Wireless Engineering and Technology, 2012, 3, 83-85
doi:10.4236/wet.2012.32013 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/wet)
83
An Electrically Scanned Lens Antenna for 2-D Scanning
*
Zong-xin Wang, Da-peng Fan
State Key Lab of Millimeter Waves, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
Email: wangzx@seu.edu.cn
Received November 25
th
, 2011; revised December 17
th
, 2011; accepted January 30
th
, 2012
ABSTRACT
An electrically scanned lens antenna for two dimensional scanning is presented. The antenna system is composed of a
(N × 1) feed array, a binary diffractive dielectric lens (BDL) and a voltage-controlled ferroelectric lens (VCFL). The
feeds at different offset foci of the BDL generate receiving beams pointing to different angles to perform beam scanning
in one dimension; the VCFL made of ferroelectric slabs which show linear permittivity gradient when loaded with cor-
responding DC voltages generate linear phase shift to steer the beam in the other dimension.
Keywords: Electrically Scanning; Binary Diffractive Lens; Voltage-Controlled Ferroelectric Lens
1. Introduction
The traditional phased array antenna (PAA) is composed
of many radiating elements each with a phase shifter.
Beams of different scanning angles are formed by shift-
ing the phase of the signal of each radiating element.
Compared with mechanism scanning antennas, PAA
systems have many good characteristics such as high
scanning speed, no mechanical inertia and the ability to
generate agile beams under computer control, however, a
PAA system usually consists of thousands of radiating
elements (N × M, N rows and M columns) and each with
a phase shifter, which make the system very complex and
expensive. Phase shifters using ferroelectric materials
have been proposed [1,2] and based on this concept a
new concept of phased array depending on voltage-con-
trolled ferroelectric lens (VCFL) has been given by J. B.
L. Rao [3], etc. The new phased array system contains
only (N + M) electrically controlled units for generating
scanning beams, and the unit number is far less than (N ×
M), so the complexity and cost of system can be reduced
markedly. In this paper, we present a novel lens antenna
consist of a (N × 1) feed array, a binary diffractive di-
electric lens (BDL) [4] and a VCFL. To generate electri-
cally controlled scanning beams there need only an
N-channel electric switch and M voltage-controllers.
2. Antenna Configuration and Simulation
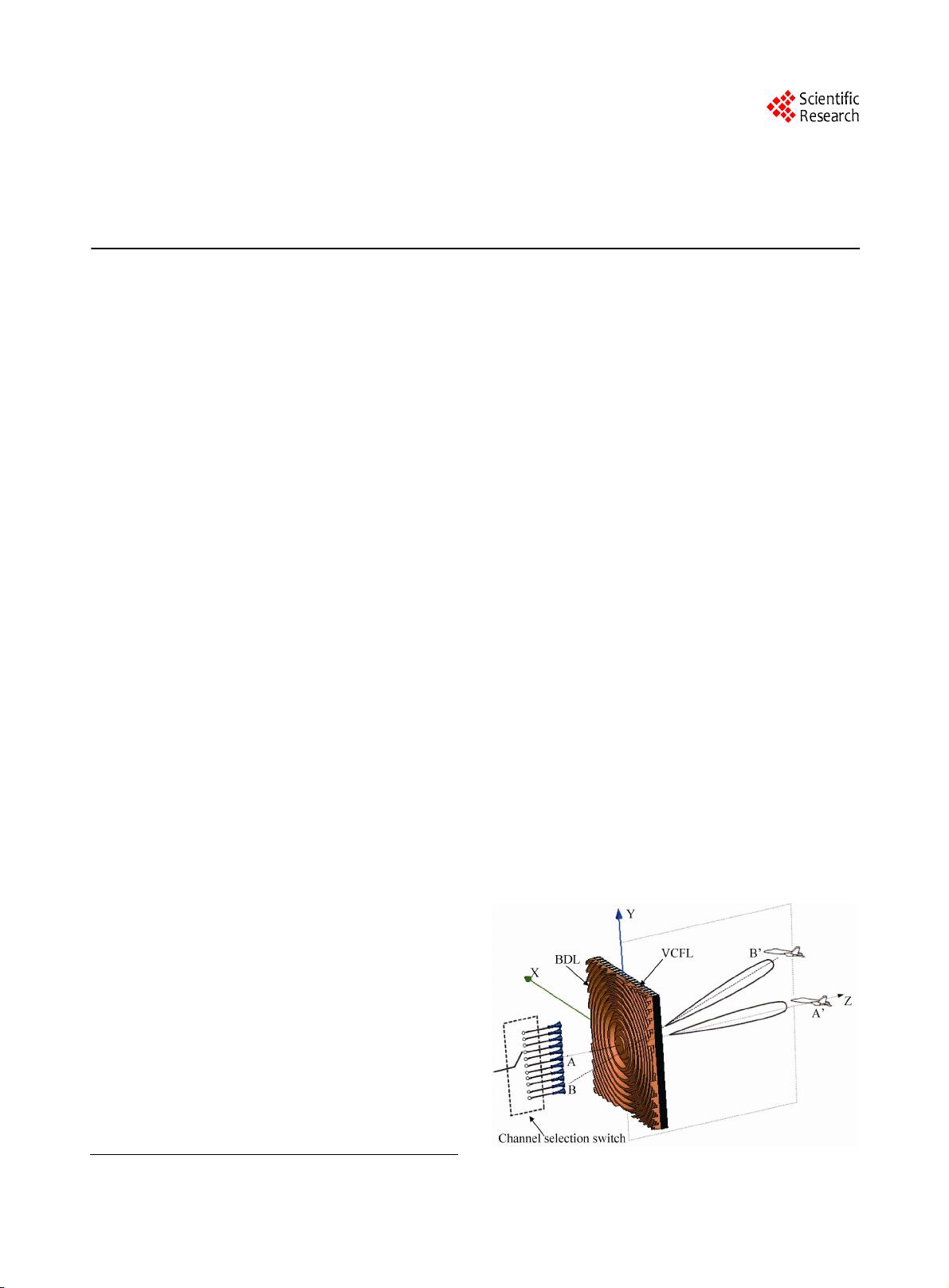
The configuration of the proposed antenna system is
shown in Figure 1, where the system consists of a (N × 1)
feed array, a BDL and a VCFL. Cross section of a BDL
along x-axis is shown in Figure 2, the BDL has the same
focusing property as that of a common hyperbolic lens,
however, the BDL has the advantages of low profile and
weight, and what is most import is that the BDL can be
integrated with the VCFL into a seamless compound lens
profited from its planar structure. The (N × 1) feed array
is set at the focal plane of the BDL, the feed at different
offset positions will generate different scanning beams
pointing to corresponding direction in the YOZ plane, for
example, receiving beams generated by feed A and feed
B point to the target at A’ and B’ respectively. All the
beams generated by the (N × 1) feed array perform the
scanning in the YOZ plane. The VCFL is made up of
ferroelectric slabs sandwiched between conducting plates
[3] as shown in Figure 3.
The dielectric constants
123
,,
n
of the ferro-
electric slabs can be changed by applying and varying the
DC electric field which is controlled by the computer.
Figure 1. The proposed antenna system.
*
Supported by NSFC (61071046).
Copyright © 2012 SciRes. WET









