没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
首页正态分布乘积等于正态分布的证明
正态分布乘积等于正态分布的证明
各种正态分布的的乘积,包括单变量,多变量正态分布的乘积为正态分布的乘积的证明。
资源详情
资源推荐

Tina Memo No. 2003-003
Internal Report
Products and Convolutions of Gaussian Probability Density
Functions
P.A. Bromiley
Last updated
14 / 8 / 2014
Imaging Sciences Research Group, Institute of Population Health,
School of Medicine, University of Manchester,
Stopford Building, Oxford Road,
Manchester, M13 9PT.

Products and Convolutions of Gaussian Probability
Density Functions
P. A. Bromiley
Imaging Sciences Research Group, Institute of Population Health,
School of Medicine, University of Manchester,
Manchester, M13 9PT, UK
paul.bromiley@manchester.ac.uk
Abstract
It is well known that the product and the convolution of Gaussian probability density functions (PDFs)
are also Gaussian functions. This document provides proofs of this for several cases; the product of
two univariate Gaussian PDFs, the product of an arbitrary number of univariate Gaussian PDFs, the
product of an arbitrary number of multivariate Gaussian PDFs , and the convolution of two univari-
ate Gaussian PDFs. These results are useful in calculating the effects of smoothing applied as an
intermediate step in various algorithms.
1 The Product of Two Univariate Gaussian PDFs
Let f(x) and g(x) be Gaussian PDFs with arbitrary means µ
f
and µ
g
and standard deviations σ
f
and σ
g
f(x) =
1
√
2πσ
f
e
−
(x−µ
f
)
2
2σ
2
f
and g(x) =
1
√
2πσ
g
e
−
(x−µ
g
)
2
2σ
2
g
Their product is
f(x)g(x) =
1
2πσ
f
σ
g
e
−
(x−µ
f
)
2
2σ
2
f
+
(x−µ
g
)
2
2σ
2
g
Examine the term in the exponent
β =
(x − µ
f
)
2
2σ
2
f
+
(x − µ
g
)
2
2σ
2
g
Expanding the two quadratics and collecting te r ms in powers of x gives
β =
(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)x
2
− 2(µ
f
σ
2
g
+ µ
g
σ
2
f
)x + µ
2
f
σ
2
g
+ µ
2
g
σ
2
f
2σ
2
f
σ
2
g
Dividing through by the coefficient of x
2
gives
β =
x
2
− 2
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
x +
µ
2
f
σ
2
g
+µ
2
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
This is again a quadratic in x, and so Eq. 2 is a Gaussian function. Compare the terms in Eq. 5 to a the usual
Gaussian form
P (x) =
1
√
2πσ
e
−
(x−µ)
2
2σ
2
=
1
√
2πσ
e
−
(x
2
−2µx+µ
2
)
2σ
2
Since a term ǫ that is independent of x can be added to complete th e square in β, this is suffic ent to complete the
proof in cases where the normalisation can be ignored. The product of two Gaussian PDFs is proportional to a
Gaussian PDF with a mean that is half the coefficient of x in Eq. 5 and a standard deviation that is the square
root of half of the denominator i.e.
σ
fg
=
s
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
and µ
fg
=
µ
f
σ
2
g
+ µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
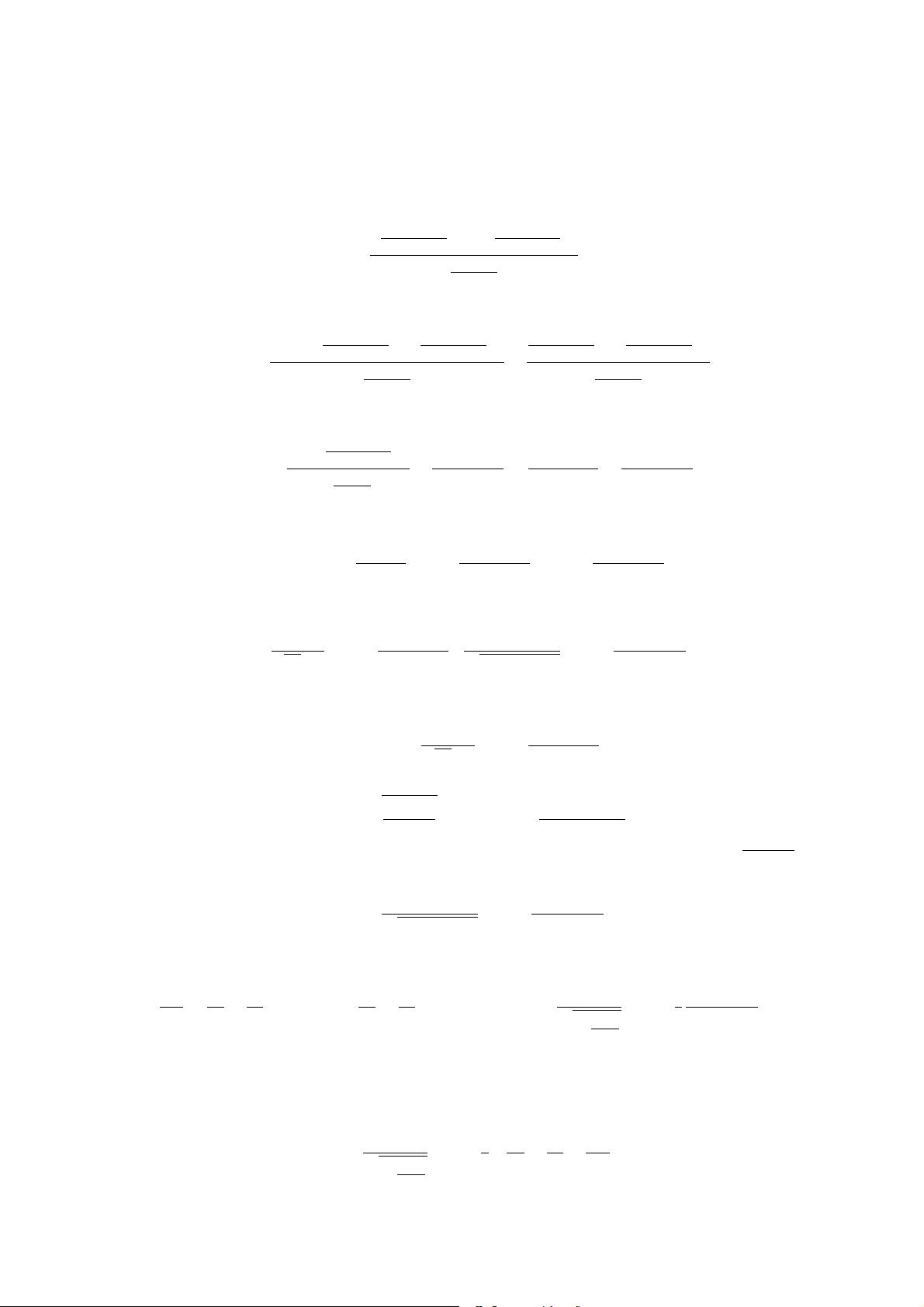
i.e. the variance σ
2
fg
is twice the harmonic mean of the individual variances σ
2
f
and σ
2
g
, and the mean µ
fg
is the
sum of the individual means µ
f
and µ
g
weighted by their variances. In general, the product is not itself a PDF
as, due to the presence of the scaling factor, it will not have the corr e ct nor malis ation.
The product f(x)g(x) can now be written in the usual Gaus s ian form directly, with an unknown scaling constant
(this may be sufficient in cases where renormalisation can be applied). Alternatively, proceeding from Eq. 5,
suppose that ǫ is the term required to complete the square in β i.e.
ǫ =
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
−
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
2σ
2
f
σ
2
g
(σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
)
= 0
Adding this term to β gives
β =
x
2
− 2x
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
+
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
2σ
2
f
σ
2
g
(σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
)
+
µ
2
f
σ
2
g
+µ
2
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
−
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
2σ
2
f
σ
2
g
(σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
)
After some manipulation, this reduces to
β =
x −
µ
f
σ
2
g
+µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
2
2
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f
+σ
2
g
+
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
2(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
=
(x − µ
fg
)
2
2σ
2
fg
+
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
2(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
Substituting back into Eq. 2 gives
f(x)g(x) =
1
2πσ
f
σ
g
exp
"
−
(x − µ
fg
)
2
2σ
2
fg
#
exp
"
−
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
2(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
#
Multiplying by σ
fg
/σ
fg
and rearranging gives
=
1
√
2πσ
fg
exp
"
−
(x − µ
fg
)
2
2σ
2
fg
#
1
q
2π(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
exp
"
−
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
2(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
#
Therefore, the product of two Gaussians PDFs f(x) and g(x) is a scaled Gaussian PDF
f(x)g(x) =
S
fg
√
2πσ
fg
exp
"
−
(x − µ
fg
)
2
2σ
2
fg
#
where
σ
fg
=
s
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
and µ
fg
=
µ
f
σ
2
g
+ µ
g
σ
2
f
σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
(1)
and the scaling factor S is itself a Gaussian PDF on both µ
f
and µ
g
with standard deviation
q
σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
S
fg
=
1
q
2π(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
exp
"
−
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
2(σ
2
f
+ σ
2
g
)
#
These can be wr i tt en more conveniently as
1
σ
2
fg
=
1
σ
2
f
+
1
σ
2
g
, µ
fg
=
µ
f
σ
2
f
+
µ
g
σ
2
g
!
σ
2
fg
and S
fg
=
1
r
2π
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f g
exp
"
−
1
2
(µ
f
− µ
g
)
2
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
fg
#
(2)
It is much easier to generate a proof by induction for the scaling factor of products of larger numbers of Gaussians
if it is written in the form of a sum of terms, each of which involves a single subscript i.e. the parameters of a
single Gaussian PDF. Appendix A provides the necessary proof, giving
S
fg
=
1
r
2π
σ
2
f
σ
2
g
σ
2
f g
exp
"
−
1
2
µ
2
f
σ
2
f
+
µ
2
g
σ
2
g
−
µ
2
fg
σ
2
fg
!#
(3)
3
剩余12页未读,继续阅读
huangkai222
- 粉丝: 2
- 资源: 1
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
收起
我的内容管理
收起
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

会员权益专享
最新资源
- zigbee-cluster-library-specification
- JSBSim Reference Manual
- c++校园超市商品信息管理系统课程设计说明书(含源代码) (2).pdf
- 建筑供配电系统相关课件.pptx
- 企业管理规章制度及管理模式.doc
- vb打开摄像头.doc
- 云计算-可信计算中认证协议改进方案.pdf
- [详细完整版]单片机编程4.ppt
- c语言常用算法.pdf
- c++经典程序代码大全.pdf
- 单片机数字时钟资料.doc
- 11项目管理前沿1.0.pptx
- 基于ssm的“魅力”繁峙宣传网站的设计与实现论文.doc
- 智慧交通综合解决方案.pptx
- 建筑防潮设计-PowerPointPresentati.pptx
- SPC统计过程控制程序.pptx
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功