层级遍历与广度优先搜索:Java组织树算法的深度解析
发布时间: 2024-08-28 02:16:00 阅读量: 18 订阅数: 16 

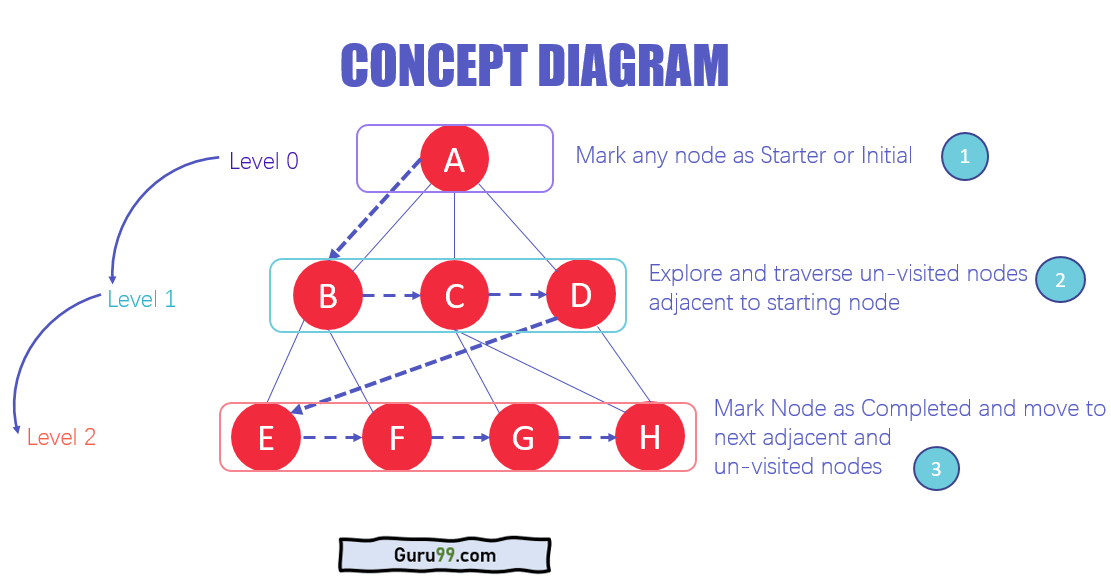
# 1. 树结构与遍历基础
树结构是一种重要的数据结构,它由节点和边组成,其中每个节点代表一个元素,而边代表节点之间的关系。树结构在计算机科学中有着广泛的应用,例如文件系统、网络路由和语法分析。
遍历树结构是访问和处理树中节点的过程。有两种主要的遍历算法:深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)。DFS沿着一条路径深入遍历树,而BFS逐层遍历树。
这两种遍历算法各有其优缺点。DFS在查找特定节点时效率更高,而BFS在遍历树的所有节点时效率更高。在实际应用中,选择哪种遍历算法取决于具体问题和数据结构。
# 2. 层级遍历算法
### 2.1 广度优先搜索(BFS)算法
#### 2.1.1 BFS算法的原理和实现
广度优先搜索(BFS)算法是一种层级遍历算法,它从根节点开始,逐层遍历树中的节点。BFS算法的实现通常使用队列数据结构,具体步骤如下:
1. 将根节点入队。
2. 只要队列不为空,就从队列中取出队首元素并访问它。
3. 将队首元素的子节点依次入队。
4. 重复步骤2和3,直到队列为空。
#### 2.1.2 BFS算法的应用场景
BFS算法广泛应用于各种场景,包括:
- 文件系统目录遍历
- 图论中的最短路径问题
- 社交网络中的朋友关系遍历
### 2.2 深度优先搜索(DFS)算法
#### 2.2.1 DFS算法的原理和实现
深度优先搜索(DFS)算法也是一种层级遍历算法,它从根节点开始,沿着树的一条分支一直向下遍历,直到遇到叶节点。然后,它回溯到上一个未访问过的节点,继续向下遍历。DFS算法的实现通常使用栈数据结构,具体步骤如下:
1. 将根节点压入栈中。
2. 只要栈不为空,就从栈顶弹出元素并访问它。
3. 将弹出元素的子节点依次压入栈中。
4. 重复步骤2和3,直到栈为空。
#### 2.2.2 DFS算法的应用场景
DFS算法也广泛应用于各种场景,包括:
- 文件系统目录遍历
- 图论中的连通性问题
- 迷宫求解
# 3. Java中组织树算法的实现
### 3.1 基于队列的BFS算法
#### 3.1.1 代码实现和分析
```java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个树结构
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
// 使用队列进行BFS遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.println(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
}
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
1. 创建一个队列`queue`,并把根节点`root`入队。
2. 循环遍历队列:
- 从队列中取出队首元素`node`。
- 访问`node`的值。
- 如果`node`有左子节点,则将左子节点入队。
- 如果`node`有右子节点,则将右子节点入队。
3. 重复步骤2,直到队列为空。
**参数说明:**
- `queue`:用于BFS遍历的队列。
- `root`:树的根节点。
#### 3.1.2 性能优化技巧
- **使用数组代替链表实现队列:**数组的访问速度比链表快。
- **批量出队:**一次性出队多个元素,减少出队操作次数。
- **使用双端队列:**双端队列可以同时进行入队和出队操作,提高效率。
### 3.2 基于栈的DFS算法
#### 3.2.1 代码实现和分析
```java
import java.util.Stack;
public class DFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个树结构
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
// 使用栈进行DFS遍历
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
System.out.println(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
}
}
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
1. 创建一个栈`stack`,并把根节点`root`入栈。
2. 循环遍历栈:
- 从栈顶弹出元素`node`。
- 访问`node`的值。
- 如果`node`有右子节点,则将右子节点入栈。
- 如果`node`有左子节点,则将左子节点入栈。
3. 重复步骤2,直到栈为空。
**参数说明:**
- `stack`:用于DFS遍历的栈。
- `root`:树的根节点。
#### 3.2.2 性能优化技巧
- **使用数组代替链表实现栈:**数组的访问速度比链表快。
- **批量入栈:**一次性入栈多个元素,减少入栈操作次数。
- **使用双端队列:**双端队列可以同时进行入栈和出栈操作,提高效率。
# 4. 组织树算法的应用
### 4.1 文件系统目录遍历
#### 4.1.1 BFS算法的应用
在文件系统中,目录结构通常以树形结构组织。BFS算法可以用来遍历目录树,并按层级顺序访问每个目录和文件。
**代码实现:**
```java
import java.io.File;
public class BFSFileTraversal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File root = new File("root_directory");
Queue<File> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
File current = queue.poll();
System.out.println(current.getName());
if (current.isDirectory()) {
for (File file : current.listFiles()) {
queue.offer(file);
}
}
}
}
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
1. 从根目录开始,将根目录加入队列。
2. 从队列中取出第一个目录,并打印其名称。
3. 如果该目录是目录,则将该目录下的所有文件和目录加入队列。
4. 重复步骤2和3,直到队列为空。
**参数说明:**
* `root`:根目录对象。
* `queue`:用于存储目录的队列。
#### 4.1.2 DFS算法的应用
DFS算法也可以用来遍历目录树,但它会深度优先地探索每个目录。
**代码实现:**
```java
import java.io.File;
public class DFSFileTraversal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File root = new File("root_directory");
Stack<File> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
File current = stack.pop();
System.out.println(current.getName());
if (current.isDirectory()) {
for (File file : current.listFiles()) {
stack.push(file);
}
}
}
}
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
1. 从根目录开始,将根目录压入栈。
2. 从栈中弹出栈顶目录,并打印其名称。
3. 如果该目录是目录,则将该目录下的所有文件和目录压入栈。
4. 重复步骤2和3,直到栈为空。
**参数说明:**
* `root`:根目录对象。
* `stack`:用于存储目录的栈。
### 4.2 图论中的最短路径问题
#### 4.2.1 BFS算法在最短路径问题中的应用
在图论中,最短路径问题是指在给定图中,找到从一个顶点到另一个顶点的最短路径。BFS算法可以用来解决最短路径问题。
**代码实现:**
```java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BFSShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 图的邻接表表示
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化图
// ...
int start = 1; // 起始顶点
int end = 5; // 结束顶点
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(start);
Map<Integer, Integer> distance = new HashMap<>(); // 存储每个顶点到起始顶点的距离
distance.put(start, 0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int current = queue.poll();
if (current == end) {
break;
}
for (int neighbor : graph.get(current)) {
if (!distance.containsKey(neighbor)) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
distance.put(neighbor, distance.get(current) + 1);
}
}
}
if (distance.containsKey(end)) {
System.out.println("最短路径长度:" + distance.get(end));
} else {
System.out.println("不存在从起始顶点到结束顶点的路径。");
}
}
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
1. 初始化图的邻接表表示。
2. 将起始顶点加入队列,并将其距离设置为0。
3. 从队列中取出第一个顶点,并将其所有未访问的邻居加入队列,同时更新其距离。
4. 重复步骤3,直到队列为空或找到结束顶点。
5. 如果找到结束顶点,则输出最短路径长度;否则,输出不存在路径。
**参数说明:**
* `graph`:图的邻接表表示。
* `start`:起始顶点。
* `end`:结束顶点。
* `queue`:用于存储顶点的队列。
* `distance`:存储每个顶点到起始顶点的距离。
#### 4.2.2 DFS算法在最短路径问题中的应用
DFS算法也可以用来解决最短路径问题,但其效率通常不如BFS算法。
**代码实现:**
```java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DFSShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 图的邻接表表示
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化图
// ...
int start = 1; // 起始顶点
int end = 5; // 结束顶点
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(start);
Map<Integer, Integer> distance = new HashMap<>(); // 存储每个顶点到起始顶点的距离
distance.put(start, 0);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int current = stack.pop();
if (current == end) {
break;
}
for (int neighbor : graph.get(current)) {
if (!distance.containsKey(neighbor)) {
stack.push(neighbor);
distance.put(neighbor, distance.get(current) + 1);
}
}
}
if (distance.containsKey(end)) {
System.out.println("最短路径长度:" + distance.get(end));
} else {
System.out.println("不存在从起始顶点到结束顶点的路径。");
}
}
}
```
**逻辑分析:**
1. 初始化图的邻接表表示。
2. 将起始顶点压入栈,并将其距离设置为0。
3. 从栈中弹出栈顶顶点,并将其所有未访问的邻居压入栈,同时更新其距离。
4. 重复步骤3,直到栈为空或找到结束顶点。
5. 如果找到结束顶点,则输出最短路径长度;否则,输出不存在路径。
**参数说明:**
* `graph`:图的邻接表表示。
* `start`:起始顶点。
* `end`:结束顶点。
* `stack`:用于存储顶点的栈。
* `distance`:存储每个顶点到起始顶点的距离。
# 5. 组织树算法的扩展
### 5.1 最优二叉搜索树
#### 5.1.1 最优二叉搜索树的定义和特点
最优二叉搜索树(Optimal Binary Search Tree,简称OBST)是一种二叉搜索树,其具有以下特点:
- 对于给定的一组关键字和它们的访问频率,OBST 可以最小化查找、插入和删除操作的平均成本。
- OBST 的构建基于动态规划算法,它通过递归地计算子问题的最优解来求解全局最优解。
#### 5.1.2 最优二叉搜索树的构建算法
OBST 的构建算法如下:
```java
public static Node buildOBST(int[] keys, int[] frequencies) {
int n = keys.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n][n];
int[][] root = new int[n][n];
// 计算子问题的最优解
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][i] = frequencies[i];
}
for (int l = 2; l <= n; l++) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n - l; i++) {
int j = i + l - 1;
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int r = i; r <= j; r++) {
int cost = dp[i][r - 1] + dp[r + 1][j];
if (cost < dp[i][j]) {
dp[i][j] = cost;
root[i][j] = r;
}
}
dp[i][j] += sum(frequencies, i, j);
}
}
// 递归构建OBST
return buildOBST(root, keys, 0, n - 1);
}
private static Node buildOBST(int[][] root, int[] keys, int i, int j) {
if (i > j) {
return null;
}
int r = root[i][j];
Node node = new Node(keys[r]);
node.left = buildOBST(root, keys, i, r - 1);
node.right = buildOBST(root, keys, r + 1, j);
return node;
}
private static int sum(int[] frequencies, int i, int j) {
int sum = 0;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
sum += frequencies[k];
}
return sum;
}
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
- `dp`数组存储子问题的最优解,其中`dp[i][j]`表示区间`[i, j]`内的最优解。
- `root`数组存储子问题的根节点,其中`root[i][j]`表示区间`[i, j]`内的最优根节点。
- 算法首先计算子问题的最优解,然后递归地构建OBST。
- `sum`函数计算区间`[i, j]`内频率的总和。
### 5.2 哈夫曼树
#### 5.2.1 哈夫曼树的定义和特点
哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)是一种二叉树,其具有以下特点:
- 哈夫曼树的叶子节点代表不同的符号,每个符号都有一个权重。
- 哈夫曼树的内部节点不代表任何符号,其权重等于其子节点权重的和。
- 哈夫曼树的编码长度最短,即对于给定的符号集和权重,哈夫曼树可以生成最短的编码。
#### 5.2.2 哈夫曼树的构建算法
哈夫曼树的构建算法如下:
```java
public static Node buildHuffmanTree(int[] frequencies) {
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.frequency - b.frequency);
// 将符号和权重添加到优先队列
for (int i = 0; i < frequencies.length; i++) {
queue.add(new Node(i, frequencies[i]));
}
// 构建哈夫曼树
while (queue.size() > 1) {
Node left = queue.poll();
Node right = queue.poll();
Node parent = new Node(-1, left.frequency + right.frequency);
parent.left = left;
parent.right = right;
queue.add(parent);
}
return queue.poll();
}
```
**代码逻辑分析:**
- `PriorityQueue`用于存储符号和权重,并根据权重对符号进行排序。
- 算法从优先队列中取出权重最小的两个符号,并创建一个新的父节点,其权重等于两个子节点权重的和。
- 算法将父节点添加到优先队列中,并重复此过程,直到优先队列中只剩下一个节点,该节点即为哈夫曼树的根节点。
# 6. 总结与展望
在本文中,我们深入探讨了组织树算法及其在计算机科学中的广泛应用。从树结构和遍历基础到层级遍历算法,我们逐步深入了解了BFS和DFS算法的原理、实现和应用场景。
在Java中,我们探讨了基于队列的BFS算法和基于栈的DFS算法的实现,并提供了性能优化技巧。此外,我们还展示了组织树算法在文件系统目录遍历和图论中的最短路径问题中的应用。
最后,我们扩展了组织树算法,讨论了最优二叉搜索树和哈夫曼树的概念和构建算法。这些算法在数据结构、编码和压缩等领域具有重要意义。
随着计算机科学的不断发展,组织树算法在未来仍将发挥着至关重要的作用。在人工智能、机器学习和数据科学等领域,树结构和遍历算法将继续成为解决复杂问题的关键工具。
展望未来,我们期待着组织树算法的进一步创新和应用,以应对不断变化的计算需求。
0
0





