Lattice ispMACH 4A系列:高性能可编程逻辑器件
需积分: 10 174 浏览量
更新于2024-07-24
收藏 1.15MB PDF 举报
ispMACH 4A系列是Lattice公司提供的高性能E2CMOS工艺的CPLD(复杂可编程逻辑器件)解决方案,其特点是架构灵活、易于使用且提供可靠的硅产品和软件工具。这款CPLD适用于快速逻辑设计,确保了用户在开发过程中的稳定性和效率。
ispM4A5-12864-10YI是该系列中的一员,它提供了从32到512个宏观单元的密度选择,同时实现100%的利用率和100%的引脚保留,支持5V或3.3V工作电压。这一型号的特点包括:
1. **卓越的一次到位(First-Time-Fit)和重构(re-fit)特性**:设计更改后无需重新布局,方便系统集成,确保了在设计变化后的无缝对接。
2. **速度锁定(SpeedLocking)技术**:通过使用最多20个产品术语(product terms)来驱动输出,ispM4A5能够提供高达5.0ns的典型延迟时间(tPD)和182MHz的最大频率(fCNT),从而确保了固定时序性能的稳定性。
3. **高速接口**:无论是商业级(5.0ns tPD)还是工业级(7.5ns tPD),以及182MHz的极限频率,ispM4A5表现出极高的数据传输速度。
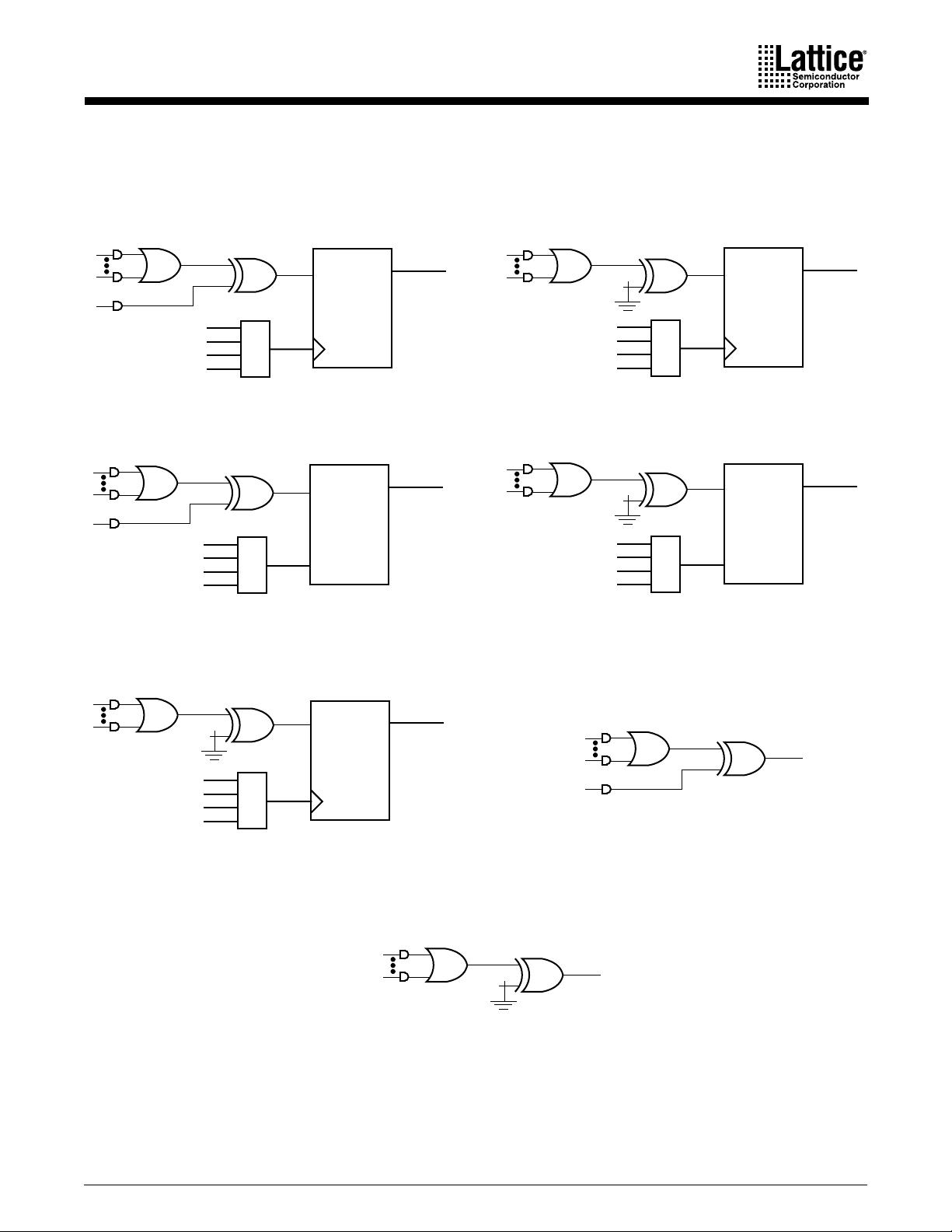
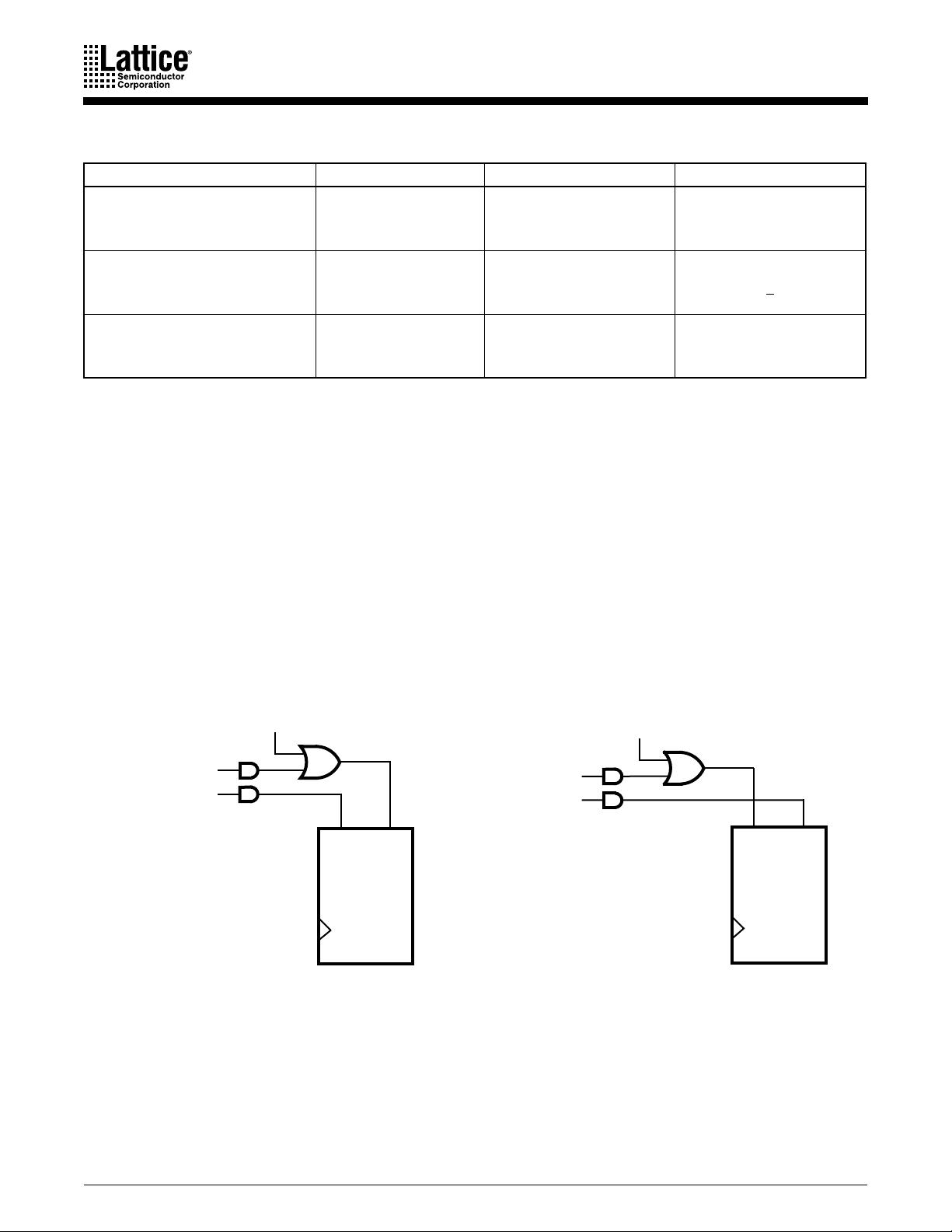
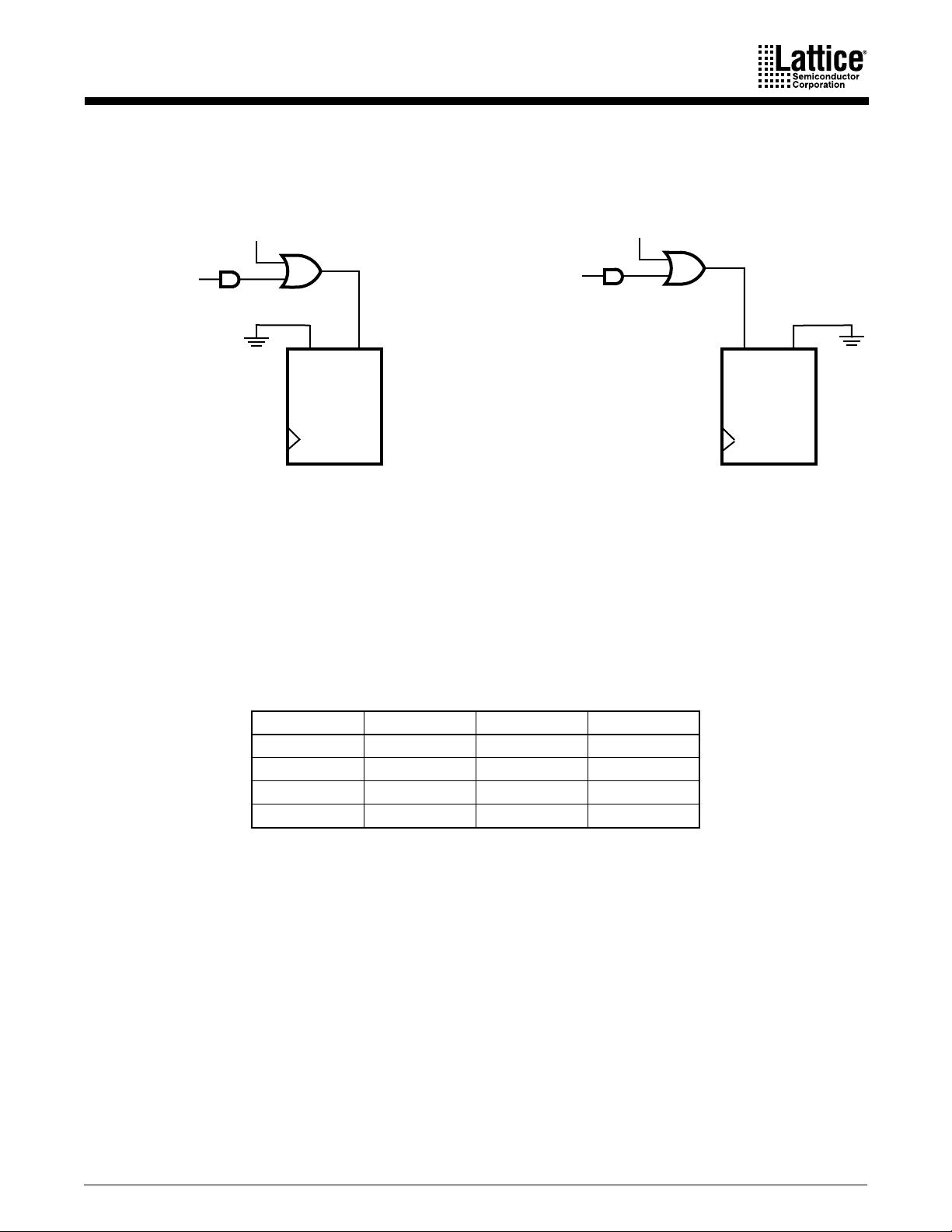
4. **丰富的功能集**:包括多样的设计风格支持,如D/T寄存器和触发器、同步或异步模式、专用输入寄存器、可编程极性、重置/预置信号交换等,提供了极大的设计灵活性。
5. **高级系统集成特性**:ispM4A5兼容3.3V和5V的JEDEC标准操作,支持JTAG(IEEE 1149.1)进行边界扫描测试,便于自动化设备的测试。此外,它还具备5V和3.3V的JTAG内系统编程能力,符合PCI标准,并能在混合供电电压系统设计中安全运行。
6. **封装选项**:ispM4A5提供多种封装类型,如PLCC、PQFP、TQFP、BGA、FBGA和cBGA,满足不同应用对引脚数和封装需求。
ispM4A5-12864-10YI是一款高度灵活且性能优越的CPLD,适合各种高性能应用,通过强大的功能和广泛的兼容性,极大地简化了用户的设计流程,降低了成本并加快了产品的上市时间。
2021-09-08 上传
3054 浏览量
点击了解资源详情
139 浏览量
161 浏览量
198 浏览量
2023-05-31 上传
131 浏览量
2023-06-13 上传
129 浏览量
张跃龙爱编程
- 粉丝: 37
- 资源: 3