Android算法基础入门:实例解析与实战应用
发布时间: 2024-09-10 02:53:28 阅读量: 216 订阅数: 79 


软件工程与算法全攻略:从基础概念到实战项目的全面解析
# 1. Android算法概述
Android系统的底层是建立在Linux内核之上的,其应用层的开发涉及大量的编程语言和框架。算法作为计算机科学的核心,不仅在后端服务中扮演着重要角色,同样在移动应用中也起着至关重要的作用。在Android开发中,算法优化可以体现在UI渲染、数据处理、系统资源管理等多个方面。掌握并优化算法应用,对于提升应用性能、改善用户体验都有着决定性的影响。本章将简要介绍算法在Android中的重要性以及基本概念。
# 2. 算法基础理论
## 2.1 数据结构基础
数据结构是存储、组织数据的方式,它是算法运行的基础。在Android开发中,合理地选择和使用数据结构可以极大地提升应用性能。
### 2.1.1 数组、链表与队列
数组是一种简单的线性数据结构,它在内存中是一块连续的空间。每个元素可以通过下标直接访问,具有常数时间复杂度的查找速度。但其插入和删除元素操作的时间复杂度较高,尤其是当涉及到元素的移动时。数组的缺点是其大小不可变,一旦创建,大小就固定了。
```java
// 示例代码:数组的基本操作
int[] numbers = new int[5]; // 创建一个初始大小为5的数组
numbers[0] = 1; // 数组元素赋值
int firstElement = numbers[0]; // 通过下标访问数组元素
```
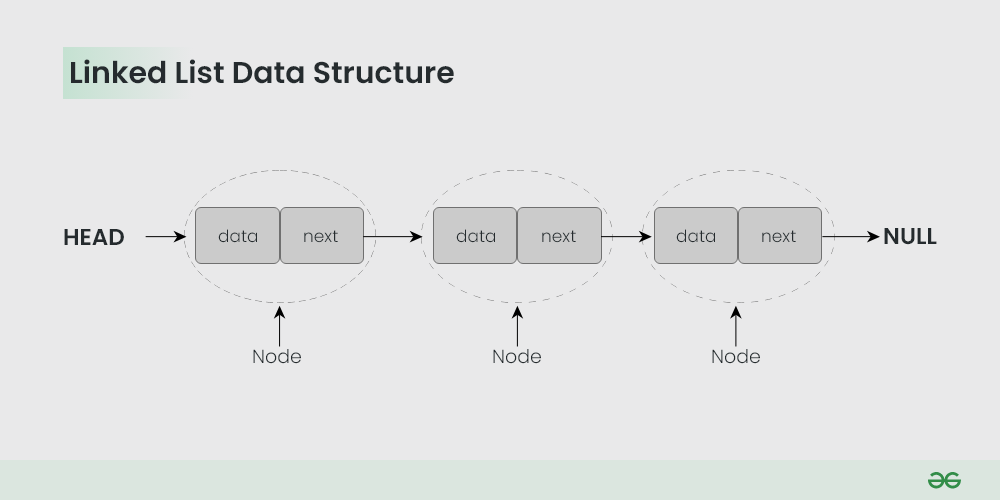
链表是一种包含多个节点的数据结构,每个节点都包含数据部分和指向下一个节点的链接。链表插入和删除操作的时间复杂度较低,因为它不需要像数组那样移动元素。但是,访问特定位置的元素时,链表需要从头开始遍历,时间复杂度为线性。
```java
// 示例代码:链表的节点定义和链表操作
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(1); // 创建一个头节点
head.next = new ListNode(2); // 连接新节点
// 通过头节点遍历链表
```
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,它有两个基本操作:入队(enqueue)和出队(dequeue)。队列广泛用于任务调度和消息传递等场景。在Android中,消息队列管理着应用的UI事件,保证了用户界面的响应性。
```java
// 示例代码:队列的基本操作
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 使用LinkedList实现队列
queue.offer(1); // 入队操作
Integer first = queue.poll(); // 出队操作,返回并移除队列头部的元素
```
### 2.1.2 栈的操作和应用
栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,它的主要操作包括压栈(push)和出栈(pop)。栈在很多算法中扮演了重要的角色,例如函数调用的追踪和解析表达式等。
```java
// 示例代码:栈的基本操作
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // 使用Stack类实现栈
stack.push(1); // 压栈操作
Integer top = stack.peek(); // 查看栈顶元素但不移除
Integer popped = stack.pop(); // 出栈操作,移除并返回栈顶元素
```
### 2.1.3 树结构及其遍历
树是一种分层的数据结构,可以用来表示具有层次关系的数据。树通常由节点构成,每个节点都可能有一个或多个子节点。在Android中,视图结构是一种特殊的树状结构,用来管理应用的用户界面布局。
树的遍历通常分为深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS)。深度优先遍历会沿着一条路径走到底,然后回溯到上一个分叉点继续进行,常见的有递归方式和栈方式。广度优先遍历则逐层从上至下访问每个节点,通常使用队列来实现。
```java
// 示例代码:二叉树的创建和遍历
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
// 二叉树的前序遍历(递归方式)
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
System.out.print(root.val + " "); // 访问根节点
preorderTraversal(root.left); // 遍历左子树
preorderTraversal(root.right); // 遍历右子树
}
// 二叉树的层序遍历(队列方式)
void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.val + " "); // 访问节点
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left); // 入队左子节点
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right); // 入队右子节点
}
}
```
在以上示例中,我们展示了如何定义树节点、如何通过递归方式和队列方式实现二叉树的遍历。不同的遍历方法在算法中有不同的应用场景,例如前序遍历适合于深度优先搜索,而层序遍历适合于找到树的最短路径。
## 2.2 排序和搜索算法
排序和搜索是算法中最基本的操作,它们在数据处理中占据着核心地位。在Android开发中,排序用于对数据集合进行排序,而搜索用于在集合中快速找到特定数据。
### 2.2.1 常见排序算法
排序算法负责将一组数据按照一定的顺序进行排列。根据算法的效率和适用场景的不同,有多种排序算法可供选择。常用的排序算法包括冒泡排序、选择排序、插入排序、快速排序、归并排序和堆排序等。
```java
// 示例代码:快速排序的一个快速实现
void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high); // 选取基准元素并进行划分
quickSort(arr, low, pivot - 1); // 对左分区进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, pivot + 1, high); // 对右分区进行快速排序
}
}
// 快速排序中的划分过程
int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
swap(arr, i, j); // 交换元素
}
}
swap(arr, i + 1, high); // 将基准元素放到正确的位置
return i + 1;
}
void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
```
快速排序是一种非常高效的排序算法,其平均时间复杂度为O(n log n)。它通过分而治之的策略,把大数据集分割成小数据集来实现排序。快速排序适合处理大量数据,但其最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(n^2),因此在实际应用中需要考虑避免这种情况,比如通过随机选取基准元素来优化。
### 2.2.2 搜索算法的原理和应用
搜索算法负责从一组数据中找到特定元素的位置。最简单的搜索方法是线性搜索,它对集合中的每个元素进行逐一比较,直到找到目标元素。当数据集合是有序的时候,我们可以使用二分搜索来提高搜索效率。
```java
// 示例代码:二分搜索的一个简单实现
int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2; // 防止溢出
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid; // 找到目标元素,返回位置
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1; // 在右半部分查找
} else {
high = mid - 1; // 在左半部分查找
}
}
return -1; // 未找到目标元素
}
```
二分搜索算法的时间复杂度为O(log n),相比线性搜索在处理大数据集时有明显的优势。但在使用二分搜索之前,数据集必须是有序的,否则需要先进行排序。排序和搜索算法是数据处理和优化的基础,在Android开发中,它们是提高应用性能的重要手段。
## 2.3 复杂度分析
复杂度分析是对算法性能的评估,它关注算法运行时的资源消耗,主要包括时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
### 2.3.1 时间复杂度和空间复杂度
时间复杂度用来衡量算法的运行时间随着输入数据量的增
0
0





