【Python数据处理中的图解】:图算法的应用详解
发布时间: 2024-09-11 21:08:41 阅读量: 174 订阅数: 40 

# 1. 图算法简介和应用场景
在计算机科学和数学领域,图算法是用来解决图论问题的一系列算法和技术。图是一种由顶点(节点)以及连接这些顶点的边组成的抽象数据结构,能够有效表达实体之间的复杂关系。图算法广泛应用于社交网络分析、网络优化、推荐系统、生物信息学等多个领域。
## 1.1 图算法在社交网络中的应用
在社交网络中,用户和用户之间的连接关系可以用图来表示,图算法可以帮助我们理解网络的结构特性,比如社区检测、影响力扩散和传播等。例如,通过识别社交网络中的关键节点(中心人物),我们可以对信息的传播路径和范围进行预测和控制。
## 1.2 图算法在推荐系统中的应用
推荐系统利用图算法来挖掘用户和物品之间的隐含关系,通过分析用户的历史行为数据生成个性化推荐。例如,基于图的协同过滤算法通过构建用户-物品的二部图,计算节点间的相似性,从而对用户可能感兴趣的商品进行推荐。
## 1.3 图算法在路网规划中的应用
在路网规划与分析中,地图可以被建模为一个加权有向图,其中节点代表路口,边代表路段,边的权重可以表示距离、行驶时间或者成本。图算法,特别是最短路径算法,比如迪杰斯特拉算法和弗洛伊德算法,在计算两点间的最优路径、交通流量预测和拥堵分析中发挥着重要作用。
在接下来的章节中,我们将深入探索图算法的基础理论,了解其复杂度分析,并且通过Python编程实现具体的图算法案例,进一步扩展和优化算法以适应各种实际问题。
# 2. 图算法的基础理论
## 2.1 图的基本概念
### 2.1.1 图的定义和表示方法
图是图算法中的基础数据结构,它由顶点(vertices)和边(edges)组成。顶点表示实体,边表示实体间的关系。图可以是有向的(边具有方向)或无向的(边没有方向)。
在数学和计算机科学中,图可以表示为G(V, E),其中V代表顶点集合,E代表边集合。一个边可以表示为两个顶点的有序对(u, v),其中u和v是V中的元素,并称作这条边的端点。
图的表示方法主要有以下几种:
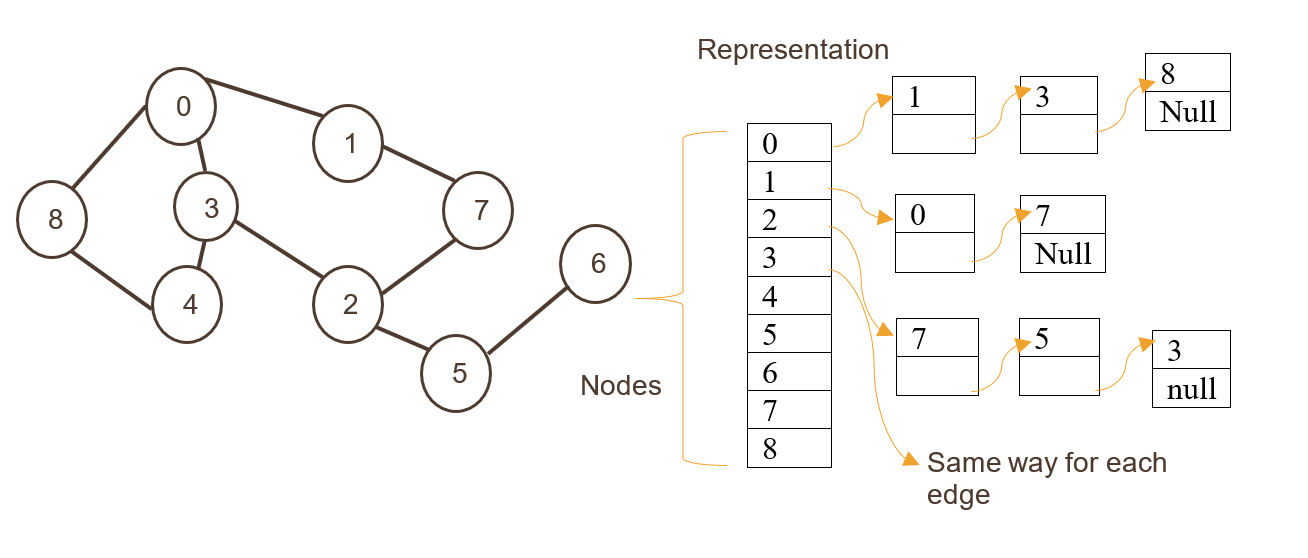
- 邻接矩阵:使用二维数组表示图,适合于稀疏图。
- 邻接表:使用链表或数组表示每个顶点的邻居,适合于稠密图。
- 边表:存储图的边信息,包括边的起点和终点。
**邻接矩阵示例代码:**
```python
import numpy as np
# 创建一个4个顶点的空无向图
V = 4
G = np.zeros((V, V), dtype=int)
# 添加边 (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (2, 3)
G[0][1] = G[1][0] = 1
G[0][2] = G[2][0] = 1
G[1][2] = G[2][1] = 1
G[2][3] = G[3][2] = 1
print("Adjacency Matrix:")
print(G)
```
**邻接表示例代码:**
```python
# 创建一个空图
graph = {i: [] for i in range(V)}
# 添加边 (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (2, 3)
graph[0].append(1)
graph[1].append(0)
graph[0].append(2)
graph[2].append(0)
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(1)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[3].append(2)
print("Adjacency List:")
for key in graph:
print(f"{key}: {graph[key]}")
```
### 2.1.2 图的遍历算法
图的遍历算法主要有深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)。
**深度优先搜索**:
- 概念:尽可能深地搜索图的分支。
- 方法:使用递归实现或栈实现。
- 用途:拓扑排序,解决迷宫问题等。
**广度优先搜索**:
- 概念:先访问离根节点最近的节点,然后访问离根节点次近的节点。
- 方法:使用队列实现。
- 用途:找到最短路径,拓扑排序等。
**DFS Python代码实现:**
```python
def dfs(graph, start, visited=None):
if visited is None:
visited = set()
visited.add(start)
print(start, end=' ')
for next in graph[start] - visited:
dfs(graph, next, visited)
return visited
visited = dfs(graph, 0)
```
**BFS Python代码实现:**
```python
from collections import deque
def bfs(graph, start):
visited = set()
queue = deque([start])
while queue:
vertex = queue.popleft()
if vertex not in visited:
print(vertex, end=' ')
visited.add(vertex)
queue.extend(graph[vertex] - visited)
return visited
visited = bfs(graph, 0)
```
## 2.2 图算法的基本类型
### 2.2.1 最短路径算法
最短路径问题旨在找出加权图中两个顶点之间的最短路径。最常见的算法是Dijkstra算法和Floyd-Warshall算法。
**Dijkstra算法**:
- 算法步骤:
- 创建最短路径树集合S,最初包含起始顶点。
- 创建一个距离表,记录源点到每个顶点的最短路径长度估计值。
- 对于未访问的顶点,选择距离表中距离最小的顶点作为下一个访问的顶点。
- 更新未访问顶点的距离表值。
- 应用场景:GPS导航,网络中的路由算法等。
**Dijkstra算法Python实现:**
```python
import sys
def dijkstra(graph, src):
dist = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph}
dist[src] = 0
priority_queue = [(0, src)]
while priority_queue:
current_distance, current_vertex = priority_queue.pop(0)
for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items():
distance = current_distance + weight
if distance < dist[neighbor]:
dist[neighbor] = distance
priority_queue.append((distance, neighbor))
return dist
dijkstra_result = dijkstra(graph, 0)
```
### 2.2.2 最小生成树算法
最小生成树是加权无向图的一个子集,它是一个树结构,包含图中所有的顶点,并且边的总权重尽可能小。
**Kruskal算法**:
- 算法步骤:
- 将图中的所有边按照权重从小到大排序。
- 初始化一个最小生成树,开始时为空。
- 遍历排序后的边列表,将当前边加入最小生成树中,如果加入后没有形成环,则这条边被接受。
- 重复步骤3直到最小生成树中有V-1条边。
- 应用场景:网络设计,电路布线等。
**Kruskal算法Python实现:**
```python
class DisjointSet:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.parent = {}
for vertex in vertices:
self.parent[vertex] = vertex
def find(self, item):
if self.parent[item] != item:
self.parent[item] = self.find(self.parent[item])
return self.parent[item]
def union(self, set1, set2):
root1 = self.find(set1)
root2 = self.find(set2)
if root1 != root2:
sel
```
0
0





