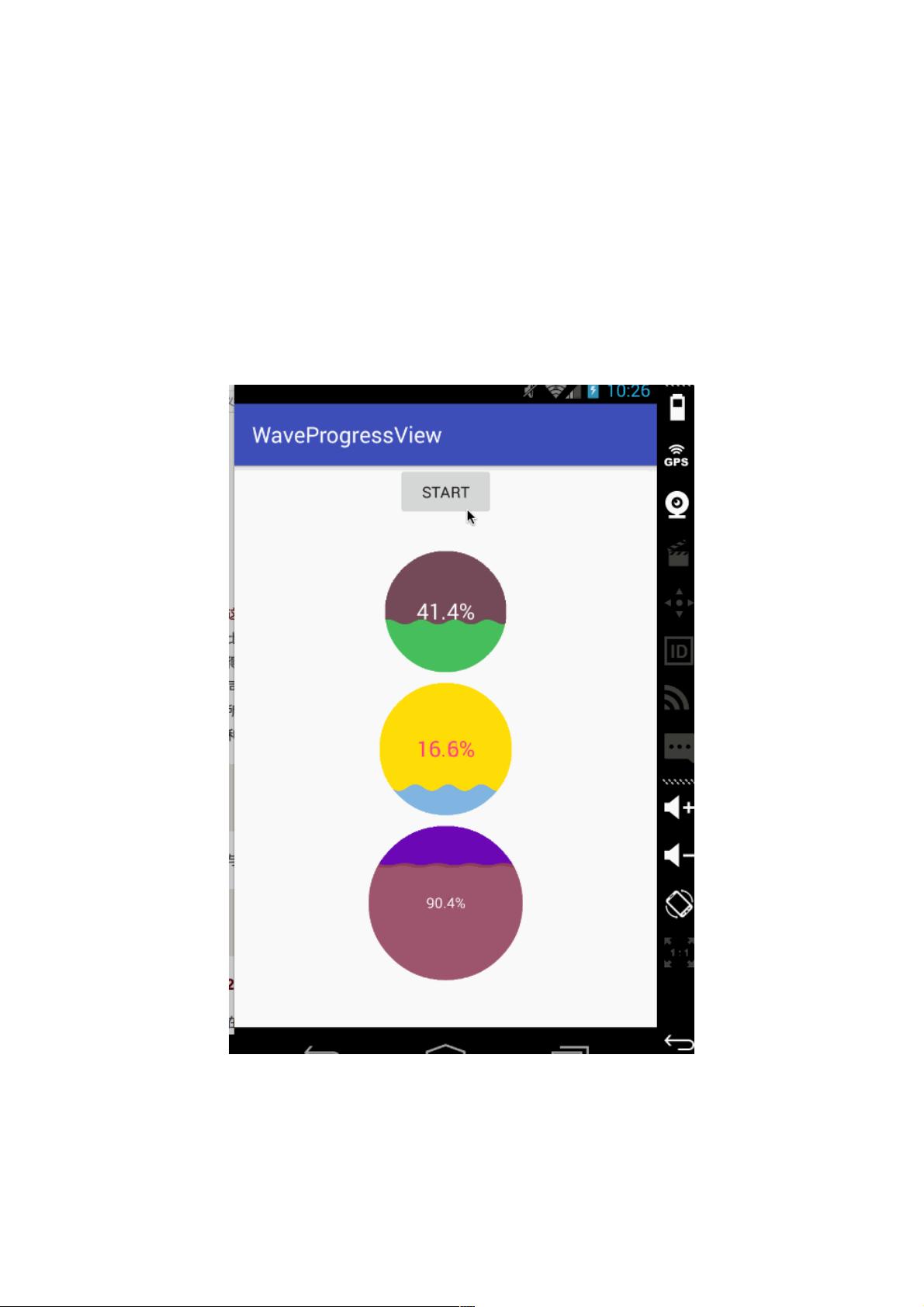
Android自定义View:水波纹进度球效果实现解析
102 浏览量
更新于2024-09-01
收藏 174KB PDF 举报
"这篇教程将介绍如何在Android中实现一个自定义的水波纹进度球效果,通过自定义View来创建美观的UI组件。"
在Android应用开发中,自定义View是实现独特UI设计和交互的关键。对于设计师提出的独特视觉效果,如水波纹进度球,开发者需要具备自定义View的技能。下面我们将详细讲解如何实现这个效果。
首先,自定义View的基本步骤包括定义自定义属性、重写`onMeasure()`方法来确定控件尺寸以及重写`onDraw()`方法来绘制View的内容。
1. **自定义属性**: 在XML布局中定义自定义View的属性可以使我们在布局文件中方便地配置View的样式。在这个例子中,我们需要以下属性:
- `radius`: 进度球的半径,可以是尺寸或引用其他资源。
- `radius_color`: 水波纹的颜色。
- `progress_text_color`: 进度文本的颜色。
- `progress_text_size`: 进度文本的字体大小。
- `progress_color`: 进度条的颜色。
- `progress`: 当前进度,浮点数形式。
- `maxProgress`: 最大进度,浮点数形式。
我们在资源文件的` attrs.xml `中声明这些属性,并在构造函数中使用`TypedArray`来获取它们的值。
2. **重写onMeasure()**: 这个方法用于计算View的宽度和高度。根据定义的属性和约束,我们需要确定View的大小,以便正确地在屏幕上显示。
3. **重写onDraw()**: 这是自定义View的核心部分,我们在这里绘制水波纹进度球的效果。这通常涉及到使用`Canvas`对象进行绘图操作,如画圆、画弧线、画文字等。为了实现水波纹效果,可能需要用到`Path`对象来绘制动态的波纹形状,并通过动画来模拟波动的过程。同时,还要考虑进度的更新,适时改变画布上进度条和进度文本的显示。
为了实现水波纹效果,我们可以使用`ObjectAnimator`或`ValueAnimator`来创建动画,改变波纹的半径和位置,从而模拟波纹扩散的效果。同时,根据`progress`和`maxProgress`属性,调整进度条的长度,并更新进度文本。
此外,需要注意的是,为了保证性能,我们应该尽量优化`onDraw()`方法,避免不必要的计算和绘制操作,确保视图的流畅性。
总结起来,实现水波纹进度球效果需要对Android图形系统有深入理解,包括`Canvas`、`Paint`、`Path`以及动画系统的运用。通过这个过程,开发者不仅可以创建出独特的UI组件,还能提升对Android系统底层机制的掌握。在实际项目中,这样的自定义View可以显著提升应用的用户体验和视觉吸引力。
747 浏览量
724 浏览量
322 浏览量
202 浏览量
162 浏览量
142 浏览量
110 浏览量
weixin_38663415
- 粉丝: 3
- 资源: 891
最新资源
- 3561VI.zip
- minisdp:无服务器 WebRTC 的较小 sdp
- 易语言源码易语言信息框DIY工具源码.rar
- nadatrace_shiny
- omnibear:Micropub浏览器扩展
- docker-workflow-tutorial
- DOM-manip_wk6_day5_wkend_hw
- 因子模型和套利定价理论(APT)
- material-ui-tree:具有material-ui v4的React树组件
- java-ssm框架图书管理系统(附sql)
- fruit-catcher1
- Python-Code-Generation:使用语言模型编写python代码
- 销售代理评估表DOC格式
- 初级java笔试题-ISTE-120:使用面向对象方法解决信息领域问题的第一门课程。学生将学习使用面向对象的方法设计软件解决方案,使用UML对
- 易语言源码易语言保存超级列表框到excel格式源码.rar
- covid-risk:根据德国RKI(Robert-Koch-Institut)的交互式世界地图,显示高风险COVID-19区域