"SLAM定位与建图技术探究:视觉感知与自动驾驶"
需积分: 0 177 浏览量
更新于2024-04-02
收藏 7.77MB PDF 举报
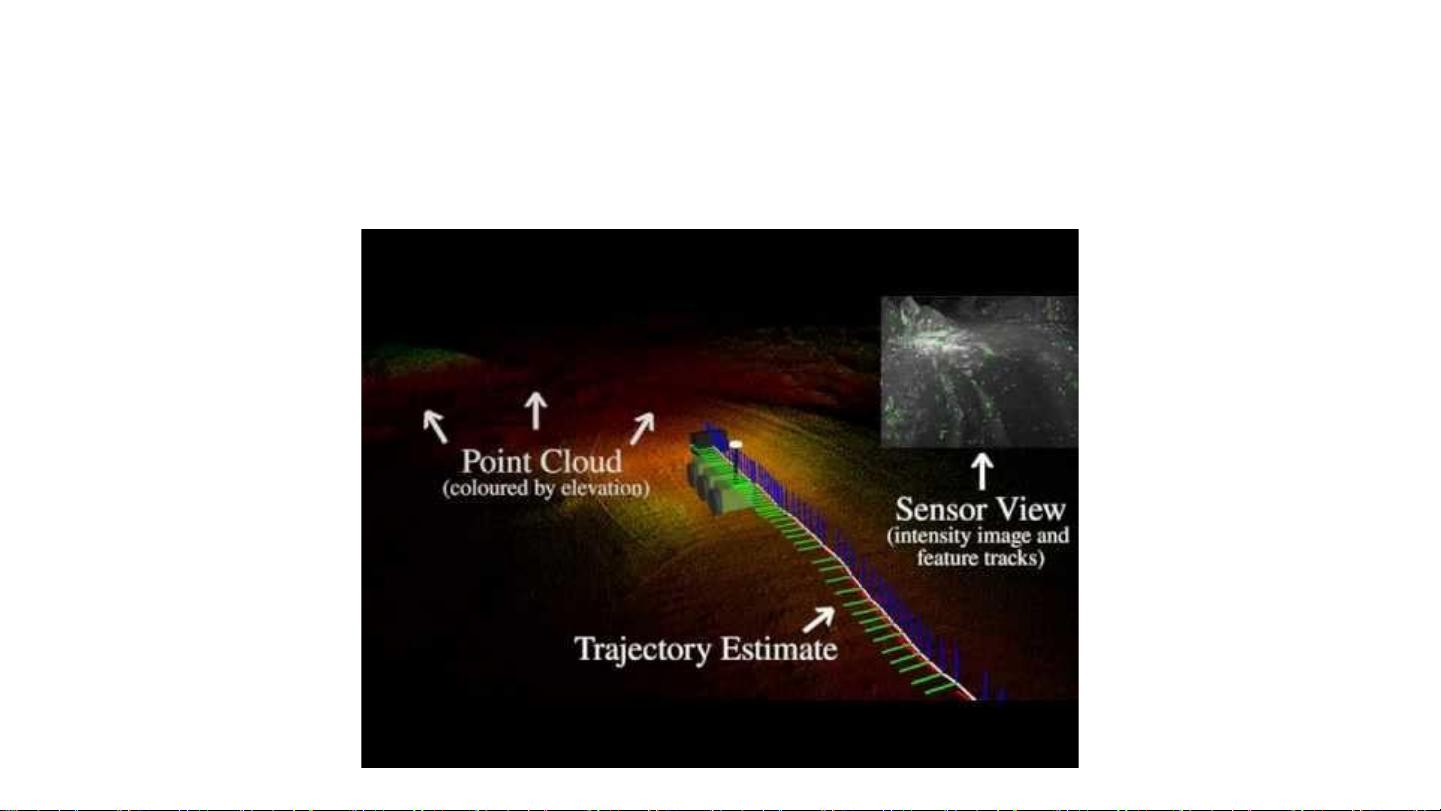
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) is a crucial component in the field of visual perception for autonomous driving. It involves both the process of determining the position and orientation of a camera in real-time (known as localization) and simultaneously creating a map of the environment the camera is traversing. This is achieved through a combination of techniques such as optical flow, stereo vision, visual odometry, and scene flow.
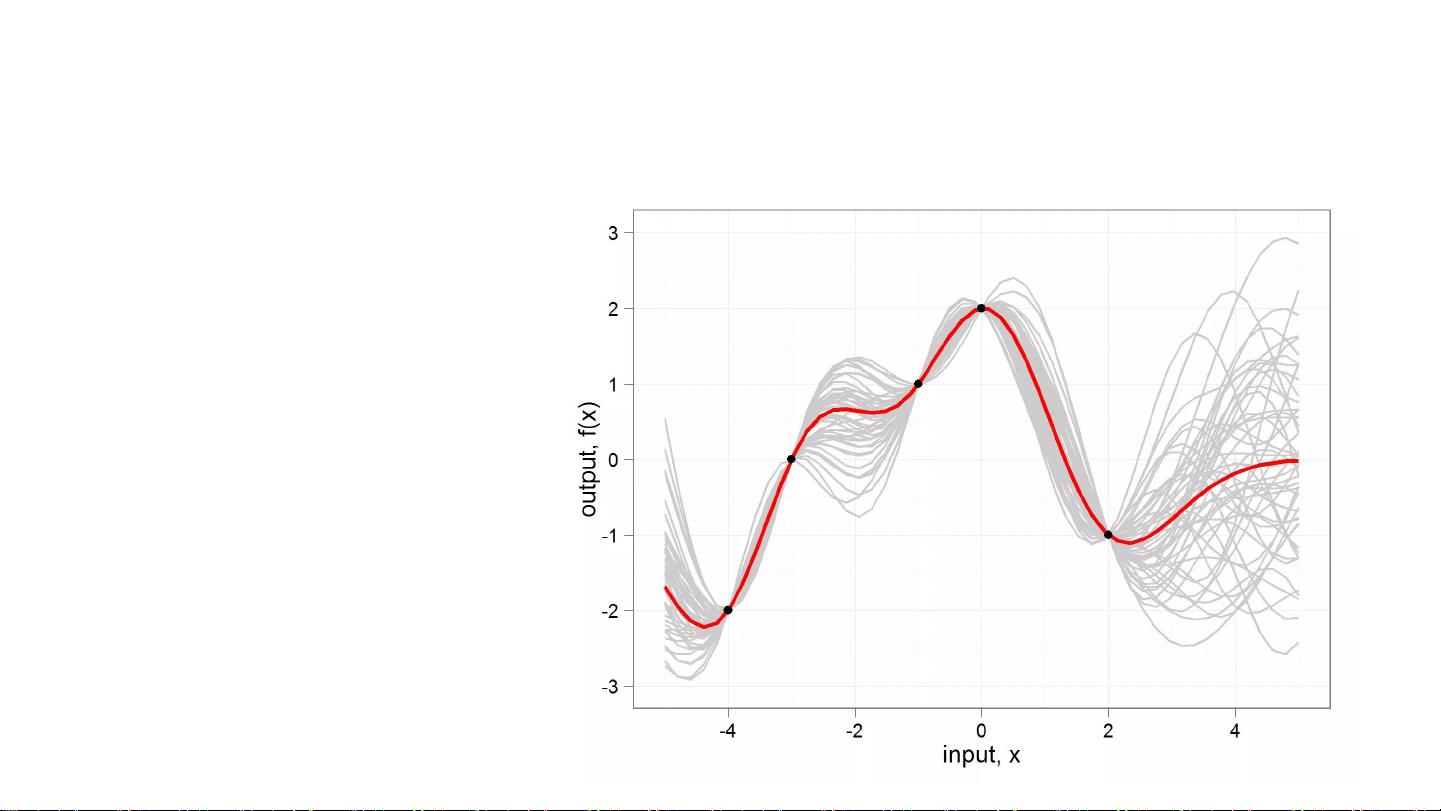
One common approach to SLAM is relative continuous-time SLAM, which utilizes cubic B-splines and Gaussian Process Regression to accurately estimate the camera's position and orientation in relation to its surroundings. This method is motivated by the need for high precision and robustness in autonomous driving applications.
Another important aspect of SLAM is long-term lidar SLAM, which focuses on maintaining an up-to-date map of the environment and interpreting scene flow information to improve localization accuracy. This involves ongoing map maintenance and the integration of new data to ensure that the map remains current and relevant for navigation purposes.
Overall, SLAM plays a vital role in enabling autonomous vehicles to navigate complex environments with confidence and accuracy. By combining sophisticated algorithms and sensor technologies, SLAM provides a reliable solution for building and updating maps while simultaneously determining the vehicle's position in the environment. This capability is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of autonomous driving systems in a wide range of real-world scenarios.
2023-08-20 上传
2023-07-01 上传
2023-06-17 上传
2024-05-28 上传
2023-07-19 上传
2023-09-05 上传
史努比狗狗
- 粉丝: 28
- 资源: 318
最新资源
- 构建Cadence PSpice仿真模型库教程
- VMware 10.0安装指南:步骤详解与网络、文件共享解决方案
- 中国互联网20周年必读:影响行业的100本经典书籍
- SQL Server 2000 Analysis Services的经典MDX查询示例
- VC6.0 MFC操作Excel教程:亲测Win7下的应用与保存技巧
- 使用Python NetworkX处理网络图
- 科技驱动:计算机控制技术的革新与应用
- MF-1型机器人硬件与robobasic编程详解
- ADC性能指标解析:超越位数、SNR和谐波
- 通用示波器改造为逻辑分析仪:0-1字符显示与电路设计
- C++实现TCP控制台客户端
- SOA架构下ESB在卷烟厂的信息整合与决策支持
- 三维人脸识别:技术进展与应用解析
- 单张人脸图像的眼镜边框自动去除方法
- C语言绘制图形:余弦曲线与正弦函数示例
- Matlab 文件操作入门:fopen、fclose、fprintf、fscanf 等函数使用详解