Python时间序列预测准确性提升秘籍
发布时间: 2024-08-31 19:45:28 阅读量: 99 订阅数: 44 

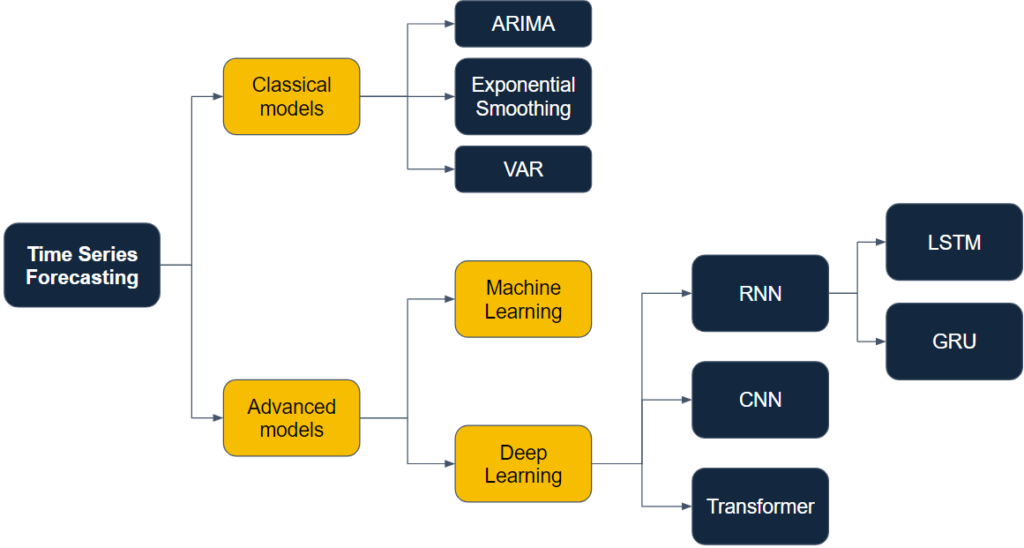
# 1. 时间序列预测简介
时间序列预测是数据分析领域中的一个重要分支,它涉及到数据在连续时间间隔内的一系列观测值。这类数据通常会呈现出某种自相关性,即历史数据与未来数据之间存在一定的关联关系。在本章节中,我们将首先探讨时间序列预测的基本概念,然后介绍其在不同行业中的应用价值,并分析其面临的挑战以及常见的解决方案。
时间序列预测之所以重要,是因为它可以帮助企业和组织提前预见到未来趋势和模式,从而做出更加明智的决策。例如,在金融市场中,投资者可能会利用股价的历史数据来预测未来的股票走势;而在零售业务中,公司可以基于销售历史预测未来的销售量,以便更好地管理库存。
然而,时间序列数据通常会受到诸多因素的影响,如季节性波动、经济周期、突发事件等,这些都使得准确预测变得尤为困难。接下来的章节将详细介绍如何通过数据准备、模型构建和实践应用等一系列步骤来提升预测的准确性。我们将从数据收集和探索性分析开始,逐步深入到模型的评估与验证,并最终探讨如何在实际业务场景中部署模型,以及如何监控预测效果并不断优化。
# 2. 数据准备与预处理
在深入时间序列预测模型构建之前,确保我们所使用的数据是高质量的至关重要。数据的准备与预处理是整个预测流程的基础,直接影响到最终预测的准确性。在这一章节中,我们将详细介绍数据的收集、探索性分析、清洗、预处理以及特征工程的相关技术与方法。
## 2.1 数据收集和探索性分析
### 2.1.1 数据来源与收集方法
时间序列数据广泛存在于经济、金融、气象、医疗、工业生产等多个领域。数据收集的第一步是确定数据来源。例如,股票价格数据可以从金融市场数据提供商如Yahoo Finance、Google Finance获取,而零售销售数据可能需要从零售商或供应商的内部数据库中提取。数据收集方法包括但不限于API调用、数据库查询、爬虫抓取、手动录入等。
数据收集后,我们需要对数据进行初步的检查和了解,确保数据的完整性。例如,利用Python进行数据获取的代码示例如下:
```python
import pandas as pd
import yfinance as yf
# 使用yfinance库获取股票数据
def get_stock_data(ticker, start_date, end_date):
stock = yf.Ticker(ticker)
hist = stock.history(start=start_date, end=end_date)
return hist
# 调用函数获取特定股票的历史数据
data = get_stock_data('AAPL', '2020-01-01', '2023-01-01')
print(data.head())
```
### 2.1.2 数据分布与季节性分析
对时间序列数据进行探索性分析是理解数据本质特征的重要步骤。我们首先需要检查数据的基本分布,例如均值、标准差、偏度和峰度等统计特性。此外,绘制时间序列图能够直观地识别数据的趋势和季节性模式。
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制时间序列图
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 7))
plt.plot(data['Close'], label='Close Price')
plt.title('Time Series Plot of Stock Price')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price in USD')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
```
季节性分析则通常采用季节性分解的方法,例如利用Python的statsmodels库进行季节性分解。
```python
import statsmodels.api as sm
# 季节性分解
decomposition = sm.tsa.seasonal_decompose(data['Close'], model='multiplicative')
fig = decomposition.plot()
plt.show()
```
## 2.2 数据清洗与预处理技术
### 2.2.1 缺失值处理
在现实世界的数据集中,数据缺失是一种常见现象。缺失值的处理方法包括删除含有缺失值的行或列、填充缺失值。填充缺失值可以采用均值、中位数、众数或基于模型的预测方法。
```python
# 填充缺失值
data_filled = data.fillna(method='ffill')
```
### 2.2.2 异常值检测与处理
异常值可能由多种原因造成,包括数据记录错误、测量错误或其他异常事件。异常值的检测可以使用标准差方法或箱线图识别法。处理异常值可以是删除含有异常值的记录或对异常值进行适当的调整。
```python
# 使用箱线图识别异常值
Q1 = data['Close'].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = data['Close'].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
# 计算上下限
lower_bound = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
upper_bound = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
# 标记异常值
data['is_outlier'] = ~((data['Close'] >= lower_bound) & (data['Close'] <= upper_bound))
# 删除异常值
data_cleaned = data[~data['is_outlier']]
```
### 2.2.3 数据平滑和去噪
为了减少数据中的随机波动,可以应用数据平滑技术,比如移动平均或指数平滑。数据平滑有助于识别数据中的主要趋势,减少噪声的影响。
```python
# 使用移动平均方法进行平滑
data['Rolling_Mean'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=3).mean()
# 绘制平滑后的数据图
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 7))
plt.plot(data['Close'], label='Original')
plt.plot(data['Rolling_Mean'], label='Rolling Mean')
plt.title('Time Series Smoothing')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price in USD')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
```
## 2.3 特征工程
### 2.3.1 特征提取方法
在时间序列预测中,特征提取通常涉及到从时间序列中生成新的特征,如滞后特征、滑动窗口统计特征等。这些特征可以提供模型额外的信息,从而提高预测的准确性。
```python
# 生成滞后特征
for i in range(1, 4):
data[f'lag_{i}'] = data['Close'].shift(i)
# 查看添加滞后特征后的数据
print(data.head(10))
```
### 2.3.2 特征选择技术
特征选择的目的是从现有的特征集合中挑选出最重要的特征。这样可以减少模型的复杂度,防止过拟合,同时提高模型的预测能力。
```python
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import f_regression
# 使用SelectKBest进行特征选择
selector = SelectKBest(f_regression, k='all')
selector.fit(data.drop(['is_outlier'], axis=1), data['is_outlier'])
# 查看选定特征的分数
features = data.drop(['is_outlier'], axis=1).columns
scores = selector.scores_
features_scores = pd.DataFrame({'Features': features, 'Score': scores})
print(features_scores.sort_values('Score', ascending=False))
```
### 2.3.3 特征构造与转换
特征构造是通过已有特征的组合或转换来构建新特征的过程。常见的转换方法包括标准化、归一化或进行非线性变换。
```python
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 特征标准化
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaled_features = scaler.fit_transform(data.drop(['is_outlier'], axis=1))
scaled_data = pd.DataFrame(scaled_features, columns=data.drop(['is_outlier'], axis=1).columns)
print(scaled_data.head())
```
以上章节中详细介绍了时间序列预测中数据准备与预处理阶段所需关注的各个方面。从数据的收集方法、探索性分析,到数据清洗和预处理技术,再到特征工程的方法和技巧,每一步都是为了确保预测模型能够基于高质量的数据做出准确的预测。在下一章节中,我们将探讨时间序列预测模型构建的细节,以及如何评估和优化这些模型。
# 3. 时间序列预测模型构建
## 3.1 经典时间序列预测模型
### 3.1.1 ARIMA模型及其变体
自回归积分滑动平均模型(ARIMA)是一种广泛应用于非季节性时间序列数据的预测方法。ARIMA模型通过将时间序列数据表示为自回归(AR)、差分(I)和移动平均(MA)的组合来构建预测模型。
#### ARIMA模型核心组件分析:
- **自回归(AR)部分**:当前值与过去值之间的关系,通过模型参数p表示。
- **差分(I)部分**:通过对原时间序列数据进行n阶差分来实现时间序列的平稳性。
- **移动平均(MA)部分**:当前值与过去随机误差之间的关系,通过模型参数q表示。
ARIMA模型的标准形式表示为ARIMA(p,d,q),其中p、d、q分别代表上述三个组成部分的阶数。此外,为了适应季节性数据,季节性ARIMA模型(SARIMA)被引入,增加了季节性差分、季节性AR和季节性MA的参数。
### 代码实现ARIMA模型
在使用Python的`statsmodels`库进行ARIMA模型构建时,通常执行以下步骤:
```python
import statsmodels.api as sm
import pandas
```
0
0





