CATL 2019:动力电池技术前瞻,驱动电动车未来
需积分: 10 111 浏览量
更新于2024-07-16
收藏 8.21MB PDF 举报
"CATL(宁德时代)在2019年的《电池:电动汽车关键技术视角》报告中,探讨了电动车动力系统的关键技术——电池包。作为全球领先的电池制造商,CATL对未来电池技术发展有着深远影响。电池包在电动汽车中的重要性主要体现在以下几个方面:
1. 能源效率与排放减少:电池是电动汽车的核心组成部分,它通过高效的化学储能技术(如锂离子电池)显著提升了电动汽车的能效,有助于降低碳排放,实现可持续出行。
2. 主导能量存储:电池包在电动车中的占据主导地位,负责存储并转换电能,是决定车辆行驶范围和性能的关键因素。
3. 空间与重量:由于电池包的体积庞大,它占据了车辆相当大的空间,并对车辆的整体设计和重量分配产生重大影响。
4. 成本影响:电池包作为车辆的主要成本之一,其价格和性能直接影响电动车的售价和竞争力。
5. 技术进步:电池包技术包括化学成分、封装设计、控制算法以及应用层面的创新,这些都是推动电动车普及和优化的关键要素。
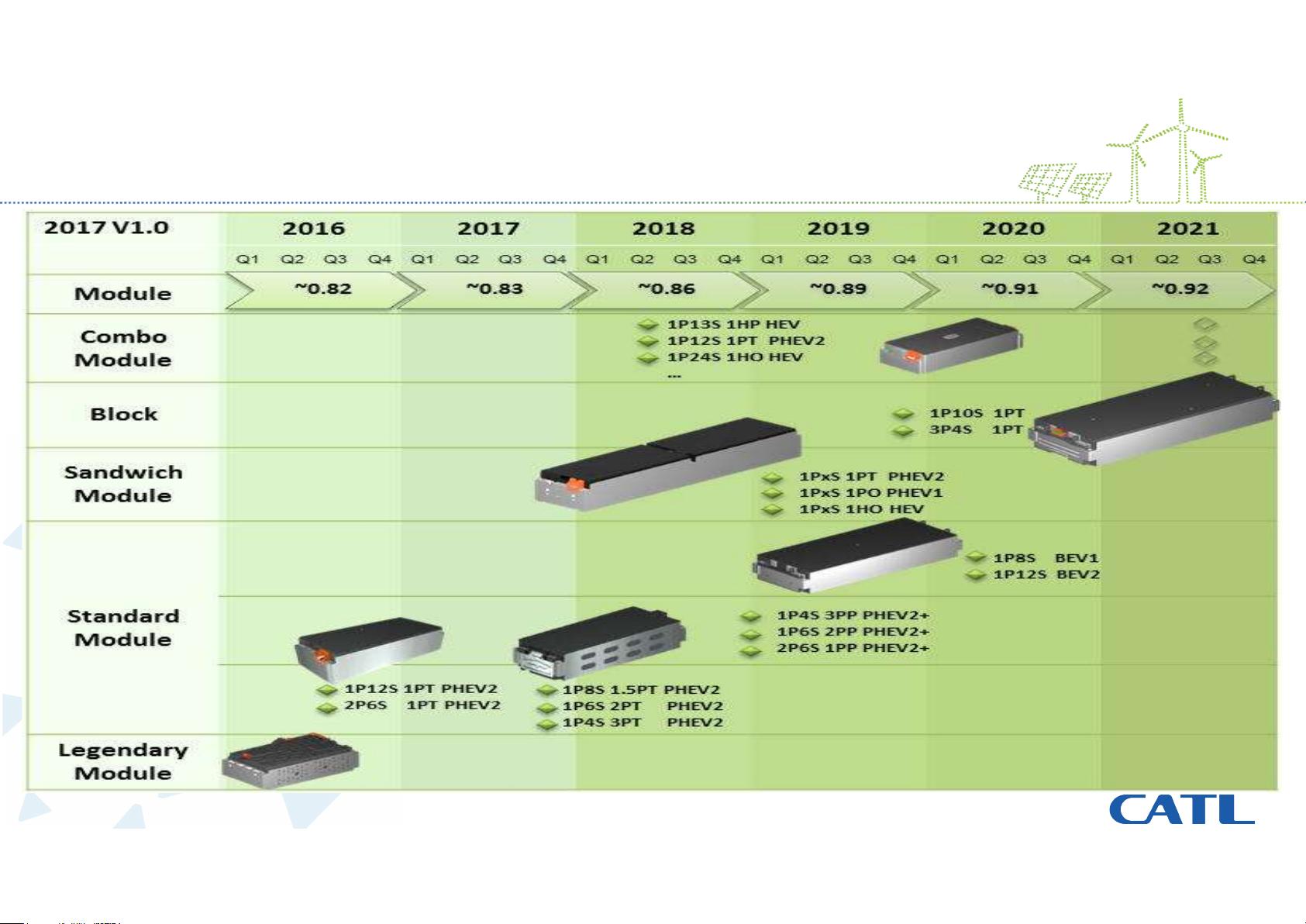
报告还详细介绍了CATL的细胞生产和模块生产路线图,强调了电池安全性、性能、寿命、成本和环境影响的五重考量。其中,安全性的核心在于高能量密度电池的滥用性能测试,例如耐穿刺、短路、过充和过放等极限情况下的表现,这些测试符合欧洲汽车工业协会(EUCAR)的严格标准。
CATL秉承着一套黄金法则哲学,致力于在确保安全的前提下,持续提升电池的性能、寿命和环境友好性。电池技术的发展不仅关乎电动车产业的进步,也是实现绿色交通转型的关键驱动力。随着CATL这样的领军企业不断推动技术创新,我们期待看到更加高效、可靠且环保的动力电池包解决方案在未来几年内的广泛应用。"
463 浏览量
199 浏览量
655 浏览量
195 浏览量
134 浏览量
169 浏览量
107 浏览量
136 浏览量
196 浏览量
2023-04-24 上传
Dukeliang
- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 2
最新资源
- uexam学之思在线考试系统 v3.0.7
- MT48LC32M16A2TG-75_IT_SDRAM_it_BGA_
- koaVote:使用Koa的非常简单的投票网站
- SubDomainizer:一种工具,用于查找子域和隐藏在其中的有趣内容,页面,文件夹和Github的外部Javascript文件
- php_demon_laravel_admin:通用PHP-ADMIN-LARAVEL快速开发库
- 在OpenGL中生成轮廓
- nodemvc:另一个节点 mvc
- app5
- artsy-timelines:一个简单的Web应用程序,用于在交互式时间轴上(通过Artsy API)呈现艺术品,艺术家,“基因”和标签
- 基于fpga的示波器(quartus13.0).zip
- 灵丹妙药:分享您生动故事的安全空间
- reinforcement_learning_agents:RL代理商库
- sim_test_
- s_task:C的等待协程库
- clas12-mcgen:所有CLAS12 MC事件生成器的集合
- Tinyxml库和学习文档以及上手即可运行的实例