没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
首页LCL型并网逆变器的实时双采样控制器设计与性能提升
LCL型并网逆变器的实时双采样控制器设计与性能提升
需积分: 10 10 下载量 93 浏览量
更新于2024-07-21
收藏 1.64MB PDF 举报
本文是一篇由华中科技大学研究人员撰写的关于LCL型并网逆变器控制技术的论文,发表在2014年IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics(电力电子交易会)第29卷第3期。LCL型并网逆变器因其在电网连接中的广泛应用而备受关注,其性能优化的关键在于注入电网电流控制器和LCL滤波器的活性衰减。 论文的核心内容集中在设计一种基于双重采样模式的实时计算方法,旨在改进LCL型并网逆变器的电流控制性能。LCL滤波器在逆变器系统中起着至关重要的作用,它在保证注入电网电流的质量的同时,能够有效地抑制由于滤波器固有特性引起的共振峰,从而简化系统的稳定控制。 作者提出的方法结合了常用的PI(比例积分)控制器和PR(比例共振)补偿器,以及利用电容电流反馈实现的活性衰减技术。这种融合策略旨在提高控制精度和效率,同时保持设计的简单性,使得系统在面对复杂电网条件时仍能表现出良好的动态响应。 在设计过程中,作者特别强调了电流控制器与活性衰减之间的协调作用。他们通过细致地处理两者之间的相互影响,确保了逆变器能够稳定、高效地工作,满足现代电力系统对电能质量的要求。此外,文章可能还探讨了实际应用中的挑战、仿真验证结果以及与其他控制策略的比较分析。 这篇论文为LCL型并网逆变器的设计提供了一种实用且高效的控制策略,有助于提升电力电子设备在分布式发电、可再生能源接入等领域的性能,是电力工程领域的重要研究成果。对于从事逆变器控制、电力系统集成或电力电子设计的工程师来说,这篇论文提供了有价值的技术参考和理论支持。
资源详情
资源推荐
BAO et al.: STEP-BY-STEP CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR LCL-TYPE GRID-CONNECTED INVERTER 1241
is adopted to damp the resonance peak caused by the LCL fil-
ter, and H
i1
is the feedback coefficient. Unipolar sinusoidal
pulsewidth modulation (SPWM) is used for the grid-connected
inverter. An outer-loop power control is usually introduced to
automatically adjust the current reference amplitude I
∗
.Thisis
beyond the scope of this paper and will not be discussed, and
the current reference amplitude I
∗
is directly given here.
The resonance frequency of the LCL filter f
r
is derived as
f
r
=
1
2π
L
1
+ L
2
L
1
L
2
C
. (1)
Fig. 1(b) shows the ASM of the LCL-type grid-connected in-
verter, where G
inv
is the transfer function of the inverter bridge.
The switching frequency of VSI is assumed to be sufficiently
high, thus G
inv
can be approximated as V
in
/V
tri
, where V
in
is
the dc-link voltage and V
tri
is the amplitude of the triangle car-
rier wave. According to Mason’s gain formula [32], the injected
grid current i
g
can be derived as
i
g
(s)=
1
H
i2
T (s)
1+T (s)
i
ref
(s) −
G
g
(s)
1+T (s)
v
g
(s)
Δ
= i
g1
(s)+i
g2
(s) (2)
where T (s) is the loop gain of the system and is expressed as
T (s)=
H
i2
G
inv
G
i
(s)
s
3
L
1
L
2
C + s
2
L
2
CH
i1
G
inv
+ s (L
1
+ L
2
)
(3)
and G
g
(s) is expressed as
G
g
(s)=
s
2
L
1
C + sCG
inv
H
i1
+1
s
3
L
1
L
2
C + s
2
L
2
CH
i1
G
inv
+ s (L
1
+ L
2
)
. (4)
i
g1
is related to the injected grid current reference i
ref
and i
g2
is related to the grid voltage v
g
. i
g1
and i
g2
are expressed as
i
g1
(s)=
1
H
i2
T (s)
1+T (s)
i
ref
(s) (5)
i
g2
(s)=−
G
g
(s)
1+T (s)
v
g
(s) . (6)
III. F
REQUENCY RESPONSES OF THE CURRENT REGULATOR
AND
CAPACITOR–CURRENT-FEEDBACK ACTIVE-DAMPING
According to (3), the bode diagram of the uncompensated
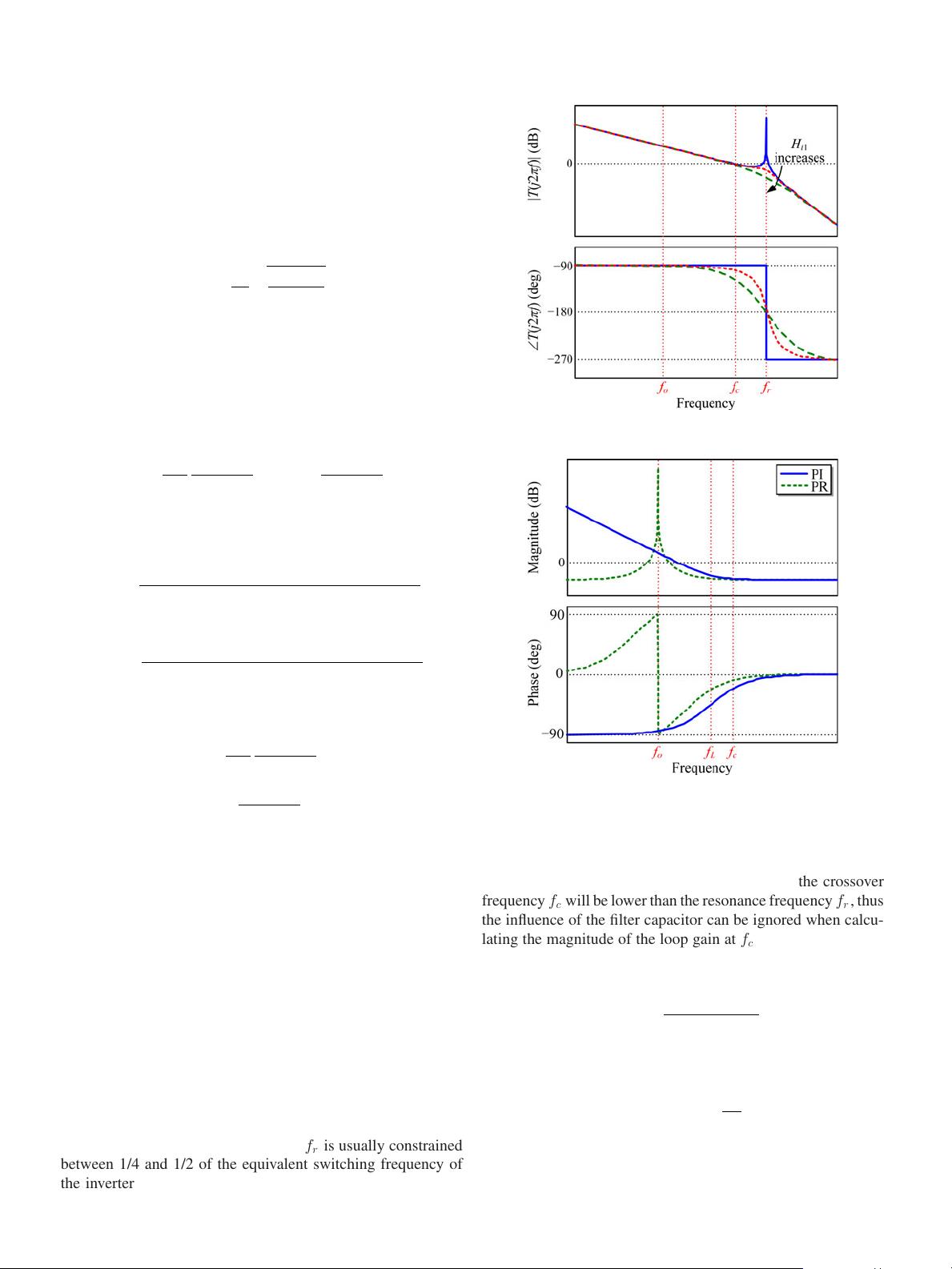
loop gain is depicted in Fig. 2. As seen, introducing the feedback
of the filter capacitor current can effectively damp the resonance
peak, and it only affects the magnitude of the loop gain at
the neighbor of the resonance frequency. However, this active-
damping method has significant impact on the phase of the
loop gain and the phase decreases at the frequencies lower than
the resonance frequency. A larger capacitor–current feedback
coefficient leads to better damping of the resonance peak, but
results in a larger negative phase shift.
The crossover frequency f
c
is typically restricted lower than
f
s
considering the effect of attenuating high-frequency noise,
where f
s
is the switching frequency of the inverter [9], and the
resonance frequency of the LCL filter f
r
is usually constrained
between 1/4 and 1/2 of the equivalent switching frequency of
the inverter (when unipolar SPWM is adopted, the equivalent
Fig. 2. Bode diagram of the loop gain without compensation.
Fig. 3. Bode diagram of PI and PR compensators.
switching frequency is 2f
s
), for the sake of effective harmonics
suppression and good dynamic response. Therefore, for a prop-
erly designed LCL-type grid-connected inverter, the crossover
frequency f
c
will be lower than the resonance frequency f
r
, thus
the influence of the filter capacitor can be ignored when calcu-
lating the magnitude of the loop gain at f
c
and the frequencies
lower than f
c
, i.e., the magnitude of T (s) can be approximated
as
|T (s)|≈
H
i2
G
inv
G
i
(s)
s (L
1
+ L
2
)
. (7)
PI compensator is adopted as the injected grid current regu-
lator and the transfer function of G
i
(s) is given by
G
i
(s)=K
p
+
K
i
s
. (8)
According to (8), the bode diagram of PI compensator is
depicted in Fig. 3. As seen, at the frequencies around the corner
frequency f
L
which is expressed as f
L
= K
i
/(2πK
p
), the slope
剩余14页未读,继续阅读
mc470791823
- 粉丝: 1
- 资源: 3
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

最新资源
- AirKiss技术详解:无线传递信息与智能家居连接
- Hibernate主键生成策略详解
- 操作系统实验:位示图法管理磁盘空闲空间
- JSON详解:数据交换的主流格式
- Win7安装Ubuntu双系统详细指南
- FPGA内部结构与工作原理探索
- 信用评分模型解析:WOE、IV与ROC
- 使用LVS+Keepalived构建高可用负载均衡集群
- 微信小程序驱动餐饮与服装业创新转型:便捷管理与低成本优势
- 机器学习入门指南:从基础到进阶
- 解决Win7 IIS配置错误500.22与0x80070032
- SQL-DFS:优化HDFS小文件存储的解决方案
- Hadoop、Hbase、Spark环境部署与主机配置详解
- Kisso:加密会话Cookie实现的单点登录SSO
- OpenCV读取与拼接多幅图像教程
- QT实战:轻松生成与解析JSON数据
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功