【环形链表的基础】:理解JavaScript中的环形数据结构
发布时间: 2024-09-14 05:40:35 阅读量: 28 订阅数: 27 

# 1. 环形链表的概念与特性
## 简介
环形链表是一种链表结构,其中每个节点指向下一个节点,且最后一个节点的指针又回到第一个节点,形成一个环。这种数据结构在计算机科学中常用于模拟循环队列、内存管理和其他需要周期性处理的任务。
## 特性
环形链表与传统的单链表或双向链表相比,具有独特的属性。其头部和尾部并不像线性链表那样有明确的界限,而是任何节点都可以看作是开始或结束。这使得环形链表在遍历时没有明显的起点和终点,而是一个闭合的圈。
## 应用场景
由于环形链表的结构特性,它特别适合处理那些需要循环重复的任务,例如,在操作系统中进行进程调度时,就可能用到环形链表来构建调度队列。在实际应用中,环形链表可以用于设计循环缓冲区、实现圆形缓冲区的游标机制等。
环形链表的应用不仅限于数据结构和算法层面,在真实世界的项目中也有广泛的应用,比如轮询调度系统的构建等。在接下来的章节中,我们会深入探讨环形链表的理论基础、如何在JavaScript中实现环形链表,以及它的应用案例和优化策略。
# 2. 环形链表的理论基础
### 2.1 单链表与环形链表的区别
#### 2.1.1 单链表结构简介
单链表是链表的一种简单形式,它由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含两个部分:数据域和指针域。数据域存储节点的数据信息,而指针域则存储指向下一个节点的引用。在单链表中,第一个节点被称为头节点,而最后一个节点的指针域指向一个空值,标志着链表的结束。
```javascript
class ListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // 数据域
this.next = null; // 指针域,指向下一个节点
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; // 头节点
}
// 添加节点到链表末尾
append(data) {
const newNode = new ListNode(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
}
}
```
在上面的JavaScript代码示例中,我们定义了一个单链表结构,包括节点类ListNode和单链表类SinglyLinkedList。 ListNode包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。SinglyLinkedList类包含一个方法append,用于在链表末尾添加新节点。
#### 2.1.2 环形链表的定义和特征
环形链表是单链表的一种变体,其中的最后一个节点的指针不是指向null,而是指向链表的头节点,形成一个闭环。这种结构特别适用于实现一些循环队列或者其他需要循环遍历的场景。
环形链表最显著的特征是它没有真正的结束点,每个节点都通过指针相互连接。在遍历环形链表时,从任何一个节点出发,都可以通过跟随指针遍历整个链表,最终回到起始节点。
### 2.2 环形链表的操作原理
#### 2.2.1 创建环形链表的基本步骤
创建一个环形链表通常包含以下步骤:
1. 创建头节点并初始化为空。
2. 创建并插入第一个节点,将其指针指向头节点,形成闭环。
```javascript
class CircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
append(data) {
const newNode = new ListNode(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head; // 形成环形链表
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
}
}
}
```
在上述代码中,我们定义了CircularLinkedList类来创建环形链表。 append方法在添加新节点时,会检查当前链表是否为空,并确保新节点的next指针指向头节点,从而维持环形结构。
#### 2.2.2 遍历环形链表的逻辑
遍历环形链表的逻辑比单链表更为复杂,因为我们需要避免无限循环的遍历。通常,我们会先判断链表是否为空,然后从头节点开始遍历,直到返回到头节点为止。
```javascript
function traverseCircularLinkedList(head) {
if (!head) return [];
let current = head;
const elements = [];
do {
elements.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
} while (current !== head);
return elements;
}
```
在遍历函数traverseCircularLinkedList中,我们首先检查链表是否为空,然后使用一个循环遍历所有节点直到再次到达头节点,并将遍历到的数据存储在数组elements中。
#### 2.2.3 环形链表的尾部连接机制
环形链表的尾部连接机制是其实现的核心,确保了链表节点的循环连接。在添加新节点时,我们需要检查是否是第一个节点,如果是,则需要将新节点的next指针指向自己,形成初始的环形结构。
```javascript
// 在添加新节点时,确保最后一个节点指向头节点
current.next = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head; // 这里保证了环形链表的结构
```
### 2.3 环形链表的时间复杂度分析
#### 2.3.1 主要操作的时间复杂度
环形链表的主要操作包括插入、删除和遍历,其时间复杂度与单链表类似,基本上都是O(n),其中n是链表中的节点数。尽管环形链表有额外的逻辑来处理尾部连接,但这个操作本身是在常数时间内完成的,因此不会影响主要操作的时间复杂度。
#### 2.3.2 环形链表与单链表性能对比
环形链表与单链表在性能上的对比主要体现在遍历和尾部操作上。环形链表的遍历可以是从链表的任何节点开始,无需额外的指针来判断是否到达链表末尾。在单链表中,遍历到尾节点时需要额外的步骤来检查节点的next是否为null。
在插入和删除操作上,两者的时间复杂度相同,但是环形链表通常需要在操作前进行更多的检查来保持结构的完整性。例如,在插入操作中,我们不仅要找到正确的插入位置,还要确保新节点的next指针指向头节点,以保持环形结构。
在实际应用中,选择环形链表还是单链表取决于特定的使用场景和性能要求。环形链表适用于那些需要循环遍历的场景,如实现循环队列、任务调度等,而单链表适用于一般线性数据处理。
# 3. ```markdown
# 第三章:环形链表的JavaScript实现
环形链表作为数据结构中的重要一环,具有独特的环形特性。在Web开发中,JavaScript的灵活与面向对象的特性使其成为实现环形链表的理想选择。在本章节中,我们将探索环形链表在JavaScript中的实现方法,理解它如何在实际编程中发挥作用。
## 3.1 JavaScript中的链表实现基础
### 3.1.1 JavaScript对象与链表节点的映射
在JavaScript中,对象可以用来表示链表中的节点。每个节点包含至少两个属性:存储数据的value属性和指向下一个节点的next属性。由于JavaScript对象的灵活性,我们可以很容易地创建节点并动态地赋予其属性和方法。
```javascript
function ListNode(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
```
在上述示例中,`ListNode`构造函数创建了一个新的链表节点,并初始化其`value`属性和`next`属性。这里的`value`属性将存储节点的数据,而`next`属性则用于指向下个节点。
### 3.1.2 链表节点的创建与初始化
创建和初始化链表节点是构建链表的第一步。JavaScript允许我们通过构造函数或对象字面量来创建节点。
```javascript
let head = new ListNode('head');
let node1 = new ListNode(1);
let node2 = new ListNode(2);
let node3 = new ListNode(3);
// 将链表连接起来
head.next = node1;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
```
上述代码创建了四个节点,并通过`next`属性将它们连成一个链表。此时,`head`指向`node1`,`node1`指向`node2`,以此类推,形成一个简单的单向链表结构。
## 3.2 环形链表的构造与操作
### 3.2.1 环形链表的构造函数
为了创建一个环形链表,我们需要在创建节点的基础上,确保链表的尾部节点指向头节点。这可以通过修改尾节点的`next`属性来实现。
```javascript
function CircularLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
}
CircularLinkedList.prototype.append = function(value) {
let newNode = new ListNode(value);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
newNode.next = this.head;
}
```
在构造函数`CircularLinkedList`中,我们定义了`append`方法来添加新的节点到链表尾部,并确保新的尾节点指向头节点,从而构造出环形链表。
### 3.2.2 插入和删除节点的方法
环形链表中的插入和删除操作需要特别注意,因为这些操作可能会影响到循环的连续性。
```javascript
CircularLinkedList.prototype.insert = function(position, value) {
if (position === 0) {
let newNode = new ListNode(value);
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.head.next = this.head; // 保持环形特性
} else {
let newNode = new ListNode(value);
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (index < position - 1 && current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
}
CircularLinkedList.prototype.delete = function(value) {
if (this.head === null) return null;
if (this.head.value === value) {
if (this.head.next === this.head) {
this.head = null;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = this.head.next;
this.head = this.head.next;
}
} else {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
while (current.value !== value && current.next !== this.head) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current.value === value) {
previous.next = current.next;
}
}
}
```
在`insert`方法中,我们根据位置参数`position`,将新节点插入到指定位置。`delete`方法则用于删除具有特定值的节点。这两个方法都需要处理边界条件,如删除头节点时的特殊情况。
### 3.2.3 访问特定节点的函数
访问特定节点是链表操作中常见的需求。在环形链表中,需要特别注意,一旦遍历完一次链表,我们应该停止遍历,否则会导致无限循环。
```javascript
CircularLinkedList.prototype.find = function(value) {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current !== this.head && current.value !== value) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
if (current.value === value) {
return current;
}
return null;
}
```
`find`方法从头节点开始遍历,当找到匹配的值或者遍历回到头节点时停止。这个方法返回找到的节点,如果没有找到,则返回`null`。
## 3.3 环形链表的边界处理
### 3.3.1 判断环形链表的边界条件
在环形链表的编程实践中,理解并处理边界条件至关重要。环形链表的边界条件主要表现为尾部节点的处理,以及循环的结束。
### 3.3.2 避免无限循环的策略
避免无限循环是环形链表编程中需要特别注意的事项。通常需要设置一些标志或断点来确保循环能够适时结束。
```javascript
CircularLinkedList.prototype.display = function() {
let current = this.head;
if (this.head === null) {
console.log('The list is empty.');
return;
}
do {
console.log(current.value);
current = current.next;
} while (current !== this.head);
}
```
`display`方法用于打印链表的所有节点,利用`do-while`循环避免了无限循环的情况。当`current`再次回到`this.head`时,停止循环,从而安全地打印出所有节点。
### 表格示例
在探讨环形链表的边界处理时,我们可以通过表格来比较单向链表和环形链表在插入、删除等操作上的差异:
| 操作 | 单向链表 | 环形链表 |
|----------|---------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|
| 插入 | 在指定位置插入一个新节点 | 在指定位置插入一个新节点,连接尾部到头节点 |
| 删除 | 删除指定值的节点 | 删除指定值的节点,需要避免断环 |
| 遍历 | 从头节点遍历至尾节点 | 遍历一圈即可,避免无限循环 |
| 检索 | 检索直到找到或遍历完整个链表 | 遍历一圈即可,避免无限循环 |
通过对比表中的内容,我们可以清晰地看到环形链表与单向链表在操作上的不同之处,以及在实现时需要注意的特定细节。
## 代码块和逻辑分析
在本章节的介绍中,我们已经展示了如何用JavaScript实现环形链表的基础结构和一些核心方法。理解每个代码块的逻辑和参数是掌握环形链表实现的关键。
```javascript
let cList = new CircularLinkedList();
cList.append('Node1');
cList.append('Node2');
cList.append('Node3');
// 输出链表
cList.display(); // Node1 Node2 Node3 Node1 Node2 Node3 ...
```
上述代码块展示了一个完整的环形链表实现和使用过程,从构造环形链表开始,到添加节点,再到遍历展示链表节点。每一步操作都遵循了环形链表的特性,保持了链表的闭合循环。
在继续深入之前,希望本章内容已经为读者提供了一个良好起点,让我们在下一章节继续探索环形链表的更多应用和优化策略。
```
# 4. 环形链表的应用案例
环形链表作为一种数据结构,它的优势在于能够高效地模拟和处理循环相关的场景。在本章中,我们将详细探讨环形链表在算法设计和实际项目开发中的应用案例,从而加深对其实际价值和用途的理解。
## 4.1 环形链表在算法中的应用
环形链表在算法问题中特别有用,其中一个经典的例子是约瑟夫问题(Josephus Problem)。
### 4.1.1 约瑟夫问题的解决方案
约瑟夫问题是一个著名的数学问题,其描述为:编号为1到n的n个人围成一圈,从编号为1的人开始报数,每数到m的人出列,接着从下一个人开始继续报数并出列,直到所有人都出列为止。问题要求求出一个出列序列。
环形链表是解决这一问题的直观且有效的方式。以下是使用环形链表解决约瑟夫问题的JavaScript代码实现:
```javascript
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
append(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
josephusProblem(m) {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
while (current.next !== current) {
let counter = 1;
while (counter !== m) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
counter++;
}
previous.next = current.next;
console.log(`${current.value} is out`);
current = current.next;
}
console.log(`Last man standing: ${current.value}`);
}
}
// 示例:创建环形链表并解决约瑟夫问题
const clist = new CircularLinkedList();
for (let i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
clist.append(i);
}
clist.josephusProblem(3); // 假设m=3
```
在上述代码中,`CircularLinkedList`类表示环形链表,其中`append`方法用于在链表末尾添加新节点。`josephusProblem`方法模拟了约瑟夫问题的报数过程,每次数到m就将当前节点从链表中断开,并输出该节点的值。这个过程一直持续到链表中只剩下一个节点,即最后的“幸存者”。
该问题的解决方案展示了环形链表如何在循环逻辑中发挥其独特的优势。
### 4.1.2 循环队列的实现
循环队列是一种使用固定大小数组实现的队列结构,它利用数组的首尾相连来模拟循环的性质。这里,环形链表也可以用来实现循环队列,尽管通常我们会使用数组,但使用链表可以动态扩展队列的大小。
```javascript
// 环形链表实现的循环队列
class CircularQueue {
constructor(capacity) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
enqueue(value) {
if (this.size === this.capacity) {
throw new Error("Queue is full");
}
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.tail.next = this.head;
}
this.size++;
}
dequeue() {
if (this.size === 0) {
throw new Error("Queue is empty");
}
let value = this.head.value;
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.size === 1) {
this.tail = null;
}
this.size--;
return value;
}
}
// 示例:创建循环队列并进行入队和出队操作
const queue = new CircularQueue(5);
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 输出: 1
console.log(queue.dequeue()); // 输出: 2
```
这个`CircularQueue`类用环形链表实现了一个循环队列。`enqueue`方法用于添加元素到队列尾部,`dequeue`方法用于移除队列头部的元素。当队列满时,`enqueue`方法会抛出错误;当队列空时,`dequeue`方法同样会抛出错误。此代码演示了环形链表如何有效地实现队列操作。
## 4.2 环形链表在实际项目中的运用
环形链表不仅在理论算法问题中有其特定应用,在实际的软件项目中也扮演着重要的角色。
### 4.2.1 游戏开发中的环形结构
在游戏开发中,环形链表常用于构建和管理游戏对象,尤其是那些需要循环出现或以循环形式进行交互的对象。例如,玩家角色可以围绕一个虚拟环形赛道进行竞速,每个玩家位置的更新,以及最终的排名判定都可以用环形链表来管理。
```javascript
// 简单示例:模拟游戏中的环形赛道管理
class RaceCar {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class RaceTrack {
constructor() {
this赛车 = new CircularLinkedList();
}
addCar(car) {
this赛车.append(new RaceCar(car));
}
nextLap() {
// 假设每个赛车完成了一圈
let current = this赛车.head;
while (current) {
if (current.next === this赛车.head) {
// 到达最后一个赛车,准备开始新的一圈
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
console.log(`${current.value.name} is now leading the race`);
}
}
// 示例:创建赛道和赛车
const track = new RaceTrack();
track.addCar('Car1');
track.addCar('Car2');
track.addCar('Car3');
track.nextLap(); // 输出: Car1 is now leading the race
```
在这个游戏中,`RaceCar`代表赛车对象,`RaceTrack`类利用`CircularLinkedList`管理赛车对象。`nextLap`方法可以模拟赛车完成一整圈的情况。这个简化的例子说明了环形链表如何在游戏开发中应用,以实现流畅的循环交互和状态更新。
### 4.2.2 轮询调度系统的构建
轮询调度是一种常见的任务调度方法,它涉及循环地对一组任务进行检查,并对满足条件的任务执行相应的操作。环形链表为轮询调度提供了一种高效的数据结构支持。
```javascript
class Task {
constructor(id, condition) {
this.id = id;
this.condition = condition;
}
}
class PollingScheduler {
constructor() {
this.tasks = new CircularLinkedList();
this.running = false;
}
addTask(task) {
this.tasks.append(task);
}
startPolling() {
this.running = true;
let current = this.tasks.head;
setImmediate(() => {
while (this.running && current) {
if (current.value.condition()) {
console.log(`Task ${current.value.id} executed`);
current = current.next;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
if (current === this.tasks.head) {
break;
}
}
});
}
stopPolling() {
this.running = false;
}
}
// 示例:创建任务并启动轮询调度
const scheduler = new PollingScheduler();
scheduler.addTask(new Task(1, () => Math.random() > 0.5));
scheduler.addTask(new Task(2, () => true));
scheduler.startPolling();
```
在这个`PollingScheduler`类中,我们使用环形链表存储任务。`startPolling`方法启动一个轮询过程,不断地检查每个任务的条件,并执行符合条件的任务。这个例子演示了环形链表如何帮助管理复杂的轮询调度任务。
通过以上应用案例的介绍,我们了解了环形链表不仅仅是一种理论上的数据结构,它在现实世界中的应用广泛,可以解决各种循环相关的问题。无论是作为算法问题的解决方案,还是在游戏开发与调度系统中,环形链表都显示了其独特的价值和作用。
# 5. 环形链表的进阶与优化
## 5.1 环形链表的复杂操作
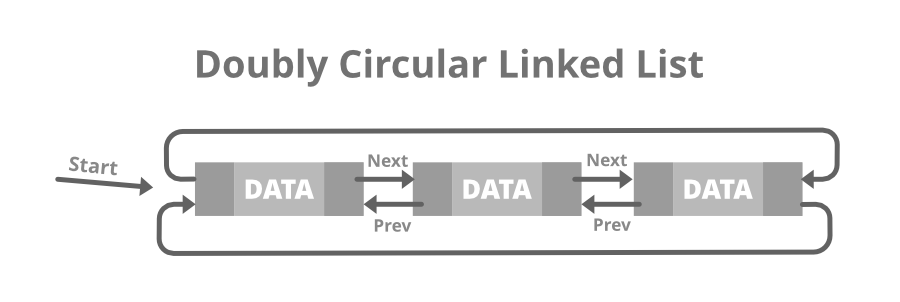
### 5.1.1 双向环形链表的构建
在实际应用中,双向环形链表的需求更加频繁,因为它允许数据在两个方向上遍历,提供了更多灵活性。双向环形链表中,每个节点通常包含数据域、指向前驱节点的指针和指向后继节点的指针。
```javascript
class DoublyCircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
// 添加节点到双向环形链表
append(data) {
let newNode = new Node(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let tail = this.head;
while (tail.next !== this.head) {
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
}
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
}
// 遍历双向环形链表
display() {
let head = this.head;
if (!head) {
console.log('The list is empty.');
return;
}
console.log('Forward: ');
do {
console.log(head.data + ' ', end=' ');
head = head.next;
} while (head !== this.head);
console.log('\nBackward: ');
do {
console.log(head.data + ' ', end=' ');
head = head.prev;
} while (head !== this.head);
console.log();
}
}
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
// 使用示例
let dcList = new DoublyCircularLinkedList();
dcList.append(1);
dcList.append(2);
dcList.append(3);
dcList.display();
```
以上代码展示了如何在JavaScript中实现一个双向环形链表,并提供了添加节点和打印链表的方法。
### 5.1.2 环形链表的排序与搜索算法
尽管环形链表排序和搜索的实现比数组或数组列表更复杂,但它们仍然是可能的。排序可以通过归并排序实现,搜索则可以通过遍历链表进行。
```javascript
function mergeSort(node) {
// 归并排序的实现略
}
function search(node, key) {
let current = node;
do {
if (current.data === key) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
} while (current !== node);
return null;
}
```
这里的`mergeSort`函数负责实现归并排序算法,`search`函数则提供了一个线性搜索实现。
## 5.2 环形链表的性能优化
### 5.2.1 内存管理与垃圾回收
环形链表的内存管理需要格外注意,因为不正确的内存回收可能导致内存泄漏。在JavaScript中,垃圾回收通常由运行时自动处理,但我们必须确保正确地管理节点的引用。
```javascript
let cache = new Map();
// 创建节点时记录到缓存中
function createNode(data) {
let newNode = new Node(data);
cache.set(newNode, null);
return newNode;
}
// 在节点不再需要时,手动删除引用以帮助垃圾回收
function deleteNode(node) {
cache.delete(node);
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
```
在上面的代码中,我们使用了一个`Map`对象`cache`来存储对节点的引用,当我们删除一个节点时,通过删除`cache`中的记录来帮助垃圾回收器回收不再使用的节点。
### 5.2.2 避免和处理内存泄漏
内存泄漏是指程序在分配内存后未能释放不再使用的内存。在环形链表操作中,需要特别注意避免循环引用,因为它们会阻止垃圾回收器回收内存。
```javascript
// 引用计数和标记清理算法的简单模拟
function referenceCounting() {
// 引用计数逻辑略
}
function markAndSweep() {
// 标记-清扫算法逻辑略
}
// 例子:设置一个定时器来模拟内存泄漏
setTimeout(() => {
// 模拟内存泄漏代码略
}, 1000);
```
在这个例子中,`referenceCounting`和`markAndSweep`函数分别代表了不同的垃圾回收策略。在实际编码中,我们还需要确保不再需要的资源能够及时被垃圾回收器识别,避免内存泄漏。
通过本章内容,我们已经深入探讨了环形链表的复杂操作和性能优化方法。这些进阶技术能够帮助我们在实际应用中更好地管理和使用环形链表,同时确保我们的应用具有良好的性能和稳定性。
0
0





