首页
np.random.randint(-5, 5, (1, y))
np.random.randint(-5, 5, (1, y))
时间: 2023-04-01 19:00:29
浏览: 111
产生5个不同的随机数
立即下载
此程序简单易上手,一次产生5个不同的随机数,对VB语言的学习有一定帮助
这是一个关于 Python 的问题,我可以回答。np.random.randint(-5, 5, (1, y)) 是用于生成一个大小为 (1, y) 的数组,数组中的元素是 -5 到 4 之间的随机整数。其中,y 是一个变量,表示数组的列数。
阅读全文
相关推荐
Math,random 随机数
Math,random: 随机数的 各个位获取 相加
python编程语言-春节烟花代码.docx
self.y = center[1] + np.random.normal(0, explosion_size) self.vx = np.random.uniform(-explosion_speed, explosion_speed) self.vy = np.random.uniform(-explosion_speed, explosion_speed) - 0.5 self....
np.random.randint与np.random的区别
np.random.randint 和 np.random 都是 numpy 库中的随机数生成器。 区别在于: - np.random.randint 用于生成整数随机数,可以指定生成的随机数的范围和数量。 - np.random 可以生成各种类型的随机数,...
# 随机生成一个样本数据 y_true = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=100) y_pred = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=100)
y_true = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=100) y_pred = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=100) 其中,np.random.randint(0, 2, size=100) 表示生成一个大小为100的随机整数数组,每个整数的范围是[0,2),即0或1...
x1 = np.random.randint
根据提供的引用内容,没有找到与np.random.randint()相关的信息。但是,可以根据提供的信息介绍如何使用np.random生成随机整数数组...y = np.random.randint(0, 5, (2, 3)) print(y) # 输出:[[1 4 0] # [3 2 1]]
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, 10) #y = np.random.randint(n_classes, size=n_samples)
这这段这段代码这段代码使用这段代码使用了这段代码使用了Num这段代码使用了NumPy这段代码使用了NumPy库这段代码使用了NumPy库中这段代码使用了NumPy库中的这段代码使用了NumPy库中的random这段代码使用了NumPy库中...
2、根据一组测试数据,绘制包含若干个五角星的3D散点图,并将位于指定值范围的五角星设置成指定的颜色:若10<z<20,设置五角星的颜色为#C71585 ;若z>=20,设置五角星的颜色为#008B8B;其他情况设置五角星的颜色为黄色 。 测试数据如下: x = np.random.randint(0, 40, 30) y = np.random.randint(0, 40, 30) z = np.random.randint(0, 40, 30)
y = np.random.randint(0, 40, 30) z = np.random.randint(0, 40, 30) # 创建3D图像 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # 绘制五角星 for i in range(len(x)): color = 'yellow' # ...
逐行解释np.random.seed(0) X = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 2)) y = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]) data = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([X, y.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1), columns=["x1", "x2", "y"]) print(data)
- X = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(6, 2)):生成一个6行2列的NumPy数组X,其中元素是0到9之间的随机整数。 - y = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]):生成一个包含6个元素的NumPy数组y,其中前三个元素为0,后三...
这是一个oritenteering problem.是一个 a variant of 'TSP' .拓展的TSP问题。现在有c为travel times,score to visit each node(s) time budget(T). Determine a subset of nodes to vist and in which order, so that the total collected score is maximized and a given time budget is not exceeded. PS: Start frome and return to node 0.n = 20 # generate locations np.random.seed(0) loc_x = np.random.randint(0, 100, n) loc_y = np.random.randint(0, 100, n) # generate scores s = np.random.randint(1, 10, n) # calculate travel time c = {(i,j):((loc_x[i] - loc_x[j])**2 + (loc_y[i] - loc_y[j])**2)**.5 for i in range(n) for j in range(n)} # time budget T = 300 请补充完整这个代码,用python 和 gurobi
loc_y = np.random.randint(0, 100, n) s = np.random.randint(1, 10, n) # calculate travel time c = {(i,j):((loc_x[i] - loc_x[j])**2 + (loc_y[i] - loc_y[j])**2)**.5 \ for i in range(n) for j in range(n...
import numpy as np from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(42) # 设置随机种子,保证每次运行结果相同 x = np.random.randn(100, 3) y = x.dot(np.array([4, 5, 6])) + np.random.randn(100) * 0.1 def loss_function(w, x, y): return 0.5 * np.mean((np.dot(x, w) - y) ** 2) def gradient_function(w, x, y): return np.dot(x.T, np.dot(x, w) - y) / len(y) def SGD(x, y, w_init, alpha, max_iter): w = w_init for i in range(max_iter): rand_idx = np.random.randint(len(y)) x_i = x[rand_idx, :].reshape(1, -1) y_i = y[rand_idx] grad_i = gradient_function(w, x_i, y_i) w = w - alpha * grad_i return w fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) W0 = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) W1 = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1) W0, W1 = np.meshgrid(W0, W1) W2 = np.array([SGD(x, y, np.array([w0, w1, 0]), 0.01, 1000)[2] for w0, w1 in zip(np.ravel(W0), np.ravel(W1))]) W2 = W2.reshape(W0.shape) ax.plot_surface(W0, W1, W2, cmap='coolwarm') ax.set_xlabel('w0') ax.set_ylabel('w1') ax.set_zlabel('loss') plt.show() 代码11行为何报错
但是由于 np.random.randint() 返回的是整数类型,因此索引应该使用整数值而不是浮点数值。 为了修复这个错误,可以将第11行代码修改为以下形式: python x_i = x[int(rand_idx), :].reshape(1, -1) 这样...
noise = np.random.randint(0, 100, (len(X_train), 784)) X_train_mod = X_train+noise noise = np.random.randint(0, 100, (len(X_test), 784)) X_test_mod = X_test + noise y_train_mod = X_train y_test_mod = X_test
首先,用NumPy中的random模块生成一个矩阵noise,该矩阵的大小为(len(X_train), 784),其中X_train是训练集数据,784是每张图片的像素数量。这个矩阵中每个元素的取值范围是[0,100),即0到99之间的整数。 然后,将...
image=np.array(grayImage,dtype=float) percent=0.001 num=int(percent*image.shape[0]*image.shape[1]) for i in range(num): temp1=np.random.randint(image.shape[0]) temp2=np.random.randint(image.shape[1]) scale=150 noise=np.random.poisson(scale,1) image[temp1][temp2]+=noise out=image if out.min()<0: low_clip=-1. else: low_clip=0. out=np.clip(out,low_clip,255) expon_image=np.uint8(out) print(expon_image.shape) cv2.imshow("expon_image",expon_image) k=cv2.waitKey(0)优化这段代码的for循环
rand_y = np.random.randint(0, image.shape[1], num) scale = 150 noise = np.random.poisson(scale, num) # 对图像进行操作 image[rand_x, rand_y] += noise # 调整像素值范围 out = np.clip(image, 0, 255) #...
x:0-4,10*10 np.random.randint y:[1,2,,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5]
y = np.random.randint(1, 6, 10) print("x:\n", x) print("y:", y) 输出结果如下: x: [[3 4 0 0 3 1 0 3 0 4] [2 1 3 3 1 3 1 2 3 1] [4 0 3 1 2 3 0 2 1 4] [3 4 4 4 0 2 3 4 3 3] [4 1 3 1 1 3 ...
def random_shift_events(event_tensor, max_shift=20, resolution=(224, 224)): H, W = resolution x_shift, y_shift = np.random.randint(-max_shift, max_shift + 1, size=(2,)) event_tensor[:, 0] += x_shift event_tensor[:, 1] += y_shift valid_events = (event_tensor[:, 0] >= 0) & (event_tensor[:, 0] < W) & (event_tensor[:, 1] >= 0) & (event_tensor[:, 1] < H) event_tensor = event_tensor[valid_events] return event_tensor这个函数什么意思
函数首先随机生成一个x和y方向的平移距离,然后将事件张量中的x和y坐标分别加上这个随机平移距离。最后,该函数返回经过平移后的事件张量,其中不合法的事件(即超出了分辨率范围的事件)被删除。
from sklearn.naiva_bayes import Multinomia|NB x:0-4,10*10 np.random.randint y:[1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5]
x = np.random.randint(0, 5, size=(10, 10)) y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) clf = MultinomialNB() clf.fit(x, y) # 预测结果 y_pred = clf.predict(x) print(y_pred) 这段代码中,我生成了...
def En(image): x, y,_ = image.shape # 获取图片大小 radius = np.random.randint(10, int(min(x, y)), 1) # pos_x = np.random.randint(0, (min(x, y) - radius), 1) # 获取人脸光照区域的中心点坐标 pos_y = np.random.randint(0, (min(x, y) - radius), 1) # 获取人脸光照区域的中心坐标 pos_x = int(pos_x[0]) pos_y = int(pos_y[0]) radius = int(radius[0]) strength = 100 for j in range(pos_y - radius, pos_y + radius): for i in range(pos_x-radius, pos_x+radius): distance = math.pow((pos_x - i), 2) + math.pow((pos_y - j), 2) distance = np.sqrt(distance) if distance < radius: result = 1 - distance / radius result = result*strength # print(result) image[i, j, 0] = min((image[i, j, 0] + result),255) image[i, j, 1] = min((image[i, j, 1] + result),255) image[i, j, 2] = min((image[i, j, 2] + result),255) image = image.astype(np.uint8) return image对此函数进行文件夹内部图像处理
pos_y = np.random.randint(0, (min(x, y) - radius), 1) pos_x = int(pos_x[0]) pos_y = int(pos_y[0]) radius = int(radius[0]) strength = 100 for j in range(pos_y - radius, pos_y + radius): for i in...
请你解释这段代码X_resampled, y_resampled = resample(X, y, random_state=np.random.randint(100))
在这段代码中,np.random.randint(100)用于生成一个0到99之间的随机整数作为随机种子值。通过设置相同的随机种子值,可以确保每次运行代码时得到相同的重采样结果。 重采样可以用于处理数据不平衡问题,即某一...
oneshot = False self.terrain_y.append(y) counter -= 1 if counter == 0: counter = self.np_random.randint(TERRAIN_GRASS / 2, TERRAIN_GRASS) if state == GRASS and hardcore: state = self.np_random.randint(1, _STATES_) oneshot = True else: state = GRASS oneshot = True
代码通过self.np_random.randint(1, _STATES_)生成一个1到_STATES_之间的随机整数,将其存储在state变量中,并将oneshot设置为True,表示下一个障碍物只需要生成一次。如果当前状态为GRASS且hardcore为False,表示下...
代码改进:import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs def distEclud(arrA,arrB): #欧氏距离 d = arrA - arrB dist = np.sum(np.power(d,2),axis=1) #差的平方的和 return dist def randCent(dataSet,k): #寻找质心 n = dataSet.shape[1] #列数 data_min = dataSet.min() data_max = dataSet.max() #生成k行n列处于data_min到data_max的质心 data_cent = np.random.uniform(data_min,data_max,(k,n)) return data_cent def kMeans(dataSet,k,distMeans = distEclud, createCent = randCent): x,y = make_blobs(centers=100)#生成k质心的数据 x = pd.DataFrame(x) m,n = dataSet.shape centroids = createCent(dataSet,k) #初始化质心,k即为初始化质心的总个数 clusterAssment = np.zeros((m,3)) #初始化容器 clusterAssment[:,0] = np.inf #第一列设置为无穷大 clusterAssment[:,1:3] = -1 #第二列放本次迭代点的簇编号,第三列存放上次迭代点的簇编号 result_set = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(dataSet), pd.DataFrame(clusterAssment)],axis = 1,ignore_index = True) #将数据进行拼接,横向拼接,即将该容器放在数据集后面 clusterChanged = True while clusterChanged: clusterChanged = False for i in range(m): dist = distMeans(dataSet.iloc[i,:n].values,centroids) #计算点到质心的距离(即每个值到质心的差的平方和) result_set.iloc[i,n] = dist.min() #放入距离的最小值 result_set.iloc[i,n+1] = np.where(dist == dist.min())[0] #放入距离最小值的质心标号 clusterChanged = not (result_set.iloc[:,-1] == result_set.iloc[:,-2]).all() if clusterChanged: cent_df = result_set.groupby(n+1).mean() #按照当前迭代的数据集的分类,进行计算每一类中各个属性的平均值 centroids = cent_df.iloc[:,:n].values #当前质心 result_set.iloc[:,-1] = result_set.iloc[:,-2] #本次质心放到最后一列里 return centroids, result_set x = np.random.randint(0,100,size=100) y = np.random.randint(0,100,size=100) randintnum=pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(x), pd.DataFrame(y)],axis = 1,ignore_index = True) #randintnum_test, randintnum_test = kMeans(randintnum,3) #plt.scatter(randintnum_test.iloc[:,0],randintnum_test.iloc[:,1],c=randintnum_test.iloc[:,-1]) #result_test,cent_test = kMeans(data, 4) cent_test,result_test = kMeans(randintnum, 3) plt.scatter(result_test.iloc[:,0],result_test.iloc[:,1],c=result_test.iloc[:,-1]) plt.scatter(cent_test[:,0],cent_test[:,1],color = 'red',marker = 'x',s=100)
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, size=100) randintnum = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(x), pd.DataFrame(y)], axis=1, ignore_index=True) cent_test, result_test = kMeans(randintnum, 3) plt.scatter(result_test....
CSDN会员
开通CSDN年卡参与万元壕礼抽奖
海量
VIP免费资源
千本
正版电子书
商城
会员专享价
千门
课程&专栏
全年可省5,000元
立即开通
全年可省5,000元
立即开通
最新推荐
精细金属掩模板(FMM)行业研究报告 显示技术核心部件FMM材料产业分析与市场应用
精细金属掩模板(FMM)作为OLED蒸镀工艺中的核心消耗部件,负责沉积RGB有机物质形成像素。材料由Frame、Cover等五部分组成,需满足特定热膨胀性能。制作工艺包括蚀刻、电铸等,影响FMM性能。适用于显示技术研究人员、产业分析师,旨在提供FMM材料技术发展、市场规模及产业链结构的深入解析。
【创新未发表】斑马算法ZOA-Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测Matlab源码 9515期.zip
CSDN海神之光上传的全部代码均可运行,亲测可用,直接替换数据即可,适合小白; 1、代码压缩包内容 主函数:Main.m; 调用函数:其他m文件;无需运行 运行结果效果图; 2、代码运行版本 Matlab 2024b;若运行有误,根据提示修改;若不会,可私信博主; 3、运行操作步骤 步骤一:将所有文件放到Matlab的当前文件夹中; 步骤二:双击打开除Main.m的其他m文件; 步骤三:点击运行,等程序运行完得到结果; 4、仿真咨询 如需其他服务,可私信博主或扫描博主博客文章底部QQ名片; 4.1 CSDN博客或资源的完整代码提供 4.2 期刊或参考文献复现 4.3 Matlab程序定制 4.4 科研合作 智能优化算法优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测系列程序定制或科研合作方向: 4.4.1 遗传算法GA/蚁群算法ACO优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测 4.4.2 粒子群算法PSO/蛙跳算法SFLA优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测 4.4.3 灰狼算法GWO/狼群算法WPA优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测 4.4.4 鲸鱼算法WOA/麻雀算法SSA优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测 4.4.5 萤火虫算法FA/差分算法DE优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测 4.4.6 其他优化算法优化Kmean-Transformer-LSTM负荷预测
Angular实现MarcHayek简历展示应用教程
资源摘要信息:"MarcHayek-CV:我的简历的Angular应用" Angular 应用是一个基于Angular框架开发的前端应用程序。Angular是一个由谷歌(Google)维护和开发的开源前端框架,它使用TypeScript作为主要编程语言,并且是单页面应用程序(SPA)的优秀解决方案。该应用不仅展示了Marc Hayek的个人简历,而且还介绍了如何在本地环境中设置和配置该Angular项目。 知识点详细说明: 1. Angular 应用程序设置: - Angular 应用程序通常依赖于Node.js运行环境,因此首先需要全局安装Node.js包管理器npm。 - 在本案例中,通过npm安装了两个开发工具:bower和gulp。bower是一个前端包管理器,用于管理项目依赖,而gulp则是一个自动化构建工具,用于处理如压缩、编译、单元测试等任务。 2. 本地环境安装步骤: - 安装命令`npm install -g bower`和`npm install --global gulp`用来全局安装这两个工具。 - 使用git命令克隆远程仓库到本地服务器。支持使用SSH方式(`***:marc-hayek/MarcHayek-CV.git`)和HTTPS方式(需要替换为具体用户名,如`git clone ***`)。 3. 配置流程: - 在server文件夹中的config.json文件里,需要添加用户的电子邮件和密码,以便该应用能够通过内置的联系功能发送信息给Marc Hayek。 - 如果想要在本地服务器上运行该应用程序,则需要根据不同的环境配置(开发环境或生产环境)修改config.json文件中的“baseURL”选项。具体而言,开发环境下通常设置为“../build”,生产环境下设置为“../bin”。 4. 使用的技术栈: - JavaScript:虽然没有直接提到,但是由于Angular框架主要是用JavaScript来编写的,因此这是必须理解的核心技术之一。 - TypeScript:Angular使用TypeScript作为开发语言,它是JavaScript的一个超集,添加了静态类型检查等功能。 - Node.js和npm:用于运行JavaScript代码以及管理JavaScript项目的依赖。 - Git:版本控制系统,用于代码的版本管理及协作开发。 5. 关于项目结构: - 该应用的项目文件夹结构可能遵循Angular CLI的典型结构,包含了如下目录:app(存放应用组件)、assets(存放静态资源如图片、样式表等)、environments(存放环境配置文件)、server(存放服务器配置文件如上文的config.json)等。 6. 开发和构建流程: - 开发时,可能会使用Angular CLI来快速生成组件、服务等,并利用热重载等特性进行实时开发。 - 构建应用时,通过gulp等构建工具可以进行代码压缩、ES6转译、单元测试等自动化任务,以确保代码的质量和性能优化。 7. 部署: - 项目最终需要部署到服务器上,配置文件中的“baseURL”选项指明了服务器上的资源基础路径。 8. 关于Git仓库: - 压缩包子文件的名称为MarcHayek-CV-master,表明这是一个使用Git版本控制的仓库,且存在一个名为master的分支,这通常是项目的主分支。 以上知识点围绕Angular应用“MarcHayek-CV:我的简历”的创建、配置、开发、构建及部署流程进行了详细说明,涉及了前端开发中常见的工具、技术及工作流。
管理建模和仿真的文件
管理Boualem Benatallah引用此版本:布阿利姆·贝纳塔拉。管理建模和仿真。约瑟夫-傅立叶大学-格勒诺布尔第一大学,1996年。法语。NNT:电话:00345357HAL ID:电话:00345357https://theses.hal.science/tel-003453572008年12月9日提交HAL是一个多学科的开放存取档案馆,用于存放和传播科学研究论文,无论它们是否被公开。论文可以来自法国或国外的教学和研究机构,也可以来自公共或私人研究中心。L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire
深入剖析:内存溢出背后的原因、预防及应急策略(专家版)
 参考资源链接:[Net 内存溢出(System.OutOfMemoryException)的常见情况和处理方式总结](https://wenku.csdn.net/doc/6412b784be7fbd1778d4a95f?spm=1055.2635.3001.10343) # 1. 内存溢出的概念及影响 内存溢出,又称
Java中如何对年月日时分秒的日期字符串作如下处理:如何日期分钟介于两个相连的半点之间,就将分钟数调整为前半点
在Java中,你可以使用`java.time`包中的类来处理日期和时间,包括格式化和调整。下面是一个示例,展示了如何根据给定的日期字符串(假设格式为"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")进行这样的处理: ```java import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.ZoneId; import java.time.ZonedDateTime; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args
Crossbow Spot最新更新 - 获取Chrome扩展新闻
资源摘要信息:"Crossbow Spot - Latest News Update-crx插件" 该信息是关于一款特定的Google Chrome浏览器扩展程序,名为"Crossbow Spot - Latest News Update"。此插件的目的是帮助用户第一时间获取最新的Crossbow Spot相关信息,它作为一个RSS阅读器,自动聚合并展示Crossbow Spot的最新新闻内容。 从描述中可以提取以下关键知识点: 1. 功能概述: - 扩展程序能让用户领先一步了解Crossbow Spot的最新消息,提供实时更新。 - 它支持自动更新功能,用户不必手动点击即可刷新获取最新资讯。 - 用户界面设计灵活,具有美观的新闻小部件,使得信息的展现既实用又吸引人。 2. 用户体验: - 桌面通知功能,通过Chrome的新通知中心托盘进行实时推送,确保用户不会错过任何重要新闻。 - 提供一个便捷的方式来保持与Crossbow Spot最新动态的同步。 3. 语言支持: - 该插件目前仅支持英语,但开发者已经计划在未来的版本中添加对其他语言的支持。 4. 技术实现: - 此扩展程序是基于RSS Feed实现的,即从Crossbow Spot的RSS源中提取最新新闻。 - 扩展程序利用了Chrome的通知API,以及RSS Feed处理机制来实现新闻的即时推送和展示。 5. 版权与免责声明: - 所有的新闻内容都是通过RSS Feed聚合而来,扩展程序本身不提供原创内容。 - 用户在使用插件时应遵守相关的版权和隐私政策。 6. 安装与使用: - 用户需要从Chrome网上应用店下载.crx格式的插件文件,即Crossbow_Spot_-_Latest_News_Update.crx。 - 安装后,插件会自动运行,并且用户可以对其进行配置以满足个人偏好。 从以上信息可以看出,该扩展程序为那些对Crossbow Spot感兴趣或需要密切跟进其更新的用户提供了一个便捷的解决方案,通过集成RSS源和Chrome通知机制,使得信息获取变得更加高效和及时。这对于需要实时更新信息的用户而言,具有一定的实用价值。同时,插件的未来发展计划中包括了多语言支持,这将使得更多的用户能够使用并从中受益。
"互动学习:行动中的多样性与论文攻读经历"
多样性她- 事实上SCI NCES你的时间表ECOLEDO C Tora SC和NCESPOUR l’Ingén学习互动,互动学习以行动为中心的强化学习学会互动,互动学习,以行动为中心的强化学习计算机科学博士论文于2021年9月28日在Villeneuve d'Asq公开支持马修·瑟林评审团主席法布里斯·勒菲弗尔阿维尼翁大学教授论文指导奥利维尔·皮耶昆谷歌研究教授:智囊团论文联合主任菲利普·普雷教授,大学。里尔/CRISTAL/因里亚报告员奥利维耶·西格德索邦大学报告员卢多维奇·德诺耶教授,Facebook /索邦大学审查员越南圣迈IMT Atlantic高级讲师邀请弗洛里安·斯特鲁布博士,Deepmind对于那些及时看到自己错误的人...3谢谢你首先,我要感谢我的两位博士生导师Olivier和Philippe。奥利维尔,"站在巨人的肩膀上"这句话对你来说完全有意义了。从科学上讲,你知道在这篇论文的(许多)错误中,你是我可以依
【Java内存管理终极指南】:一次性解决内存溢出、泄漏和性能瓶颈
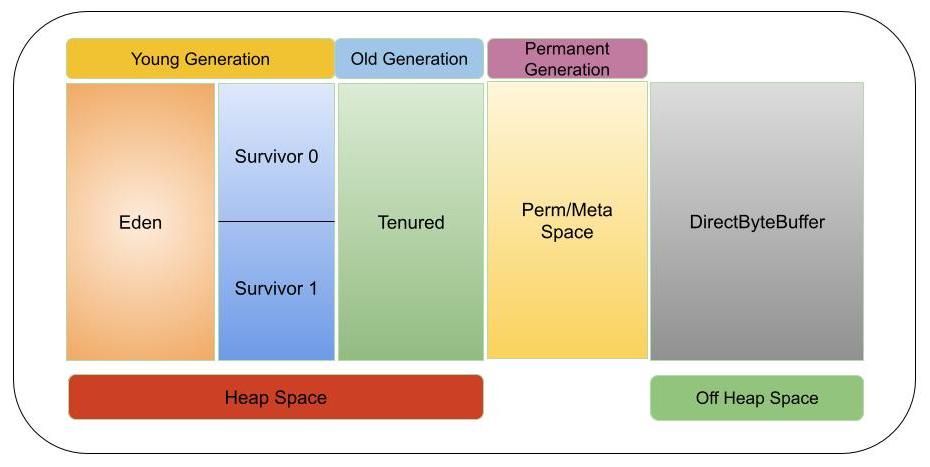 参考资源链接:[Net 内存溢出(System.OutOfMemoryException)的常见情况和处理方式总结](https://wenku.csdn.net/doc/6412b784be7fbd1778d4a95f?spm=1055.2635.3001.10343) # 1. Java内存模型
c 语言return用法
在C语言中,`return`关键字用于结束函数的执行并返回一个值给函数调用者(如果函数声明了返回类型)。它的基本语法如下: ```c return_type function_name(parameters) { // 函数体内的代码 if (条件) { return value; // 可选的,直接返回一个特定值 } else { // 可能的计算后返回 result = some_computation(); return result; } } ``` 当`return`被执行时,控制权会立即从当前函数转移