rainy': 0.7, 'Sunny': 0.3},
'Sunny': {'Rainy': 0.4, 'Sunny': 0.6}}
emission_probability = {'Rainy': {'walk': 0.1, 'shop': 0.4, 'clean': 0.5},
'Sunny': {'walk': 0.6, 'shop': 0.3, 'clean': 0.1}}
observations = ['walk', 'shop', 'clean']
# 将HMM模型转换为有向图
G = nx.MultiDiGraph()
for state in states:
for observation in observations:
G.add_edge(state, observation, weight=emission_probability[state][observation])
# 为每个观测序列计算最可能的状态序列
def viterbi(obs, states, start_p, trans_p, emit_p):
V = [{}]
path = {}
# 初始化
for y in states:
V[0][y] = start_p[y] * emit_p[y][obs[0]]
path[y] = [y]
# 对序列中的每个观测运行Viterbi算法
for t in range(1, len(obs)):
V.append({})
newpath = {}
for cur_state in states:
(prob, state) = max((V[t-1][prev_state] * trans_p[prev_state][cur_state] * emit_p[cur_state][obs[t]], prev_state) for prev_state in states)
V[t][cur_state] = prob
newpath[cur_state] = path[state] + [cur_state]
path = newpath
# 返回最终路径和概率
(prob, state) = max((V[t][y], y) for y in states)
return (prob, path[state])
# 使用Viterbi算法
prob, path = viterbi(observations, states, start_probability, transition_probability, emission_probability)
print("概率为:", prob)
print("路径为:", path)
```
在该示例中,我们构建了一个简单的HMM模型,并使用Viterbi算法来预测给定观测序列最可能的状态序列。该算法在传统语音识别系统中非常重要,而深度学习方法则在此基础上进一步提高了识别的准确度。
## 2.3 端到端语音识别系统
### 2.3.1 端到端系统的基本概念
端到端的语音识别系统试图通过单一的模型直接从声学信号到文本输出,消除了传统语音识别中声学模型、语言模型和解码步骤的分离。这使得系统的训练和优化更为简洁和高效。
端到端系统的关键技术之一是连接时序分类(CTC)损失,它允许在输入和输出序列长度不匹配时进行训练。另一个关键技术是注意力机制,它能够帮助模型在解码过程中关注到输入序列中最相关的部分。
### 2.3.2 端到端系统的关键技术分析
一个典型的端到端系统是基于循环神经网络(RNN)的。随着长短期记忆(LSTM)和门控循环单元(GRU)的引入,RNN对于长序列数据的处理能力得到了显著增强。这些架构为端到端语音识别提供了强大的支持。
注意力机制的引入进一步改善了系统性能,尤其是对于远距离依赖关系的捕捉。注意力机制允许模型在生成输出时动态地聚焦于输入序列的特定部分,这在处理长句子时尤其有用。
下面是一个简化的端到端语音识别系统使用LSTM网络的示例:
```python
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, TimeDistributed
# 假设我们已经准备了输入数据x和输出标签y
# ...
# 构建模型
model = Sequential()
```
0
0





