深入解析Win32结构化异常处理的底层原理与实践
需积分: 9 90 浏览量
更新于2024-07-21
1
收藏 648KB PDF 举报
本文档深入探讨了Windows 32(Win32)平台上的结构化异常处理(Structured Exception Handling,简称SEH)技术。作者Matt Pietrek以其作品《Windows 95 System Programming Secrets》知名,他在NuMega Technologies Inc.任职,以丰富的经验和专业视角剖析了这一核心操作系统功能。
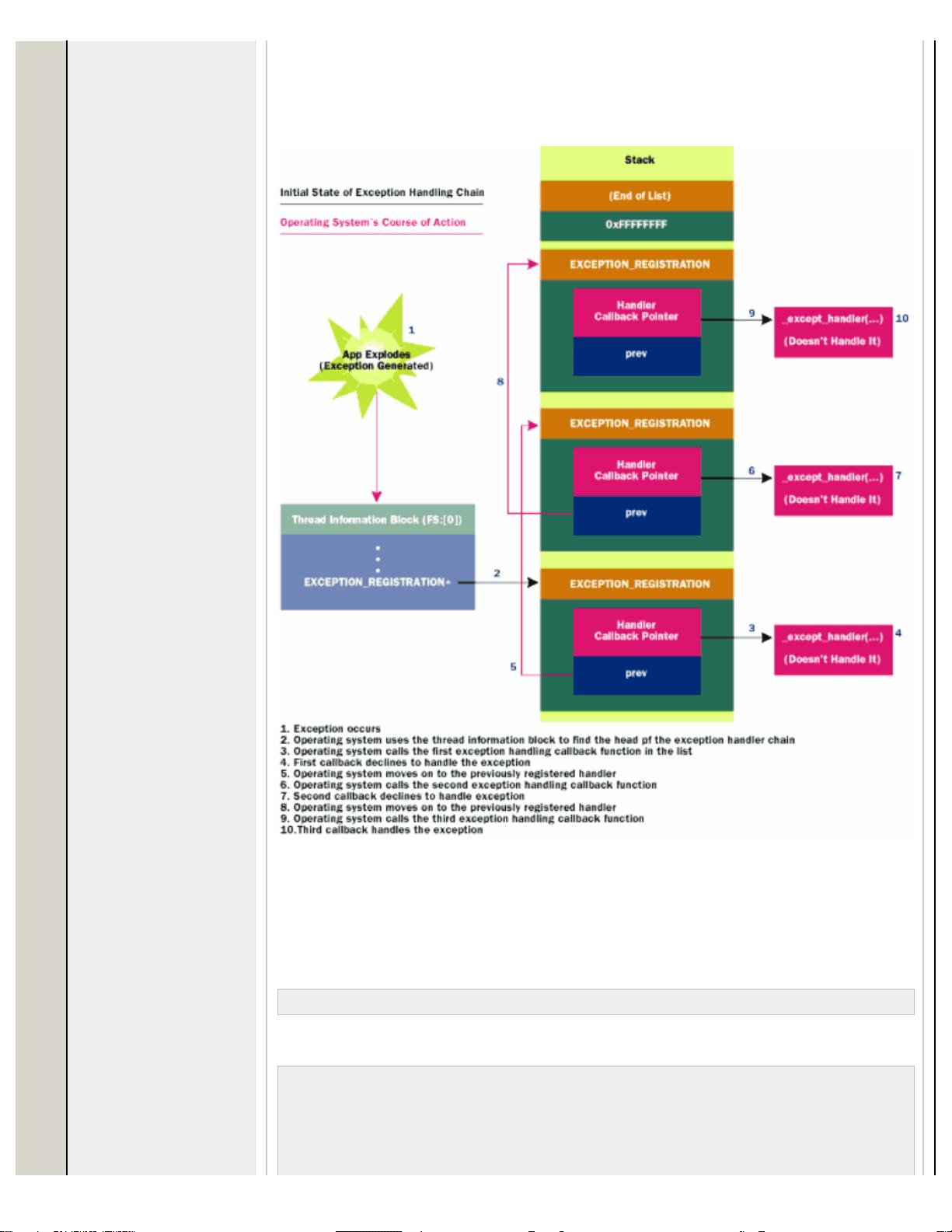
SEH是Windows操作系统提供的一种关键服务,它允许程序员在程序中进行异常管理,确保程序在遇到错误或中断时能够优雅地处理,而非简单地崩溃。通常,当我们谈论SEH时,会涉及到C++中的关键字如`try`, `finally`, 和 `except`,这些用于定义异常处理块的结构。然而,尽管市面上有许多关于SEH的教材和SDK文档,它们往往侧重于如何在特定编译器的运行时环境中使用这些关键字。
文档指出,尽管有详细的指导,但在Win32的底层,SEH其实是一种更深层次的技术。它涉及到操作系统级的异常处理机制,包括异常的抛出、捕获、恢复以及处理器状态的管理。这与通常的编程模型不同,后者主要关注的是在应用程序级别处理异常。作者强调,理解这一点对于充分利用SEH的潜力至关重要,因为这涉及到了操作系统如何在硬件和软件层面协作来管理异常情况。
为了帮助读者更好地理解,文中附带了一个名为"Exception.exe"的示例程序,大约33KB大小,它展示了实际的代码片段和应用。这个示例可能是为了直观地演示SEH的工作原理,包括异常的抛出和处理过程。
这篇“深入浅出的Win32结构化异常处理教程”对于想要掌握Windows平台异常管理的程序员来说是一份不可多得的资源。它不仅解释了高级概念,还提供了实践性的代码示例,使得读者能够深入理解并有效地利用这种关键的编程技术。无论是在编写健壮的Windows应用程序,还是在进行系统级编程时,理解和掌握SEH都是至关重要的一步。
142 浏览量
170 浏览量
2021-05-17 上传
2021-02-07 上传
2021-05-03 上传
181 浏览量
169 浏览量
150 浏览量
117 浏览量