LRU缓存优化大法:提升缓存命中率的必备技巧
发布时间: 2024-08-25 21:52:02 阅读量: 41 订阅数: 30 


提高redis缓存命中率的方法
# 1. LRU缓存概述**
LRU(最近最少使用)缓存是一种广泛应用于计算机系统中的高速缓存机制,它通过跟踪记录每个缓存项最近被访问的时间,来实现对缓存项的淘汰和替换。LRU缓存的目的是提升缓存命中率,减少系统对底层存储(如硬盘)的访问次数,从而提高系统的整体性能。
LRU缓存的基本原理是:当缓存已满时,最近最少使用的缓存项将被淘汰,为新缓存项腾出空间。这种淘汰策略可以有效地将最频繁使用的缓存项保留在缓存中,从而提高缓存命中率。
# 2. LRU缓存的实现原理
LRU缓存的实现原理主要有两种:链表实现和哈希表实现。
### 2.1 链表实现
链表实现的LRU缓存使用双向链表来存储缓存项。每个缓存项包含一个键值对和两个指针,分别指向链表的前一个和后一个节点。
```python
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, value):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.head = Node(None, None)
self.tail = Node(None, None)
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
self.cache = {} # 键值对到节点的映射
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
self.remove_node(node)
self.add_node_to_head(node)
return node.value
else:
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
node.value = value
self.remove_node(node)
self.add_node_to_head(node)
else:
node = Node(key, value)
self.cache[key] = node
self.add_node_to_head(node)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
node = self.remove_node_from_tail()
del self.cache[node.key]
def remove_node(self, node):
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
def add_node_to_head(self, node):
node.next = self.head.next
node.next.prev = node
self.head.next = node
node.prev = self.head
def remove_node_from_tail(self):
node = self.tail.prev
self.remove_node(node)
return node
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `Node`类表示链表中的一个节点,包含键值对和前后指针。
* `LRUCache`类表示LRU缓存,包含容量、链表头尾节点、键值对到节点的映射。
* `get`方法从缓存中获取值,如果命中则更新节点位置。
* `put`方法将键值对添加到缓存中,如果命中则更新值并更新节点位置。
* `remove_node`方法从链表中移除一个节点。
* `add_node_to_head`方法将一个节点添加到链表头部。
* `remove_node_from_tail`方法从链表尾部移除一个节点。
### 2.2 哈希表实现
哈希表实现的LRU缓存使用哈希表来存储键值对,并使用双向链表来记录最近使用的顺序。
```python
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, value):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.head = Node(None, None)
self.tail = Node(None, None)
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
self.cache = {} # 键到节点的映射
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
self.remove_node(node)
self.add_node_to_head(node)
return node.value
else:
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
node.value = value
self.remove_node(node)
self.add_node_to_head(node)
else:
node = Node(key, value)
self.cache[key] = node
self.add_node_to_head(node)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
node = self.remove_node_from_tail()
del self.cache[node.key]
def remove_node(self, node):
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
def add_node_to_head(self, node):
node.next = self.head.next
node.next.prev = node
self.head.next = node
node.prev = self.head
def remove_node_from_tail(self):
node = self.tail.prev
self.remove_node(node)
return node
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `Node`类表示链表中的一个节点,包含键值对和前后指针。
* `LRUCache`类表示LRU缓存,包含容量、链表头尾节点、键到节点的映射。
* `get`方法从缓存中获取值,如果命中则更新节点位置。
* `put`方法将键值对添加到缓存中,如果命中则更新值并更新节点位置。
* `remove_node`方法从链表中移除一个节点。
* `add_node_to_head`方法将一个节点添加到链表头部。
* `remove_node_from_tail`方法从链表尾部移除一个节点。
# 3. LRU缓存的优化策略
### 3.1 淘汰策略
淘汰策略决定了当缓存已满时,应该淘汰哪个缓存项。常见的淘汰策略有:
**3.1.1 最近最少使用(LRU)**
LRU策略淘汰最近最少使用的缓存项。它通过维护一个双向链表,将缓存项按使用时间顺序排列。当需要淘汰缓存项时,链表头部的缓存项将被淘汰。
**代码块:**
```python
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = {}
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
return self.cache[key]
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
self.cache[key] = value
else:
self.add_to_head(key, value)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
self.remove_from_tail()
def update_usage(self, key):
node = self.cache[key]
self.remove_node(node)
self.add_to_head(key, node.value)
def add_to_head(self, key, value):
node = Node(key, value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
self.tail = node
else:
node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = node
self.head = node
def remove_from_tail(self):
if self.tail is not None:
node = self.tail
self.tail = node.prev
if self.tail is not None:
self.tail.next = None
else:
self.head = None
del self.cache[node.key]
**逻辑分析:**
* `__init__`方法初始化缓存,包括容量、缓存字典、链表头和尾。
* `get`方法获取缓存值,如果存在则更新使用时间并返回。
* `put`方法添加或更新缓存项,如果已存在则更新使用时间,否则添加到链表头部。如果缓存已满,则从链表尾部删除最少使用的缓存项。
* `update_usage`方法更新缓存项的使用时间。
* `add_to_head`方法将缓存项添加到链表头部。
* `remove_from_tail`方法从链表尾部删除最少使用的缓存项。
**3.1.2 最近最不经常使用(LFU)**
LFU策略淘汰最近最不经常使用的缓存项。它通过维护一个哈希表,记录每个缓存项的访问次数。当需要淘汰缓存项时,访问次数最少的缓存项将被淘汰。
**代码块:**
```python
class LFUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = {}
self.freq_map = {}
self.min_freq = 0
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
return self.cache[key]
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
self.cache[key] = value
else:
self.add_to_cache(key, value)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
self.remove_least_freq()
def update_usage(self, key):
node = self.cache[key]
freq = node.freq
self.freq_map[freq].remove(node)
node.freq += 1
if node.freq not in self.freq_map:
self.freq_map[node.freq] = []
self.freq_map[node.freq].append(node)
if freq == self.min_freq and not self.freq_map[freq]:
self.min_freq += 1
def add_to_cache(self, key, value):
node = Node(key, value, 1)
self.cache[key] = node
if 1 not in self.freq_map:
self.freq_map[1] = []
self.freq_map[1].append(node)
self.min_freq = 1
def remove_least_freq(self):
while not self.freq_map[self.min_freq]:
self.min_freq += 1
node = self.freq_map[self.min_freq].pop(0)
del self.cache[node.key]
**逻辑分析:**
* `__init__`方法初始化缓存,包括容量、缓存字典、频率哈希表和最小频率。
* `get`方法获取缓存值,如果存在则更新使用频率并返回。
* `put`方法添加或更新缓存项,如果已存在则更新使用频率,否则添加到缓存和频率哈希表。如果缓存已满,则从频率哈希表中删除最小频率的缓存项。
* `update_usage`方法更新缓存项的使用频率。
* `add_to_cache`方法将缓存项添加到缓存和频率哈希表。
* `remove_least_freq`方法从频率哈希表中删除最小频率的缓存项。
### 3.2 替换策略
替换策略决定了当需要淘汰缓存项时,应该替换哪个缓存项。常见的替换策略有:
**3.2.1 随机替换**
随机替换策略随机选择一个缓存项进行替换。它简单易于实现,但可能会导致性能不佳。
**代码块:**
```python
import random
class RandomCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = {}
def get(self, key):
return self.cache.get(key)
def put(self, key, value):
if len(self.cache) >= self.capacity:
key_to_remove = random.choice(list(self.cache.keys()))
del self.cache[key_to_remove]
self.cache[key] = value
**逻辑分析:**
* `__init__`方法初始化缓存,包括容量和缓存字典。
* `get`方法获取缓存值。
* `put`方法添加或更新缓存项,如果缓存已满,则随机选择一个缓存项进行替换。
**3.2.2 二次机会算法**
二次机会算法是一种改进的随机替换策略。它为每个缓存项维护一个引用位,表示该缓存项是否最近被访问过。当需要淘汰缓存项时,算法会选择一个引用位为0的缓存项进行替换。如果引用位为1,则将其重置为0并继续搜索。
**代码块:**
```python
class SecondChanceCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = {}
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
return self.cache[key]
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self.update_usage(key)
self.cache[key] = value
else:
self.add_to_head(key, value)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
self.remove_from_tail()
def update_usage(self, key):
node = self.cache[key]
node.ref_bit = 1
self.move_to_head(node)
def add_to_head(self, key, value):
node = Node(key, value, 1)
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
self.tail = node
else:
node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = node
self.head = node
def remove_from_tail(self):
while self.tail is not None and self.tail.ref_bit == 1:
self.tail.ref_bit = 0
self.tail = self.tail.prev
if self.tail is not None:
node = self.tail
self.tail = node.prev
if self.tail is not None:
self.tail.next = None
else:
self.head = None
# 4. LRU缓存的应用场景
### 4.1 内存管理
LRU缓存广泛应用于内存管理中,尤其是在虚拟内存系统中。当物理内存不足以容纳所有正在运行的进程时,操作系统会将不经常使用的内存页换出到硬盘上的页面文件中。当需要这些页面时,操作系统会使用LRU算法从页面文件中将它们换入物理内存。
**代码示例:**
```python
import collections
class LRU_Cache:
def __init__(self, max_size):
self.max_size = max_size
self.cache = collections.OrderedDict()
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
value = self.cache.pop(key)
self.cache[key] = value
return value
else:
return None
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self.cache.pop(key)
self.cache[key] = value
if len(self.cache) > self.max_size:
self.cache.popitem(last=False)
```
**逻辑分析:**
该代码实现了基于LRU算法的内存管理缓存。它使用一个有序字典来存储缓存项,其中键是内存页地址,值是内存页内容。当需要获取一个内存页时,`get`方法会先检查缓存中是否存在该页。如果存在,它会将该页移到字典的末尾,表示该页最近被使用过。如果不存在,它会返回`None`。当需要存储一个内存页时,`put`方法会先检查缓存中是否存在该页。如果存在,它会将其移到字典的末尾。如果不存在,它会将其添加到字典中,并删除最久未使用的内存页(即字典的第一个元素)。
### 4.2 数据库缓存
LRU缓存还广泛应用于数据库缓存中。数据库缓存将经常查询的数据存储在内存中,以减少对慢速磁盘访问的次数。当需要查询数据时,数据库会先检查缓存中是否存在该数据。如果存在,它会直接从缓存中返回数据。如果不存在,它会从磁盘中加载数据并将其添加到缓存中。
**代码示例:**
```python
import sqlite3
class Database_Cache:
def __init__(self, db_file):
self.db_file = db_file
self.cache = {}
def get(self, query):
if query in self.cache:
return self.cache[query]
else:
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_file)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
self.cache[query] = result
return result
def put(self, query, result):
self.cache[query] = result
```
**逻辑分析:**
该代码实现了基于LRU算法的数据库缓存。它使用一个字典来存储缓存项,其中键是查询语句,值是查询结果。当需要执行一个查询时,`get`方法会先检查缓存中是否存在该查询。如果存在,它会直接返回查询结果。如果不存在,它会连接到数据库,执行查询,并将其结果添加到缓存中。`put`方法用于将查询结果添加到缓存中。
### 4.3 Web缓存
LRU缓存还广泛应用于Web缓存中。Web缓存将经常访问的网页存储在内存中,以减少对远程服务器的访问次数。当用户访问一个网页时,Web缓存会先检查缓存中是否存在该网页。如果存在,它会直接从缓存中返回网页。如果不存在,它会从远程服务器获取网页并将其添加到缓存中。
**代码示例:**
```python
import requests
class Web_Cache:
def __init__(self, max_size):
self.max_size = max_size
self.cache = collections.OrderedDict()
def get(self, url):
if url in self.cache:
return self.cache[url]
else:
response = requests.get(url)
self.cache[url] = response.content
if len(self.cache) > self.max_size:
self.cache.popitem(last=False)
return response.content
def put(self, url, content):
if url in self.cache:
self.cache.pop(url)
self.cache[url] = content
if len(self.cache) > self.max_size:
self.cache.popitem(last=False)
```
**逻辑分析:**
该代码实现了基于LRU算法的Web缓存。它使用一个有序字典来存储缓存项,其中键是网页URL,值是网页内容。当需要获取一个网页时,`get`方法会先检查缓存中是否存在该网页。如果存在,它会直接返回网页内容。如果不存在,它会从远程服务器获取网页并将其添加到缓存中。`put`方法用于将网页内容添加到缓存中。
# 5.1 缓存大小优化
缓存大小是影响LRU缓存性能的关键因素之一。缓存过小会导致频繁的缓存失效,而缓存过大会浪费内存资源。因此,需要根据实际应用场景和数据访问模式对缓存大小进行优化。
**5.1.1 基于经验值估算**
一种简单的缓存大小优化方法是基于经验值估算。对于大多数应用场景,缓存大小可以设置为数据访问量的10%~20%。例如,如果数据访问量为100万,则缓存大小可以设置为10万~20万。
**5.1.2 基于命中率动态调整**
更精确的缓存大小优化方法是基于命中率动态调整。通过监控缓存的命中率,可以动态调整缓存大小以达到最佳性能。如果命中率过低,则说明缓存大小过小,需要增加缓存大小;如果命中率过高,则说明缓存大小过大,可以减少缓存大小。
**5.1.3 分级缓存**
对于数据访问模式复杂或数据量非常大的场景,可以采用分级缓存策略。分级缓存将数据分为多个层级,每一层级都有不同的缓存大小和命中率要求。例如,可以将经常访问的数据放在第一层级缓存中,命中率要求较高;将不经常访问的数据放在第二层级缓存中,命中率要求较低。
## 5.2 并发控制
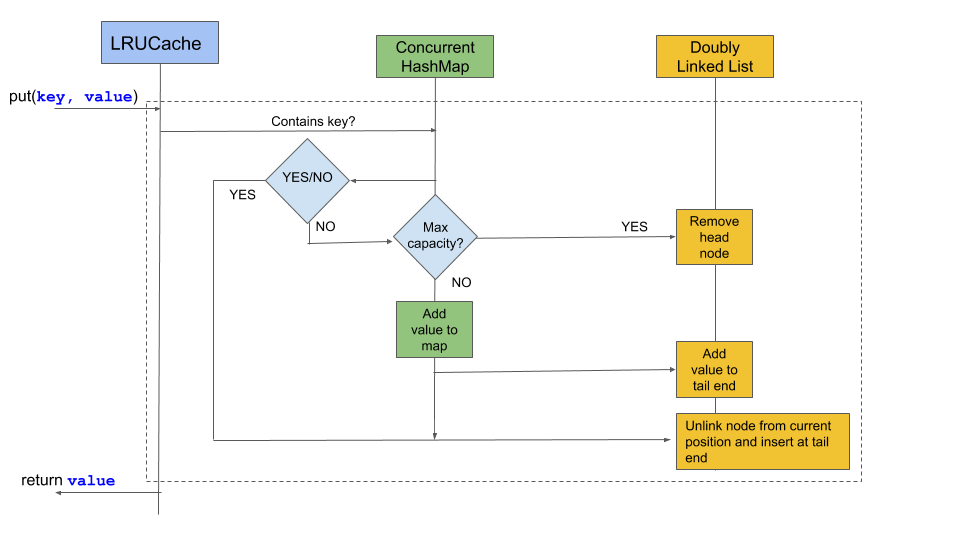
在多线程并发访问LRU缓存时,需要考虑并发控制问题。如果不进行并发控制,可能会导致缓存数据不一致或死锁。
**5.2.1 锁机制**
最简单有效的并发控制方法是使用锁机制。当一个线程访问缓存时,需要先获取锁,访问完成后再释放锁。这样可以保证同一时刻只有一个线程访问缓存,避免数据不一致。
**5.2.2 无锁数据结构**
对于高并发场景,锁机制可能会成为性能瓶颈。可以使用无锁数据结构来实现并发控制,例如无锁队列、无锁链表等。无锁数据结构通过使用原子操作和CAS(Compare and Swap)等技术,可以保证并发访问的安全性。
## 5.3 监控和维护
LRU缓存在运行过程中需要进行监控和维护,以保证其稳定性和性能。
**5.3.1 监控指标**
需要监控的指标包括缓存命中率、缓存大小、缓存淘汰次数等。通过监控这些指标,可以及时发现缓存性能问题并进行调整。
**5.3.2 定期维护**
定期维护包括清除过期数据、重建缓存等操作。过期数据会占用缓存空间,影响缓存性能。重建缓存可以解决缓存碎片化问题,提高缓存命中率。
0
0





