CNN卷积层剖析:揭秘卷积操作的原理,提升图像理解力
发布时间: 2024-07-20 05:27:31 阅读量: 24 订阅数: 36 

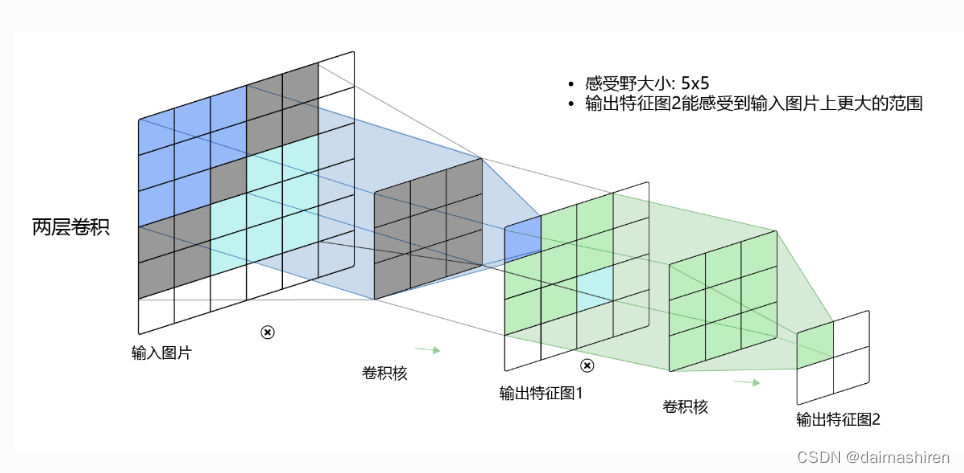
# 1. CNN卷积层概述**
卷积神经网络(CNN)中的卷积层是深度学习模型中用于特征提取的关键组件。卷积层通过应用一系列可学习的卷积核在输入数据上滑动,提取图像或其他数据类型中的空间特征。
卷积核是具有特定大小和形状的权重矩阵,在输入数据上滑动时,与输入数据中的局部区域进行逐元素乘法,并累加得到一个特征映射。特征映射反映了输入数据中特定特征的存在和分布。
卷积层通过堆叠多个卷积核,可以提取不同层次的特征,从低级的边缘和纹理到高级的语义特征。这种分层特征提取能力使得CNN在图像识别、自然语言处理和计算机视觉等任务中取得了显著的成功。
# 2. 卷积操作的原理
### 2.1 卷积核与特征映射
**卷积核(Convolutional Kernel)**:卷积核是一个小型的矩阵,通常为 3x3 或 5x5,用于在输入数据上滑动。卷积核的元素称为权重(weights),它们决定了卷积操作的输出。
**特征映射(Feature Map)**:特征映射是卷积操作的输出,它是一个新的矩阵,其大小取决于输入数据和卷积核的大小。特征映射中的每个元素表示输入数据中某个特定特征的存在或强度。
### 2.2 卷积运算过程
卷积运算是一个滑动窗口操作,卷积核在输入数据上滑动,逐个元素地执行乘法和求和操作。具体步骤如下:
1. 将卷积核与输入数据中相应位置的子区域对齐。
2. 对齐的元素逐个相乘。
3. 将乘积求和。
4. 将求和结果存储在特征映射的相应位置。
5. 重复步骤 1-4,直到卷积核遍历整个输入数据。
### 2.3 卷积操作的数学表示
卷积操作可以用数学公式表示为:
```
F(x, y) = (I * K)(x, y) = ∑∑ I(x - i, y - j) * K(i, j)
```
其中:
* F(x, y) 是特征映射中的元素
* I(x, y) 是输入数据中的元素
* K(i, j) 是卷积核中的元素
* * 表示卷积运算
* ∑∑ 表示对所有 i 和 j 求和
**代码示例:**
```python
import numpy as np
# 定义输入数据
input_data = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# 定义卷积核
kernel = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0]])
# 执行卷积运算
feature_map = np.convolve(input_data, kernel, mode='valid')
# 打印特征映射
print(feature_map)
```
**逻辑分析:**
* `np.convolve()` 函数执行卷积运算,`mode='valid'` 表示只计算卷积核完全覆盖输入数据的部分。
* 特征映射的大小为 (1, 1),因为卷积核为 3x3,输入数据为 3x3,卷积后边缘元素被舍弃。
**参数说明:**
* `input_data`:输入数据,是一个 2D 数组。
* `kernel`:卷积核,是一个 2D 数组。
* `mode`:卷积模式,可以是 `'valid'`(只计算完全覆盖的部分)、`'same'`(输出大小与输入相同)或 `'full'`(输出大小最大)。
# 3. 卷积层在图像处理中的应用
### 3.1 图像特征提取
卷积层在图像特征提取中扮演着至关重要的角色。通过卷积运算,卷积层可以从图像中提取出不同层次的特征,这些特征对于图像理解和识别至关重要。
卷积核充当特征检测器,在图像上滑动,检测特定模式和纹理。每个卷积核提取一个特定类型的特征,例如边缘、角点或对象的一部分。
**代码块:**
```python
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义一个 3x3 的卷积核
kernel = tf.constant([[1, 0, -1],
[0, 1, 0],
[-1, 0, 1]])
# 定义一张 5x5 的输入图像
image = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25]])
# 进行卷积运算
output = tf.nn.conv2d(image, kernel, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 打印输出特征映射
print(output)
```
**逻辑分析:**
这段代码演示了使用 TensorFlow 进行卷积运算。`kernel` 是一个 3x3 的卷积核,用于检测水平边缘。`image` 是一个 5x5 的输入图像。`tf.nn.conv2d` 函数执行卷积运算,产生一个 5x5 的输出特征映射。
### 3.2 图像降噪
卷积层还可用于图像降噪。噪声通常会降低图像质量并干扰图像分析。通过使用卷积核来平滑图像,卷积层可以有效地去除噪声。
**代码块:**
```python
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取一张有噪声的图像
image = cv2.imread('noisy_image.jpg')
# 定义一个 3x3 的高斯滤波器
kernel = np.array([[1, 2, 1],
[2, 4, 2],
[1, 2, 1]]) / 16
# 进行卷积运算
denoised_image = cv2.filter2D(image, -1, kernel)
# 显示去噪后的图像
cv2.imshow('Denoised Image', denoised_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
```
**逻辑分析:**
这段代码演示了使用 OpenCV 进行图像降噪。`kernel` 是一个 3x3 的高斯滤波器,用于平滑图像。`cv2.filter2D` 函数执行卷积运算,产生去噪后的图像。
### 3.3 图像增强
卷积层还可以用于图像增强。通过调整卷积核的参数,卷积层可以增强图像中的特定特征,例如边缘、纹理或颜色。
**代码块:**
```python
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义一张输入图像
image = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
# 定义一个锐化卷积核
kernel = tf.constant([[0, -1, 0],
[-1, 5, -1],
[0, -1, 0]])
# 进行卷积运算
enhanced_image = tf.nn.conv2d(image, kernel, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 打印增强后的图像
print(enhanced_image)
```
**逻辑分析:**
这段代码演示了使用 TensorFlow 进行图像增强。`kernel` 是一个锐化卷积核,用于增强图像中的边缘。`tf.nn.conv2d` 函数执行卷积运算,产生增强后的图像。
# 4. 卷积层的实践实现
### 4.1 使用TensorFlow构建卷积层
在TensorFlow中,我们可以使用`tf.keras.layers.Conv2D`层来构建卷积层。该层接受以下参数:
- `filters`:卷积核的数量
- `kernel_size`:卷积核的大小(高和宽)
- `strides`:卷积步长(高和宽)
- `padding`:填充方式("same"或"valid")
- `activation`:激活函数(例如"relu")
以下代码示例展示了如何使用TensorFlow构建一个卷积层:
```python
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义输入张量
input_tensor = tf.keras.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1))
# 构建卷积层
conv_layer = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding="same", activation="relu")(input_tensor)
```
### 4.2 卷积层超参数的优化
卷积层的超参数,如卷积核数量、卷积核大小和步长,会对模型的性能产生显著影响。因此,优化这些超参数至关重要。
超参数优化可以通过以下方法进行:
- **网格搜索**:遍历超参数的预定义值范围,并选择产生最佳性能的组合。
- **贝叶斯优化**:使用贝叶斯优化算法,在每次迭代中根据先前的结果调整超参数。
- **自动机器学习(AutoML)**:使用AutoML工具,自动搜索和优化超参数。
### 4.3 卷积层训练过程的监控
在训练卷积层模型时,监控以下指标非常重要:
- **训练损失**:衡量模型在训练集上的性能。
- **验证损失**:衡量模型在验证集上的性能。
- **训练准确率**:衡量模型在训练集上的分类准确性。
- **验证准确率**:衡量模型在验证集上的分类准确性。
通过监控这些指标,我们可以评估模型的训练进度,并及时发现过拟合或欠拟合问题。
# 5.1 深度可分离卷积
深度可分离卷积(Depthwise Separable Convolution)是一种轻量级的卷积操作,它可以有效地减少卷积层的计算量。深度可分离卷积将标准卷积分解为两个步骤:
1. **深度卷积(Depthwise Convolution):**对每个输入通道应用一个单独的卷积核,产生与输入通道数相同的特征映射。
2. **逐点卷积(Pointwise Convolution):**使用 1x1 卷积核对深度卷积产生的特征映射进行逐元素相加,生成最终的输出特征映射。
```python
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义输入数据
input_data = tf.keras.Input(shape=(224, 224, 3))
# 定义深度卷积层
depthwise_conv = tf.keras.layers.DepthwiseConv2D(
kernel_size=(3, 3),
strides=(1, 1),
padding="same",
depth_multiplier=1
)(input_data)
# 定义逐点卷积层
pointwise_conv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(
filters=128,
kernel_size=(1, 1),
strides=(1, 1),
padding="same",
activation="relu"
)(depthwise_conv)
```
深度可分离卷积的优势在于:
* **计算量减少:**与标准卷积相比,深度可分离卷积的计算量减少了约 80%。
* **参数减少:**深度可分离卷积的参数数量也比标准卷积少。
* **模型轻量化:**由于计算量和参数数量的减少,深度可分离卷积可以使模型更轻量化,更适合部署在移动设备或嵌入式系统上。
0
0





