【链式存储揭秘】:深入剖析其原理和应用


栈的链式存储:链栈的C语言实现
1. 链式存储概述**
链式存储是一种数据存储结构,其中数据元素以链表的形式组织。链表是一种非连续的线性数据结构,其中每个元素(称为节点)包含数据值和指向下一个元素的指针。
链式存储与数组等其他数据结构不同,它允许动态分配和回收内存,从而提高了内存利用率。此外,链式存储可以轻松插入和删除元素,而无需移动其他元素,这使得它非常适合于频繁更新的数据集。
2. 链式存储原理
2.1 单链表
2.1.1 节点结构
单链表是一种线性数据结构,由一组节点组成,每个节点包含两个字段:数据域和指针域。数据域存储数据元素,指针域指向下一个节点。
- struct Node {
- int data;
- Node* next;
- };
2.1.2 插入和删除操作
插入操作
在单链表中插入一个新节点,需要找到要插入节点的前一个节点,然后将新节点的指针域指向要插入节点的后一个节点,再将前一个节点的指针域指向新节点。
- void insert(Node* head, int data) {
- Node* new_node = new Node{data, nullptr};
- if (head == nullptr) {
- head = new_node;
- } else {
- Node* curr = head;
- while (curr->next != nullptr) {
- curr = curr->next;
- }
- curr->next = new_node;
- }
- }
删除操作
删除单链表中的一个节点,需要找到要删除节点的前一个节点,然后将前一个节点的指针域指向要删除节点的后一个节点。
- void delete(Node* head, int data) {
- if (head == nullptr) {
- return;
- }
- if (head->data == data) {
- head = head->next;
- } else {
- Node* curr = head;
- while (curr->next != nullptr && curr->next->data != data) {
- curr = curr->next;
- }
- if (curr->next != nullptr) {
- curr->next = curr->next->next;
- }
- }
- }
2.2 双链表
2.2.1 节点结构
双链表是一种线性数据结构,由一组节点组成,每个节点包含三个字段:数据域、前驱指针域和后继指针域。数据域存储数据元素,前驱指针域指向前一个节点,后继指针域指向后一个节点。
- struct Node {
- int data;
- Node* prev;
- Node* next;
- };
2.2.2 插入和删除操作
插入操作
在双链表中插入一个新节点,需要找到要插入节点的前一个节点和后一个节点,然后将新节点的前驱指针域指向前一个节点,后继指针域指向后一个节点,再将前一个节点的后继指针域和后一个节点的前驱指针域指向新节点。
- void insert(Node* head, int data) {
- Node* new_node = new Node{data, nullptr, nullptr};
- if (head == nullptr) {
- head = new_node;
- } else {
- Node* curr = head;
- while (curr->next != nullptr) {
- curr = curr->next;
- }
- curr->next = new_node;
- new_node->prev = curr;
- }
- }
删除操作
删除双链表中的一个节点,需要找到要删除节点的前一个节点和后一个节点,然后将前一个节点的后继指针域指向要删除节点的后一个节点,后一个节点的前驱指针域指向要删除节点的前一个节点。
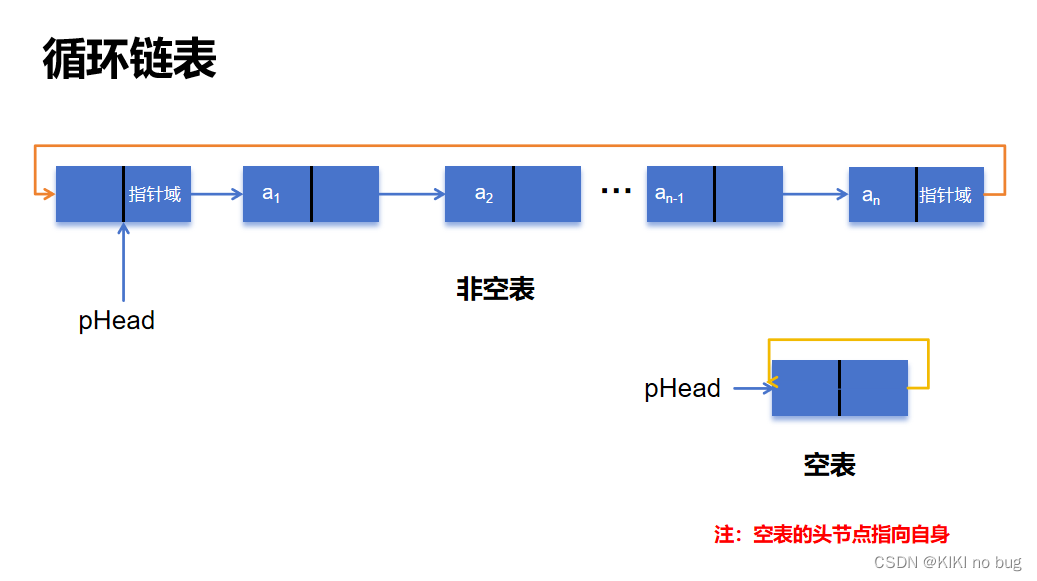
2.3 循环链表
2.3.1 节点结构
循环链表是一种线性数据结构,由一组节点组成,每个节点包含两个字段:数据域和指针域。数据域存储数据元素,指针域指向下一个节点,最后一个节点的指针域指向第一个节点,形成一个环形结构。
- struct Node {
- int data;
- Node* next;
- };
2.3.2 插入和删除操作
插入操作
在循环链表中插入一个新节点,需要找到要插入节点的后一个节点,然后将新节点的指针域指向要插入节点的后一个节点,再将要插入节点的后一个节点的指针域指向新节点。
- void insert(Node* head, int data) {
- Node* new_node = new Node{data, nullptr};
- if (head == nullptr) {
- head = new_node;
- new_node->next = new_node;
- } else {
- Node* curr = head;
- while (curr->next != head) {
- curr = curr->next;
- }
- curr->next = new_node;
- new_node->next = head;
- }
- }
删除操作
删除循环链表中的一个节点,需要找到要删除节点的前一个节点和后一个节点,然后将前一个节点的指针域指向要删除节点的后一个节点,后一个节点的前驱指针域指向要删除节点的前一个节点。
3. 链式存储应用
3.1 栈
3.1.1 栈的定义和特点
栈是一种遵循后进先出(LIFO)原则的数据结构。它允许在数据结构的一端插入和删除元素,称为栈顶。栈的典型操作包括:
- push(): 将元素压入栈顶
- pop(): 从栈顶弹出元素
- peek(): 查看栈顶元素而不将其弹出
3.1.2 栈的实现
栈可以用链表来实现。链表中的每个节点包含一个数据元素和指向下一个节点的指针。
3.2 队列
3.2.1 队列的定义和特点
队列是一种遵循先进先出(FIFO)原则的数据结构。它允许在数据结构的一端插入元素,称为队尾,并在另一端删除元素,称为队头。队列的典型操作包括:
- enqueue(): 将元素入队到队尾
- dequeue(): 从队头出队元素
- peek(): 查看队头元素而不将其出队
3.2.2 队列的实现
队列可以用链表来实现。链表中的每个节点包含一个数据元素和指向下一个节点的指针。
3.3 哈希表
3.3.1 哈希表的定义和特点
哈希表是一种使用哈希函数将键映射到值的集合。它允许快速查找、插入和删除数据。哈希函数将键转换为一个哈希值,该哈希值用于确定数据在哈希表中的位置。
3.3.2 哈希表的实现
哈希表可以用链表来实现。链表中的每个节点包含一个键值对,其中键是哈希值,值是数据。
4.1 内存管理
内存管理是链式存储优化中的关键环节,它直接影响着程序的运行效率和稳定性。链式存储中常见的内存管理策略包括内存分配策略和内存回收策略。
4.1.1 内存分配策略
内存分配策略决定了程序如何从系统中获取内存空间。常见的内存分配策略有:
- 连续分配: 将连续的一块内存空间分配给程序使用。优点是访问速度快,缺点是容易产生内存碎片。
- 非连续分配: 将不连续的内存空间分配给程序使用。优点是减少内存碎片,缺点是访问速度较慢。
- 伙伴分配: 将内存空间划分为大小相等的伙伴块,并根据程序的需要分配伙伴块。优点是减少内存碎片,缺点是分配和回收内存的开销较大。
4.1.2 内存回收策略
内存回收策略决定了程序如何释放不再使用的内存空间。常见的内存回收策略有:
- 引用计数: 为每个内存块维护一个引用计数,当引用计数为 0 时,释放该内存块。优点是简单易用,缺点是容易产生循环引用。
- 标记清除: 将所有可达的内存块标记为已使用,然后扫描内存空间并释放未标记的内存块。优点是效率较高,缺点是容易产生内存碎片。
- 分代收集: 将内存空间划分为不同的代,根据不同代的存活时间采用不同的回收策略。优点是减少内存碎片,缺点是实现复杂。
4.2 性能优化
链式存储的性能优化涉及到数据结构的选择和算法的优化。
4.2.1 数据结构的选择
选择合适的链式存储数据结构对于提高性能至关重要。常见的链式存储数据结构有:
- 单链表: 每个节点只指向下一个节点。优点是插入和删除操作简单高效,缺点是查找操作需要遍历整个链表。
- 双链表: 每个节点同时指向下一个节点和前一个节点。优点是查找操作可以从任意方向进行,缺点是插入和删除操作需要维护两个指针。
- 循环链表: 将链表的最后一个节点指向第一个节点,形成一个环。优点是查找操作可以从任意方向进行,缺点是插入和删除操作需要维护环形结构。
4.2.2 算法的优化
除了选择合适的链式存储数据结构外,算法的优化也可以提高链式存储的性能。常见的算法优化技术有:
- 尾插法: 将新节点插入到链表的尾部,减少了链表的遍历次数。
- 哨兵节点: 在链表的头部或尾部添加一个哨兵节点,简化了插入和删除操作。
- 哈希表: 通过哈希函数将元素映射到哈希表中,提高查找效率。
5. 链式存储与其他数据结构
5.1 数组
5.1.1 数组与链表的比较
| 特征 | 数组 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据存储方式 | 连续内存空间 | 非连续内存空间 |
| 插入和删除 | 效率低,需要移动数据 | 效率高,只需要修改指针 |
| 随机访问 | 效率高 | 效率低 |
| 内存占用 | 固定大小,浪费空间 | 动态分配,节省空间 |
5.1.2 数组与链表的应用场景
- **数组适用场景:**数据量小、需要频繁随机访问的场景,例如存储固定长度的字符串或数字数组。
- **链表适用场景:**数据量大、需要频繁插入和删除的场景,例如存储动态变化的列表或队列。
5.2 树
5.2.1 树与链表的比较
| 特征 | 树 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据组织方式 | 层次结构 | 线性结构 |
| 插入和删除 | 效率中等,需要搜索和更新指针 | 效率高,只需要修改指针 |
| 随机访问 | 效率低,需要遍历树 | 效率低,需要遍历链表 |
| 内存占用 | 动态分配,节省空间 | 动态分配,节省空间 |
5.2.2 树与链表的应用场景
- **树适用场景:**数据量大、需要高效搜索和排序的场景,例如存储文件系统或数据库索引。
- **链表适用场景:**数据量大、需要频繁插入和删除的场景,例如存储动态变化的列表或队列。
代码示例
6.1 区块链
6.1.1 区块链的原理
区块链是一种分布式账本技术,它将交易记录在称为区块的数据结构中。每个区块包含一组交易、前一个区块的哈希值以及时间戳。区块通过密码学技术链接在一起,形成一个不可篡改的链条。
6.1.2 区块链的应用
区块链技术在金融、供应链管理、医疗保健和政府等领域具有广泛的应用:
- **金融:**加密货币、数字资产交易、跨境支付
- **供应链管理:**商品追踪、防伪、供应链优化
- **医疗保健:**医疗记录管理、药物追踪、基因组数据共享
- **政府:**投票系统、土地登记、身份认证
代码示例:
- # 创建一个区块链节点
- node = BlockchainNode()
- # 添加一个交易到区块链
- node.add_transaction(transaction)
- # 挖掘一个新区块
- node.mine_block()
逻辑分析:
该代码示例演示了区块链节点如何添加交易并挖掘新区块。add_transaction() 方法将交易添加到交易池中,而 mine_block() 方法验证交易并将其添加到区块链中。


















