非监督学习的评估方法:评估聚类算法的性能
发布时间: 2024-09-02 10:26:06 阅读量: 33 订阅数: 51 


聚类算法性能评估指标:轮廓系数与SSE解析.md
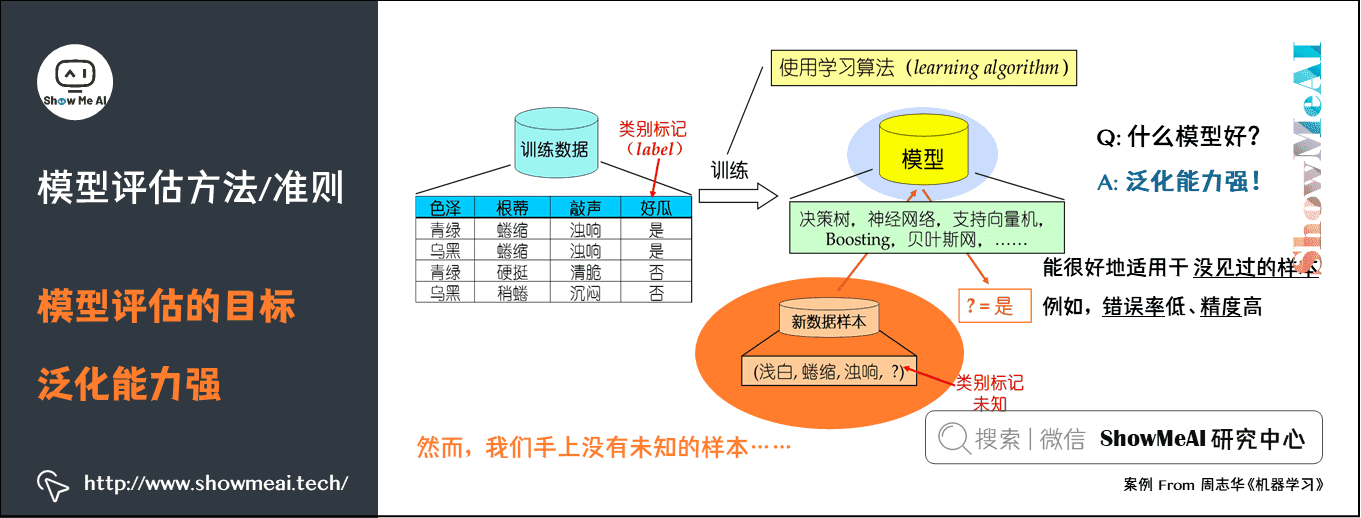
# 1. 非监督学习与聚类算法简介
聚类分析是数据挖掘和机器学习领域中一种重要的非监督学习方法,旨在将数据集中的样本根据其相似性分组成多个类别。非监督学习与监督学习不同,它不需要预先标记的训练数据来指导学习过程。聚类算法为处理大量未标记数据提供了解决方案,广泛应用于客户细分、市场分析、社交网络分析、生物信息学等多个领域。
聚类算法的基本思想是将样本点归入彼此间相似度高而与其他类中样本点相似度低的类别。算法根据不同的距离度量标准,如欧几里得距离、曼哈顿距离或余弦相似性,将样本点分组。聚类方法可以分为层次聚类、基于划分的聚类、基于密度的聚类、基于网格的聚类等。
由于聚类是一个无指导的过程,因此没有统一的"正确答案"。不同的聚类算法可能会产生不同的结果,而且如何评价聚类结果的有效性一直是一个挑战。因此,深入了解和掌握聚类算法的评估方法对于优化聚类模型,提高聚类结果的准确性和可靠性至关重要。
# 2. 聚类算法的性能评估理论
在探索聚类算法的世界中,我们不可避免地需要一些工具来衡量我们的工作。这就是为什么性能评估在聚类算法的发展中扮演着不可或缺的角色。本章将深入探讨聚类算法性能评估的理论,分析如何评价聚类结果的好坏以及如何判断聚类算法的稳定性。
## 2.1 聚类算法的性能评估指标
当我们谈到性能评估,不可避免地要从评估指标说起。聚类算法的性能评估指标大致可以分为三类:内部指标、外部指标和相对指标。这三类指标从不同的角度提供了评估聚类结果的手段。
### 2.1.1 内部指标:轮廓系数与Davies-Bouldin指数
内部指标是指只用到数据本身的信息来评估聚类结果的质量。在这里,我们将详细讨论两个常用的内部指标:轮廓系数和Davies-Bouldin指数。
#### 轮廓系数
轮廓系数(Silhouette Coefficient)是评估聚类结果好坏的一个指标,它的取值范围在-1到1之间。轮廓系数接近1表示聚类效果很好,接近-1则表示聚类效果很差。轮廓系数的计算公式为:
\[ s = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{b(i) - a(i)}{\max \{a(i), b(i)\}} \]
这里,\( a(i) \)是样本\( i \)到同簇中其他样本的平均距离,而\( b(i) \)是样本\( i \)到最近簇中所有样本的平均距离。轮廓系数考虑了簇的紧凑度和分离度。
```python
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
# 假设 data 是我们用来聚类的数据集
# 使用 KMeans 进行聚类
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=3, random_state=42)
clusters = kmeans.fit_predict(data)
# 计算轮廓系数
silhouette_avg = silhouette_score(data, clusters)
print(f"The average silhouette_score is : {silhouette_avg}")
```
#### Davies-Bouldin指数
Davies-Bouldin指数(Davies-Bouldin Index)是另一种广泛使用的内部指标,它基于类间的离散度和类内的紧凑度的比值。该指数的值越小表示聚类结果越好。其计算方式为:
\[ DB = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \max_{j \neq i} \left( \frac{\sigma_i + \sigma_j}{d(c_i, c_j)} \right) \]
其中,\( \sigma_i \) 是簇\( i \)的样本到簇中心的平均距离,\( d(c_i, c_j) \)是两个簇中心之间的距离。
接下来,我们通过一个例子来展示如何在Python中使用Davies-Bouldin指数:
```python
from sklearn.metrics import davies_bouldin_score
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
# 假设 data 是我们用来聚类的数据集
# 使用 KMeans 进行聚类
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=3, random_state=42)
kmeans.fit(data)
# 计算Davies-Bouldin指数
db_index = davies_bouldin_score(data, kmeans.labels_)
print(f"The Davies-Bouldin index is : {db_index}")
```
### 2.1.2 外部指标:Rand指数与Jaccard系数
与内部指标不同,外部指标需要一个参考标签(通常是真实的分类标签)来评估聚类结果。在本小节,我们将探讨两种常用的外部指标:Rand指数和Jaccard系数。
#### Rand指数
Rand指数(Rand Index)是衡量聚类结果与参考标签相似度的指标。它的计算公式如下:
\[ RI = \frac{a+b}{a+b+c+d} \]
其中,\( a \) 是两个样本在同一簇中的次数,\( b \) 是两个样本在不同簇中的次数,\( c \) 是两个样本在同一簇但不在同一参考簇中的次数,\( d \) 是两个样本在不同簇且不在同一参考簇中的次数。
接下来我们给出如何在Python中实现Rand指数的示例:
```python
from sklearn.metrics import rand_score
# 假设 true_labels 是真实的分类标签,clusters 是我们的聚类结果
# rand_score 是用来计算Rand指数的函数
rand_index = rand_score(true_labels, clusters)
print(f"The Rand index is : {rand_index}")
```
#### Jaccard系数
Jaccard系数是另一个衡量聚类结果与参考标签相似度的指标,它在聚类问题中尤其有用,因为它主要关注簇之间的交集。其计算公式为:
\[ J = \frac{|X \cap Y|}{|X \cup Y|} \]
其中,\( X \) 和 \( Y \) 分别是聚类结果和参考标签中的簇。
下面是用Python来实现Jaccard系数的代码示例:
```python
from sklearn.metrics import jaccard_similarity_score
# 假设 clusters 是聚类结果,true_labels 是真实的分类标签
# jaccard_similarity_score 用来计算Jaccard系数
jaccard_score = jaccard_similarity_score(true_labels, clusters)
print(f"The Jaccard similarity score is : {jaccard_score}")
```
### 2.1.3 相对指标:调整兰德系数与Dice系数
相对指标是介于内部指标和外部指标之间的一种评估方式。它们试图综合参考标签的信息和聚类算法的性质。本小节中,我们将分析调整兰德系数和Dice系数。
#### 调整兰德系数
调整兰德系数(Adjusted Rand Index, ARI)是Rand指数的一个调整版,通过减少随机选择聚类结果时的期望相似度来提供一个校正的相似度度量。其计算方式为:
\[ ARI = \frac{RI - E[RI]}{\max(RI) - E[RI]} \]
其中,\( RI \)是 Rand指数,\( E[RI] \)是随机分配标签时的期望 Rand指数。
下面是使用Python实现ARI的代码示例:
```python
from sklearn.metrics import adjusted_rand_score
# 假设 true_labels 是真实的分类标签,clusters 是我们的聚类结果
# adjusted_rand_score 是用来计算ARI的函数
adjusted_rand = adjusted_rand_score(true_labels, clusters)
print(f"The Adjusted Rand index is : {adjusted_rand}")
```
#### Dice系数
Dice系数(Dice Coefficient)是一个集合相似度度量函数,常用于衡量两个样本集的相似性。其计算公式为:
\[ D = \frac{2|X \cap Y|}{|X| + |Y|} \]
在聚类评估中,Dice系数可以帮助我们了解两个聚类簇的相似度。
下面是用Python来实现Dice系数的代码示例:
```python
from sklearn.metrics import fowlkes_mallows_score
# 假设 clusters 是聚类结果,true_labels 是真实的分类标签
# fowlkes_mallows_score 可以用来计算Dice系数
dice_score = fowlkes_mallows_score(true_labels, clusters)
print(f"The Dice similarity score is : {dice_score}")
```
## 2.2 聚类算法的稳定性评估
在进行聚类分析时,稳定性是指当输入数据发生小的扰动时,聚类结果是否保持一致。稳定性是评估聚类算法性能的一个重要方面。
### 2.2.1 稳定性的概念与重要性
稳定性(stability)是衡量聚类算法在面对不同数据集时,聚类结果一致性
0
0





