【强化学习中的PPO算法】:原理、实现和应用详解
发布时间: 2024-08-22 00:37:28 阅读量: 63 订阅数: 22 

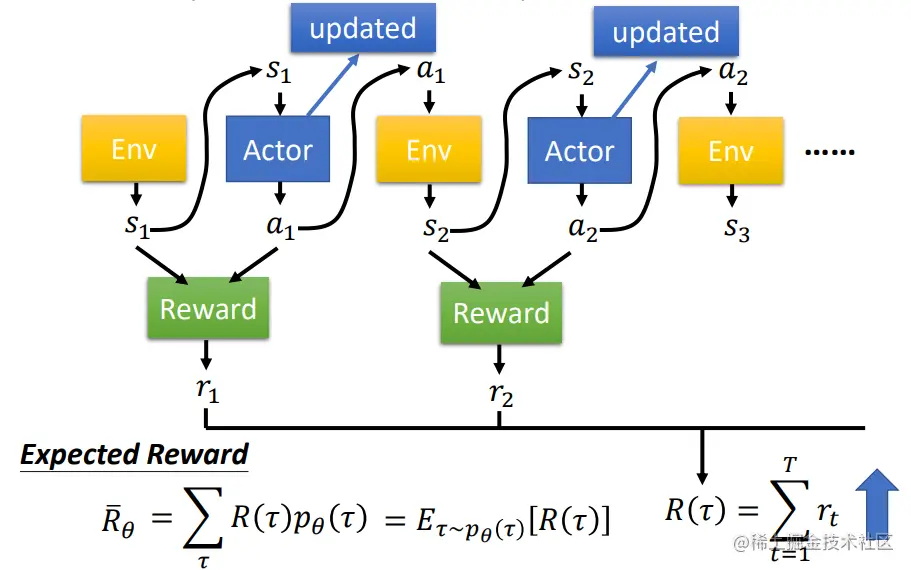
# 1. 强化学习中的PPO算法概述
强化学习是一种机器学习方法,它允许代理通过与环境交互来学习最佳行动策略。近端策略优化(PPO)算法是一种流行的强化学习算法,它通过优化代理策略的近端目标来训练代理。与其他强化学习算法相比,PPO算法具有稳定性高、收敛速度快、样本效率高等优点。
PPO算法的核心思想是使用近端策略优化方法。它通过最小化代理当前策略和目标策略之间的差异来更新策略。目标策略是根据代理过去经验计算出的,而当前策略是代理在当前状态下采取行动的策略。通过最小化这两个策略之间的差异,PPO算法可以确保代理的策略在学习过程中不会发生剧烈变化,从而提高算法的稳定性。
# 2. PPO算法的理论基础
### 2.1 强化学习的基本概念
强化学习是一种机器学习范式,其中代理通过与环境交互来学习最佳行为策略。代理根据其在环境中采取的行动获得奖励或惩罚,并根据这些反馈调整其行为。
强化学习的三个关键要素包括:
- **代理:**执行动作并与环境交互的实体。
- **环境:**代理所在的世界,提供状态和奖励。
- **奖励函数:**衡量代理行为的函数,提供正向或负向反馈。
### 2.2 策略梯度定理
策略梯度定理是强化学习中一个重要的理论概念,它提供了计算策略梯度的公式,即策略对目标函数的梯度。策略梯度用于指导代理更新其行为策略,以最大化奖励。
策略梯度定理的公式如下:
```
∇_θ J(θ) = E[∇_θ log π(a|s) Q(s, a)]
```
其中:
- θ:策略参数
- J(θ):目标函数(通常为期望奖励)
- π(a|s):策略,给定状态 s 时采取动作 a 的概率
- Q(s, a):动作-价值函数,表示在状态 s 下采取动作 a 的期望未来奖励
### 2.3 PPO算法的原理和优势
近端策略优化(PPO)算法是一种策略梯度算法,它通过限制策略更新的步长来提高策略梯度方法的稳定性。PPO算法通过以下步骤实现:
1. **收集数据:**代理与环境交互,收集状态-动作-奖励三元组。
2. **计算优势函数:**优势函数衡量每个动作的价值,高于策略在该状态下采取的平均动作。
3. **更新策略:**使用策略梯度定理更新策略参数,但限制更新步长,以防止策略发生剧烈变化。
4. **剪辑:**对策略更新进行剪辑,以确保更新步长不超过预定义的阈值。
PPO算法的优势包括:
- **稳定性:**通过限制策略更新步长,PPO算法提高了策略梯度方法的稳定性。
- **效率:**PPO算法通过使用优势函数来指导策略更新,提高了训练效率。
- **并行性:**PPO算法可以并行化,从而提高训练速度。
# 3.1 算法流程和伪代码
PPO算法的流程主要包括以下几个步骤:
1. **收集经验数据:**在环境中执行策略π,收集状态-动作-奖励序列{(s_t, a_t, r_t)}。
2. **计算优势函数:**使用优势函数A(s, a)评估每个状态-动作对的优势,表示该动作比策略π在该状态下采取其他动作的期望收益高的程度。
3. **更新策略:**使用策略梯度定理更新策略参数,使优势函数较高的动作的概率增加,而优势函数较低的动作的概率降低。
4. **更新价值函数:**使用价值函数V(s)估计每个状态的期望回报,并使用均方误差(MSE)最小化更新价值函数。
PPO算法的伪代码如下:
```python
初始化策略参数θ
初始化价值函数参数φ
for episode in num_episodes:
收集经验数据{(s_t, a_t, r_t)}
计算优势函数A(s, a)
更新策略参数θ
更新价值函数参数φ
```
### 3.2 PPO算法的超参数设置
PPO算法的超参数包括:
* **步长大小:**控制策略参数更新的幅度。
* **剪辑范围:**限制策略更新的范围,防止策略发生剧烈变化。
* **优势函数类型:**用于计算优势函数的函数类型,如GAE(广义优势估计)。
* **价值函数学习率:**控制价值函数更新的速率。
* **批次大小:**用于更新策略和价值函数的经验数据的批次大小。
超参数的设置需要根据具体的任务和环境进行调整。一般来说,较小的步长大小和剪辑范围可以提高算法的稳定性,但可能会降低收敛速度。较大的优势函数学习率可以加快价值函数的更新,但可能会导致价值函数估计不准确。
### 3.3 PPO算法的代码实现
PPO算法的代码实现可以参考以下代码块:
```python
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
class PPO:
def __init__(self, env, actor_lr, critic_lr, gamma, lam):
self.env = env
self.actor_lr = actor_lr
self.critic_lr = critic_lr
self.gamma = gamma
self.lam = lam
# 构建策略网络
self.actor = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(env.action_space.n, activation='softmax')
])
# 构建价值网络
self.critic = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
# 优化器
self.actor_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=actor_lr)
self.critic_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=critic_lr)
def collect_experience(self, num_episodes):
# 收集经验数据
experiences = []
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
# 根据策略选择动作
action = self.actor(state)
# 执行动作并获取奖励和下一个状态
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# 保存经验数据
experiences.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
state = next_state
return experiences
def compute_advantage(self, experiences, lam):
# 计算优势函数
advantages = []
for experience in experiences:
state, action, reward, next_state, done = experience
# 计算价值函数
v = self.critic(state)
v_next = self.critic(next_state)
# 计算优势函数
advantage = reward + self.gamma * (1 - done) * v_next - v
advantages.append(advantage)
return advantages
def update_policy(self, experiences, advantages):
# 更新策略参数
for experience, advantage in zip(experiences, advantages):
state, action, reward, next_state, done = experience
# 计算策略梯度
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
log_prob = tf.math.log(self.actor(state)[action])
policy_gradient = log_prob * advantage
# 更新策略参数
grads = tape.gradient(policy_gradient, self.actor.trainable_variables)
self.actor_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.actor.trainable_variables))
def update_value_function(self, experiences, advantages):
# 更新价值函数参数
for experience, advantage in zip(experiences, advantages):
state, action, reward, next_state, done = experience
# 计算价值函数目标值
target = reward + self.gamma * (1 - done) * self.critic(next_state)
# 计算价值函数损失
loss = tf.keras.losses.MSE(target, self.critic(state))
# 更新价值函数参数
grads = tf.GradientTape().gradient(loss, self.critic.trainable_variables)
self.critic_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.critic.trainable_variables))
def train(self, num_episodes, batch_size):
# 训练PPO算法
for episode in range(num_episodes):
# 收集经验数据
experiences = self.collect_experience(batch_size)
# 计算优势函数
advantages = self.compute_advantage(experiences, self.lam)
# 更新策略参数
self.update_policy(experiences, advantages)
# 更新价值函数参数
self.update_value_function(experiences, advantages)
```
# 4. PPO算法的应用
### 4.1 连续控制任务
PPO算法在连续控制任务中表现出色,因为它可以有效地处理动作空间连续的情况。以下是一些典型的连续控制任务:
#### 4.1.1 倒立摆控制
倒立摆控制是一个经典的连续控制任务,目标是通过控制摆杆的力矩,使倒立摆保持平衡。PPO算法可以有效地学习到控制摆杆的策略,使倒立摆在受到扰动时也能保持平衡。
```python
import gym
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.distributions import Normal
# 定义策略网络
class Actor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):
super(Actor, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 64)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = F.tanh(self.fc3(x))
return x
# 定义价值网络
class Critic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim):
super(Critic, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 64)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = F.linear(self.fc3(x))
return x
# 定义PPO算法
class PPO:
def __init__(self, actor, critic, env, lr=0.0003, gamma=0.99, lam=0.95, clip_param=0.2, epoch=10):
self.actor = actor
self.critic = critic
self.env = env
self.lr = lr
self.gamma = gamma
self.lam = lam
self.clip_param = clip_param
self.epoch = epoch
self.optimizer_actor = optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
self.optimizer_critic = optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
def train(self):
# 采样数据
states, actions, rewards, dones = [], [], [], []
for _ in range(self.epoch):
state = self.env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action = self.actor(state).detach().numpy()
next_state, reward, done, _ = self.env.step(action)
states.append(state)
actions.append(action)
rewards.append(reward)
dones.append(done)
state = next_state
# 计算优势函数
advantages = []
for i in range(len(rewards)):
advantage = 0
for j in range(i, len(rewards)):
advantage += (self.gamma ** (j - i)) * rewards[j] * (1 - dones[j])
advantage -= (self.gamma ** (j - i)) * self.critic(states[j]).detach().numpy()
advantages.append(advantage)
# 标准化优势函数
advantages = (advantages - np.mean(advantages)) / (np.std(advantages) + 1e-8)
# 更新策略网络
for _ in range(self.epoch):
for i in range(len(states)):
old_log_prob = self.actor(states[i]).log_prob(actions[i]).detach().numpy()
new_log_prob = self.actor(states[i]).log_prob(actions[i]).numpy()
ratio = np.exp(new_log_prob - old_log_prob)
surrogate1 = ratio * advantages[i]
surrogate2 = torch.clamp(ratio, 1 - self.clip_param, 1 + self.clip_param) * advantages[i]
actor_loss = -torch.min(surrogate1, surrogate2).mean()
self.optimizer_actor.zero_grad()
actor_loss.backward()
self.optimizer_actor.step()
# 更新价值网络
for _ in range(self.epoch):
for i in range(len(states)):
value = self.critic(states[i]).detach().numpy()
td_error = rewards[i] + self.gamma * value * (1 - dones[i]) - value
critic_loss = td_error ** 2
self.optimizer_critic.zero_grad()
critic_loss.backward()
self.optimizer_critic.step()
# 训练PPO算法
env = gym.make('InvertedPendulum-v2')
actor = Actor(env.observation_space.shape[0], env.action_space.shape[0])
critic = Critic(env.observation_space.shape[0])
ppo = PPO(actor, critic, env)
ppo.train()
```
#### 4.1.2 机器人运动控制
机器人运动控制也是一个典型的连续控制任务,目标是通过控制机器人的关节角度,使机器人执行特定的动作。PPO算法可以有效地学习到控制机器人的策略,使机器人能够完成复杂的运动任务。
### 4.2 离散控制任务
PPO算法也可以应用于离散控制任务,但需要对策略网络进行一定的修改。以下是一些典型的离散控制任务:
#### 4.2.1 游戏AI
游戏AI是离散控制任务的一个典型应用,目标是通过控制游戏角色的动作,使游戏角色完成特定的游戏目标。PPO算法可以有效地学习到控制游戏角色的策略,使游戏角色能够在游戏中取得更好的成绩。
#### 4.2.2 推荐系统
推荐系统也是一个离散控制任务,目标是通过控制推荐的内容,使用户对推荐内容的满意度最大化。PPO算法可以有效地学习到控制推荐内容的策略,使推荐系统能够为用户提供更加个性化和相关的推荐内容。
# 5.1 PPO算法的变体
### 5.1.1 APPO算法
APPO(Asynchronous Proximal Policy Optimization)算法是PPO算法的异步版本,它允许多个actor并行收集经验,从而提高了训练效率。APPO算法的原理与PPO算法基本相同,但它采用异步更新策略的方式,即每个actor独立更新自己的策略,而不再等待所有actor收集完经验后再统一更新。
### 5.1.2 SAC算法
SAC(Soft Actor-Critic)算法是PPO算法的扩展,它结合了策略梯度和值函数方法。SAC算法通过引入熵正则化项来鼓励策略探索,并使用一个目标值函数网络来稳定训练过程。与PPO算法相比,SAC算法在离散控制任务和连续控制任务上都表现出了更好的性能。
## 5.2 PPO算法的应用拓展
### 5.2.1 多智能体强化学习
PPO算法可以应用于多智能体强化学习中,其中多个智能体相互协作或竞争以实现共同目标。在多智能体强化学习中,PPO算法可以用于训练每个智能体的策略,使其能够与其他智能体协调或对抗。
### 5.2.2 强化学习中的安全约束
PPO算法可以用于强化学习中的安全约束,即在训练过程中限制智能体的行为以满足安全要求。通过在奖励函数中引入惩罚项或使用约束优化方法,PPO算法可以学习满足安全约束的策略。
0
0





