【线性时间排序算法详解】:揭秘快速排序与堆排序的实战应用,提升代码效率
发布时间: 2024-08-26 17:26:31 阅读量: 19 订阅数: 11 

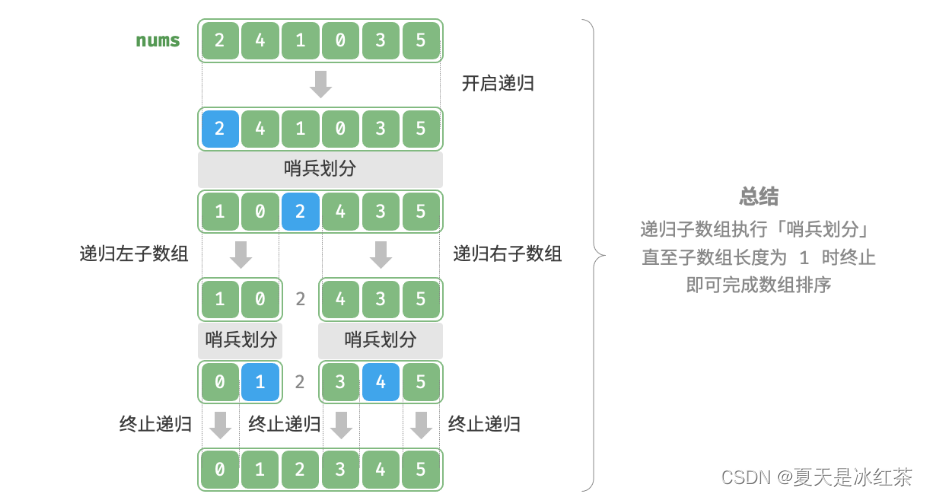
# 1. 排序算法概述
排序算法是计算机科学中至关重要的算法,用于对数据进行组织和排列。它们在各种应用中发挥着关键作用,从数据分析到机器学习。排序算法的种类繁多,每种算法都有其独特的优点和缺点。本章将提供排序算法的概述,介绍其基本概念和分类。
排序算法可以分为两大类:基于比较的排序和非基于比较的排序。基于比较的排序通过比较元素之间的值来确定它们的顺序,而非基于比较的排序则使用其他方法,例如元素的键值或哈希函数。本章将重点介绍基于比较的排序算法,包括快速排序和堆排序。
# 2. 快速排序理论与实践
### 2.1 快速排序算法原理
#### 2.1.1 分治思想与递归实现
快速排序算法遵循分治思想,将一个无序数组划分为两个子数组:一个包含所有小于或等于枢轴元素的元素,另一个包含所有大于枢轴元素的元素。然后递归地对这两个子数组应用相同的过程,直到每个子数组只有一个元素或为空。
```mermaid
graph LR
subgraph 快速排序
A[0, n-1] --> B[0, p-1]
A[0, n-1] --> C[p, n-1]
B[0, p-1] --> D[0, p-1]
C[p, n-1] --> E[p, n-1]
D[0, p-1] --> A[0, p-1]
E[p, n-1] --> A[p, n-1]
end
```
**递归实现:**
```python
def quick_sort(array, left, right):
if left < right:
pivot = partition(array, left, right)
quick_sort(array, left, pivot - 1)
quick_sort(array, pivot + 1, right)
```
#### 2.1.2 枢轴元素的选择与分区
枢轴元素的选择对于快速排序的性能至关重要。一个好的枢轴元素可以将数组大致分成大小相等的两个子数组,从而提高递归的效率。
**分区过程:**
```python
def partition(array, left, right):
pivot = array[right]
i = left - 1
for j in range(left, right):
if array[j] <= pivot:
i += 1
array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i]
array[i + 1], array[right] = array[right], array[i + 1]
return i + 1
```
### 2.2 快速排序代码实现
#### 2.2.1 C语言实现
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void quick_sort(int *array, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int pivot = partition(array, left, right);
quick_sort(array, left, pivot - 1);
quick_sort(array, pivot + 1, right);
}
}
int partition(int *array, int left, int right) {
int pivot = array[right];
int i = left - 1;
for (int j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[right];
array[right] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
int main() {
int array[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
quick_sort(array, 0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
```
#### 2.2.2 Python实现
```python
def quick_sort(array, left, right):
if left < right:
pivot = partition(array, left, right)
quick_sort(array, left, pivot - 1)
quick_sort(array, pivot + 1, right)
def partition(array, left, right):
pivot = array[right]
i = left - 1
for j in range(left, right):
if array[j] <= pivot:
i += 1
array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i]
array[i + 1], array[right] = array[right], array[i + 1]
return i + 1
array = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
quick_sort(array, 0, len(array) - 1)
print(array)
```
### 2.3 快速排序性能分析
#### 2.3.1 时间复杂度
快速排序的平均时间复杂度为 O(n log n),其中 n 是数组的长度。然而,在最坏的情况下,当数组已经有序或逆序时,时间复杂度退化为 O(n^2)。
#### 2.3.2 空间复杂度
快速排序的空间复杂度为 O(log n),因为递归调用栈的深度不会超过数组的深度。
# 3. 堆排序理论与实践
### 3.1 堆排序算法原理
#### 3.1.1 堆数据结构
堆是一种完全二叉树,其中每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值。堆有两种类型:最大堆和最小堆。在最大堆中,根节点的值是堆中最大的值,而在最小堆中,根节点的值是堆中最小的值。
#### 3.1.2 堆排序过程
堆排序算法通过将输入数组转换为最大堆,然后依次弹出堆顶元素并将其插入到数组的末尾来实现排序。堆排序过程分为以下步骤:
1. **建堆:**将输入数组转换为最大堆。
2. **弹出堆顶:**弹出堆顶元素并将其插入到数组的末尾。
3. **调整堆:**将剩余的堆调整为最大堆。
4. **重复步骤 2 和 3:**重复步骤 2 和 3,直到堆为空。
### 3.2 堆排序代码实现
#### 3.2.1 C++实现
```cpp
void heapSort(int arr[], int n) {
// 建堆
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, n, i);
}
// 依次弹出堆顶元素并插入到数组末尾
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 交换堆顶元素和数组末尾元素
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// 调整剩余的堆
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
void heapify(int arr[], int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// 找出左子节点和右子节点中较大的那个
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
// 如果最大的不是根节点,则交换根节点和最大的子节点
if (largest != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
// 递归调整子堆
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
```
#### 3.2.2 Java实现
```java
public class HeapSort {
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
// 建堆
for (int i = arr.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, i, arr.length);
}
// 依次弹出堆顶元素并插入到数组末尾
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 交换堆顶元素和数组末尾元素
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// 调整剩余的堆
heapify(arr, 0, i);
}
}
private static void heapify(int[] arr, int i, int n) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// 找出左子节点和右子节点中较大的那个
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
// 如果最大的不是根节点,则交换根节点和最大的子节点
if (largest != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
// 递归调整子堆
heapify(arr, largest, n);
}
}
}
```
### 3.3 堆排序性能分析
#### 3.3.1 时间复杂度
堆排序的时间复杂度为 O(n log n),其中 n 是数组的长度。
#### 3.3.2 空间复杂度
堆排序的空间复杂度为 O(1),因为它不需要额外的空间来存储辅助数据结构。
# 4. 快速排序与堆排序对比
### 4.1 算法原理对比
#### 4.1.1 分治与堆排序
快速排序采用分治思想,将待排序数组划分为两个子数组,分别递归排序子数组,最后合并子数组得到有序数组。
堆排序则采用堆数据结构,将待排序数组构建成一个大顶堆,不断从堆顶取出最大元素,插入到有序数组中,直到堆为空。
#### 4.1.2 枢轴元素选择与堆顶元素
快速排序中,枢轴元素的选择对排序效率至关重要。一般情况下,选择数组中位数或随机元素作为枢轴元素。
堆排序中,堆顶元素始终是当前堆中最大的元素。
### 4.2 性能对比
#### 4.2.1 时间复杂度分析
快速排序的时间复杂度为 O(n log n) 在平均情况下,但最坏情况下为 O(n^2)。
堆排序的时间复杂度始终为 O(n log n)。
| 算法 | 平均时间复杂度 | 最坏时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| 快速排序 | O(n log n) | O(n^2) |
| 堆排序 | O(n log n) | O(n log n) |
#### 4.2.2 空间复杂度分析
快速排序的空间复杂度为 O(log n),因为它使用递归调用。
堆排序的空间复杂度为 O(1),因为它不需要额外的空间。
| 算法 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 快速排序 | O(log n) |
| 堆排序 | O(1) |
### 4.3 应用场景对比
#### 4.3.1 快速排序适用场景
* 数据量较小或中等
* 数据分布相对均匀
* 需要快速排序结果
#### 4.3.2 堆排序适用场景
* 数据量较大
* 数据分布不均匀
* 需要稳定排序(即相同元素保持相对顺序)
* 需要在排序过程中进行其他操作(如查找最大值)
**代码示例:**
```python
# 快速排序
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(left) + middle + quick_sort(right)
# 堆排序
def heap_sort(arr):
def heapify(arr, n, i):
largest = i
left = 2 * i + 1
right = 2 * i + 2
if left < n and arr[left] > arr[largest]:
largest = left
if right < n and arr[right] > arr[largest]:
largest = right
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i]
heapify(arr, n, largest)
n = len(arr)
# 构建大顶堆
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(arr, n, i)
# 排序
for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i]
heapify(arr, i, 0)
return arr
```
**表格:快速排序与堆排序对比**
| 特征 | 快速排序 | 堆排序 |
|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | 平均 O(n log n),最坏 O(n^2) | O(n log n) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(log n) | O(1) |
| 稳定性 | 不稳定 | 稳定 |
| 适用场景 | 数据量较小或中等,数据分布均匀 | 数据量较大,数据分布不均匀,需要稳定排序 |
# 5. 排序算法在实战中的应用
排序算法在实际应用中发挥着至关重要的作用,广泛应用于数据预处理、机器学习和分布式大数据处理等领域。
### 5.1 数据预处理中的排序
#### 5.1.1 数据清洗与排序
数据清洗是数据预处理的重要步骤,旨在去除数据中的异常值和噪声。排序算法可以用于识别异常值,例如:
```python
import numpy as np
# 原始数据
data = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39]
# 排序数据
sorted_data = np.sort(data)
# 识别异常值(大于平均值3个标准差)
mean = np.mean(sorted_data)
std = np.std(sorted_data)
threshold = mean + 3 * std
outliers = [x for x in sorted_data if x > threshold]
print("异常值:", outliers)
```
#### 5.1.2 数据归一化与排序
数据归一化是将数据映射到特定范围的过程,以消除不同特征之间的量纲差异。排序算法可以用于对数据进行归一化,例如:
```python
# 原始数据
data = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39]
# 排序数据
sorted_data = np.sort(data)
# 最大-最小归一化
normalized_data = (sorted_data - np.min(sorted_data)) / (np.max(sorted_data) - np.min(sorted_data))
print("归一化数据:", normalized_data)
```
### 5.2 机器学习中的排序
#### 5.2.1 特征选择与排序
特征选择是机器学习中识别和选择最相关特征的过程。排序算法可以用于对特征进行排序,例如:
```python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, chi2
# 原始数据
data = pd.DataFrame({
"feature1": [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39],
"feature2": [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40],
"target": [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]
})
# 使用卡方检验对特征进行排序
selector = SelectKBest(chi2, k=2)
selector.fit(data[["feature1", "feature2"]], data["target"])
# 排序后的特征
sorted_features = selector.get_support(indices=True)
print("排序后的特征:", sorted_features)
```
#### 5.2.2 模型训练与排序
模型训练是机器学习中根据训练数据学习模型的过程。排序算法可以用于对模型进行排序,例如:
```python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
# 原始数据
data = pd.DataFrame({
"feature1": [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39],
"feature2": [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40],
"target": [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]
})
# 不同模型
models = [
LinearRegression(),
LogisticRegression(),
DecisionTreeClassifier(),
RandomForestClassifier()
]
# 使用交叉验证对模型进行排序
scores = []
for model in models:
score = cross_val_score(model, data[["feature1", "feature2"]], data["target"], cv=5).mean()
scores.append(score)
# 排序后的模型
sorted_models = np.argsort(scores)[::-1]
print("排序后的模型:", sorted_models)
```
### 5.3 大数据处理中的排序
#### 5.3.1 分布式排序技术
分布式排序技术将大数据集分解成较小的块,并在多个节点上并行处理。排序算法在分布式环境中可以有效利用计算资源,例如:
```mermaid
graph LR
subgraph 分布式排序
A[Map] --> B[Shuffle] --> C[Sort] --> D[Reduce]
end
```
#### 5.3.2 云计算平台中的排序
云计算平台提供预先配置的排序服务,可以简化大数据集的排序过程。例如:
```
# 使用 AWS EMR 运行 Spark 排序作业
spark_session = SparkSession.builder \
.master("yarn") \
.appName("Spark Sort") \
.getOrCreate()
data = spark_session.read.csv("s3://my-bucket/data.csv")
sorted_data = data.sort("column_name")
sorted_data.write.csv("s3://my-bucket/sorted_data.csv")
```
0
0





